Blog
 04/11/2018 - Fascinating, Insightful Grant Williams Interview Of Chairman Tony Deden Of Edelweiss Holdings
04/11/2018 - Fascinating, Insightful Grant Williams Interview Of Chairman Tony Deden Of Edelweiss Holdings

 04/06/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Peter Boockvar On The Monetary Experiments Of Central Banks
04/06/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Peter Boockvar On The Monetary Experiments Of Central Banks

Download the Podcast in MP3 Here
FRA: Hi, Welcome to FRA roundtable insight .. Today we have Peter boockvar, he’s the chief investment officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and advisory, he has a product called the boockreport.com b o o c k report and that has great economic inside in perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome Peter.
Peter Boockvar: Thanks Rich for having me again
FRA: Great, I thought we’d begin with some recent observation you made saying –basically we are in on the other side of an unprecedented experience of monetary largesse and experiment. Just wondering if you could elaborate on that.
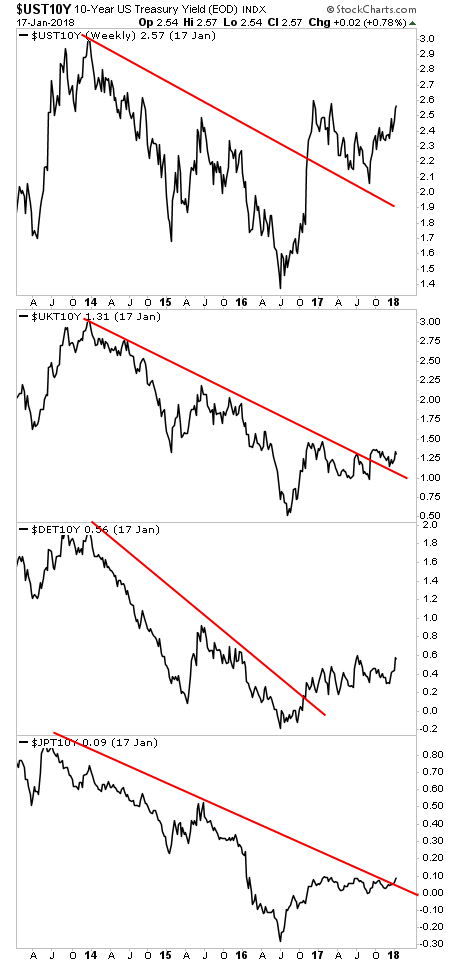
Peter Boockvar: Yeah so, the liquidity tide is beginning to go out it’s more pronounced in the US with the 6 interest rates that we’ve seen so far in addition to the fed’s balance sheet beginning to roll-off. Beginning on Monday, the trend in terms of that roll up we’ll go from $60 billion a quarter, that was $30 billion in Q4 and it will increase to $90 billion a quarter in Q2. Also as each day and month—week and month goes by when we get closer to the ECB finishing their quantitative easing program and we know the bank of Japan is and buying less JGB as they focus more on yield curve control. Had some couple rate hikes from the Bank of Canada, we’re going to get a rate hike from the Bank of England in May so this is Central Bank attempts to extricate themselves from many years have extraordinary policy so that’s why I refer to this as the other side of the mountain. Easing is very easy throwing that party is very easy trying to control the hangover in a pretty benign way if it is now the hard part.
FRA: And so are all central banks and major central banks in the world doing this or just a portion?
Peter Boockvar: Well the major ones and in in some fashion or I’m even of the ECB still doing QA they cut in half as a January. They’ll probably end up by the end of the year with another sharp Caper come October 1st. So doing this all together at the same time valuations across the world are stretch both of them fixed income and equities and there’s—creates vulnerability mean anytime central banks run a tightening cycle, the world becomes more vulnerable. Both n terms of growth –economy that’s very dependent on extraordinary low rates and also on asset prices that have become very elevated. So if you believe in a free lunch then everything will be fine, if you don’t believe in a free lunch –to 7 years of zero interest rates it can quintuple Balance sheet and negative interest rates around the world then you should be more circumstanced on how this all turns out.
FRA: Now looking at the Federal Reserve how high can interest rates go before other problems begin to set in namely the challenge of servicing the debt and also on interest rate related to derivatives?
Peter Boockvar: Well, look what happened to the VIX trade, the short VIX trade. We saw 30 basis point in the 10-year yield, 30 basis points that’s it and it blew up an entire trade. So I think that was one sign of how sensitive we are too modest changes in interest rates. Again because we’ve—so many years, attached and addicted and dependent on extraordinarily low rates both In terms of its impact on the economy and certainly asset price. Again one sign of potentially more to come, now the question is the persistent rise interest rate particularly on the short end and certainly with LIBOR. This is the rise in cost of capital, this rise in cost of servicing one debt begin to impact free cash flow and maybe not yet but we seem to be headed in that direction.
FRA: And so at some point will the Federal Reserve over and other Central bank’s be constrained are limited in is normalization process?
Peter Boockvar: Umm…That’s a good question I think that that will the restraint will occur only if something breaks and I think they seem pretty intent on raising at least two more times this year I think they’ll start a front load that to give them the option whether they want to do some fourth one of the end of the year and they claim that the shrinking of the balance sheet is like watching paint dry and then will happen in the background but we know that if something happens—if markets fall and if the economy gets impacted then the FED will certainly reevaluate that policy but the problem is that if they don’t do the type of tightening that they want to do and that it somehow gets short-circuited by the market, it tells you that the FED is trapped in what they’ve created and that—them and the ECB and the bank of England. We’ve all become Japan and we had many years of lessons to learn from the Japanese by the bank of Japan getting trapped in their monetary policy and we learned none of that lesson Bernanke suppose a student of the great depression in Japan apparently studied the wrong thing because look at the situation that we’re in and 1.625% in the U.S. of the ninth year in an economic recovery and they just started shrinking their balance sheet. So we’re in dangerous land here in terms of the solid line. If things were to fall in terms of the economy or markets. Question is what is the strike price the fed put and hows the FEDs deal with it if we hit that strike—is we going to see more cuts all of the sudden? Well, they don’t have any more rates to cut. So this is going to be an interesting situation in the coming years.
FRA: And if there is a movement into recession territory—also fall in the financial markets with the Federal Reserve and other central banks being in a position to decrease interest rates and would that mean going into negative nominal interest rate territory?
Peter Boockvar: I do not believe the FED will ever go to negative nominal interest rates think you’ll blow up the money market funds. I think they’ll be riots in the streets of Washington, particularly from the AARP. So I don’t see that being politically possible and at the same time, I think that its proven that its really not a good policy. Negative interest rates is a tax on capital. It’s a tax on banks and banks will do their best to pass it on and if they don’t then they eat it themselves, but somebody has to eat the tax. So I don’t know understand the economic model to have negative interest rates is actually a good thing. I mean I understand the concept that it may force banks to go out and lend but still taxes it’s being eaten by somebody.
FRA: What about going into negative real interest rates by maybe forcing inflation to much higher levels?
Peter Boockvar: We’ve been—we’ve been in a negative interest rate environment for 10 years now so that’s like not like anything new. It would just really be more of the same and then in fact it’s negative real interest rate is what got us into this mess anyway in terms of creating all this debt and bubble type environment that we consistently seem to get ourselves into.
FRA: Speaking of tax on capital, what do you make of the recent developments on trade in terms of trade tariffs acting as a sort of the effective tax on the global economy?
Peter Boockvar: well, optically it certainly is I believe a big negative and I say optically because I’m not sure reality wise, I mean look at the steel (Unintelligble), that’s 70% of countries that we do business with has already been exempted. Half of our aluminum imports come from Canada and they’ve already been exempt. So on a dollar basis and I’m not sure it’d have that much of an impact, it will certainly hurt since the users of steel far outweigh those that produce it trying to separate what really what the economic impact is be going to be. It’ll only be felt, I just don’t think it’ll be as much as many fear. Now of course if this spirals and that’s a big problem I’m hoping that at least with China, theres some sort of agreement that this doesn’t become Become such a big deal and then holding out hope for that. So yeah it’s a risk and I’m not comfortable with Wilbur Ross and Peter Navarro making these decisions because I think they’re way off in this obsession with trade deficits, but I’m just hopeful that it won’t be that big of an economic deal— I’m more worried about the direction of interest rates and monetary policy right now even though of course the tariffs are not a good thing.
FRA: What about the last day or two here of the sell-off in the Fang stocks and a tech sector, is some of that due to concerns by the markets on the trade issues?
Peter Boockvar: I’m not sure that’s really on that I mean certainly semiconductor stocks and certainly would be potentially impacted, we certainly export a lot of consumer electronics also to China. So yeah, potentially but I think that the backdrop to the weakness in cap. tech is a few different things that granted we know that they became such outsized portions of the major indices, when you get to 500 + billion dollar market cap you obviously dominate the global market. Evaluations for some of them got expensive, I mean Facebook on a PE ratio basis pretty modest but on a price of sales basis, it was 10 times so it’s—but that was expensive as well and then once you throw in rising interest rates when people become more sensitive to valuation and we know Amazon evaluation is off the charts and then all of the sudden, threat to their business model. You know Facebook is (unintelligible) franchise I’m sure it’ll be fine but if it means that they’re going to grow more slowly if it means that advertisers are going to be more discriminating with their spend. Then not do as much on digital –maybe put it someplace else. That affects the growth rate, that affects the multiple and in stocks that I have been over owned and over loved and for many years this is what you get and obviously today Amazon getting impacted by the talk about the White House and Trump being obsessed with them and what to do about that, there’s no room for error. When you got to the valuation of levels at these companies did and now that you have both interest rate valuation and fundamental chinks in the armor it’s obviously something really important to pay attention to again, because they were such an outsized dominant presence in so many indices, so many ETF and so many mutual funds.
FRA: Do you think the sell-off in the tech sector will continue and deepen ?
Peter Boockvar: Yes I do. I don’t think that this is somehow settled in a week with a with a modest pull-back, considering how much do stocks have run up.
FRA: And what about on the—instead of doing trade tariffs could countries in central banks look at the competitive currency devaluation in terms of making the currency weaker for a trade competitiveness?
Peter Boockvar: I think we should have seen a version of that for many years but certainly the ECB wanted a week Euro and Japan wanted weak yen and we wanted a weak dollar and things like that is always an ongoing issue. Reserve Bank Australia wants a weak USA dollar and Bank of Canada wants a weak Canadian dollar and it seems like everybody wants a weak currency and what they should be really rooting for is not a weak currency, it should be a stable currency. but everyone’s trying to steal each other’s exports and I think it’s just an ongoing thing that there’s no sign of that changing anytime soon.
FRA: Will there be another round of that particularly—for example like in the US, the US administration may be wanting a lower dollar. Do you see that happening and what would be the mechanism to actually effectuate that to happen?
Peter Boockvar: well the (unintelligible) got so beat up, administration that’s so beat up for even raising the prospect of endorsing a week or dollar so I just don’t think that that’s some place that they’re going to go to, really anytime soon. I think I’ll be very implicit and left on said that they don’t mind a weaker dollar more so than anything more out right and overt.
FRA: And what do you make of China in terms of what’s happening credit crisis increase in credit, more infrastructure projects— overall how do you see China playing out ?
Peter Boockvar: I mean China’s—I mean it is so interesting in that terms of the debt accumulation has been extraordinary and banking system has become so big that I go back and forth and how this all plays out. Because the other hand they still have pretty good growth rates and im pretty bullish on China longer-term but certainly acknowledge short-term challenges they face in trying to deliver. Now they’re not going to do an outright deleveraging, their version of the leveraging will just try to be less quick or more slowly and sort of grow into it and I hope they have success but it’s likely going to be bumps in the road.
FRA: Moving to a fast-moving area topic of cryptocurrencies, what are your thoughts on the—on that do you think that governments will allow private base cryptocurrencies to co-exist alongside government currencies. You know from the monopoly power of the government?
Peter Boockvar: I mean, I think only if there was more—use of these cryptos for transactions. I mean if they’re just going to be more speculation sources of buying and selling them I don’t think they’re really going to care, but again I think if it’s stretched replacing that the payment system then I think that’s something that would wake them up.
FRA: And would that be a major driver of what you recently mentioned as potential for 90% of Bitcoin value to get wiped out?
Peter Boockvar: Well when I when I threw that out it’s I was really just talking more technically mean when I was referring to typically when an asset or stock goes parabolic, that usually ends up falling to where the parabolic move began and that was 1 to 3000 so that that’s the number I threw out that was not based on fundamentals. It was really just—okay well this is what happened in previous episodes of massive parabolic moves and you can argue that this was probably the greatest parabolic move ever that you typically give back the entire move. Just as the NASDAQ lost almost 90% of its value in 200 to 2002.
FRA: And on the major currencies—dollar, euro, yen where do you see the trend happening over the next year on that in terms of their trend movement?
Peter Boockvar: I mean, I remain Bearish on the US dollar which I guess implies that I’m bullish on the others, it’s hard to get bullish on a yen in light of the monetary Mayhem that’s going on there. But im not excited about the dollar at all, I think the euro surprises to be on the upside as well. I would not be surprised if we saw 130 or 135 at some point because I’m relatively bullish on Commodities I just don’t like the Austrian and Canadian dollars and actually like the British pound. I think that’s the case and dealing with Brexit is everyone still pretty down on them and I think that actually turns out better than feared.
FRA: And what about gold why do you see that market this being a potential for another leg higher?
Peter Boockvar: It’s in part due to my conscious—my bearishness on the dollar and also my lack of any faith that the FED can somehow pull off this this monetary tightening in any smooth fashion. Self-landing is a rare occurrence and I think there is little to no chance that they accomplish at this time around so then the craziness that’s going on with the ECB and the Bank of Japan and I think the bull market again in December 2015 and I was really just getting started.
FRA: And are you still on agricultural fertilizers?
Peter Boockvar: I am. I am extremely bullish, I think we’re beginning to see a slow down and a decline in (unintelligible) stocks for (unintelligible)… in particular, the global demand for food is still in this perpetual rise upward so if the supply situation—can at least get contained, I think that there is a lot of upside or many asset classes that are down 50-75% from their 2011-2012 peaks and the agriculture and precious metals are two of the few that fall underneath that.
FRA: Any other asset classes that you like at this point?
Peter Boockvar: Umm… Those are the two broad ones that I like. Right now the investing landscape is getting more difficult, I mean they’re plenty of one-off situations that are interesting but in terms of looking at it from a macro perspective those are the two that intrigue me. I think bigger picture longer-term I still like emerging markets. I think that the growth rate is there and continue to be better and I think the valuation are much more attractive than in the US.
FRA: Which emerging markets in particular do you like?
Peter Boockvar: I haven’t felt like—so I still like China, again acknowledging the challenges they face, India, Vietnam, I actually like Brazil as well and I actually am warming up to Greece. The Athens stock market is down 85% from its 2007 peak.
and if the new democracy which of the opposition party—If their leader Mitsotakis wins in a possible early election this year or early next year he’s a business-friendly guy that would be a real game-changer for that country that has basically been through its own great depression over the past couple years.
FRA: Yes indeed, and that’s great insight Peter. Thank you very much your thoughts.
Peter Boockvar: Yeap, thanks for having me Rich.
FRA: And just wondering how can our listeners learn more about the your work, where can they go?
Peter Boockvar: If they’re interesting in reading my daily work, they can subscribe to boockreport.com, again its boockreport.com. B double o c k report.com and also the CIO and portfolio manager at the Bleakley Advisory Group and they can check out the website at Bleakley.com
FRA: Thank you very much Peter
Transcript by Alexander Nguyen
 04/01/2018 - What Financial Crisis Will Be Caused This Time If Interest Rates Keep Going Higher?
04/01/2018 - What Financial Crisis Will Be Caused This Time If Interest Rates Keep Going Higher?
 03/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Bill Laggner On How Blockchain Will Revolutionize The Economy
03/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Bill Laggner On How Blockchain Will Revolutionize The Economy

 03/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on Automation, Robotics and Universal Basic Income
03/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on Automation, Robotics and Universal Basic Income

Download the Podcast in MP3 Here
 03/22/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris On The Fed, Trade Tariffs, Italy, Gold & Currencies
03/22/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris On The Fed, Trade Tariffs, Italy, Gold & Currencies

Download the Podcast in MP3 here
FRA: Hi, Welcome to FRA Roundtable Insight .. today we have Yra Harris. Yra is a independent trader, successful hedge fund manager, global macro consultant trading foreign currencies, bonds, commodities and equities for over 40 years, he was also a CME director from 1997 to 2003. Welcome Yra.
Yra: Richard, nice to have you back from Argentina, I haven’t seen you the last time since you were in Singapore so–I cant really follow you. You’re like Waldo.
FRA: Ok, sure. Maybe we could begin with a feedback on what happened on this afternoon, federal reserve, FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) needing your thoughts on fed share, Jay Powell statement and press conference.
YRA: Yeah—you know, It was interesting that I was just watching the CNBC before we starting going on and Rick Santelli hit it right on target. I’m a fan of Rick, but we don’t always agree. But he had it on target. The one good thing Jay Powell did is he basically said stop relying on (unintelligible]\), because when they go out, the main stream media loves them because it’s an easy way to understand the fed for what they think is understanding… The fed so they can ask questions about it and he basically—you know—These are projections you know—they kept asking about it and asking about and Powell was very (unintelligible) when he said we made a decision today, to (unintelligible) projections and projections you know are just there. projections, they’re not worth the paper that they’re written on and if you follow the fed and their history with their dot plot, they’re a joke and as I wrote last night, you can go back 2006. Our cash in was far better at comprehending where the economy was than those dot plot projections and that’s just our—being, you know all that wisdom. So I just cant stand these dot plots I wrote in the blog last night that he should erase 50 basis points today and put to rest by doing that. Put to rest to dot plots and say yeah you know what we’re going to watch things here. But with raising 50 points and holding until the balance sheet shrunk to $3 trillion. I think he would of done the market to a much greater service because he would of let markets be markets and if there’s one thing that I really like about Jay Powell is that he does have an understanding on the way market works and he seems to be more willing to let markets work and get rid of the theoretical nonsense that fill the air ways with the feds press conference. I do applaud what he did except that I really would of like to see 50 basis points in a whole. Not that I would you know, bullish or bearish the stock I care not about that one way or another cause, I’m going to trade what I see anyway and react accordingly. But it would of put feds note to me a much more interesting position and you know what they got to stop cow toeing to the markets. You know I like what he was doing while the markets were correcting back in February. That he even had Dudley say that 10% drop is small potatoes, so we need to become more market focus than fed focus. That is the end of that story.
FRA: Now instead of the 50 basis point, the raise being only 25, do you think that the fed independence is coming under pressure by the US administration by president Donald trump?
YRA: Not yet, but it will, it will and a lot says about it again is that he talked about it last night and ill expound on it is that, look it. You read every central bank release, whether it is the ECB, Swiss National bank last week was the paradigm of it cause all they talked about was setting policies relative to the currency.
The Australian bank discusses the value of the currency, every central bank (unintelligible) everybody is out there parading this concept of independence of central banks. while they’re all discussing the importance of the currency values when setting their interest rate polices.
Certainly the Japanese, so its all being done so—with the—Donald Trump wanting to turn around the trade deficit, you can’t help but say hey maybe they are actually onto something because they have an independent central bank well—(unintelligible) the independent central bank that goes upon its course based on what its seeing here you know based on domestic economic activity, while everybody else is setting it to international standards then tariffs become the—I guess the alternative especially when the feds is raising the interest rates and they’re the only central bank really raising interest rates… I know… the bank of England went half a basis point, quarter basis point and they are project to go a quarter basis point tomorrow which we will see. But everybody is looking at the international situation and when I read the fed today there wasn’t one statement about it. Of course we did have Powell and little brainer discuss head wins to tail wins which is on the growth of the international economy but everybody goes through currency value when discussing interest policies.
FRA: So with the feds shrinking its balance sheet and raising short term rates—Likely making the US dollar stronger, will that promote tariffs more on the trade tariffs?
YRA: well I think that if the dollar got stronger, you would see much more action… But the dollar hasn’t gotten stronger, so there’s something else or a few other things that are seem to be weighing on the dollar. Now Powell was asked about that and he spoke to—you know—enhance growth, I’m not sure that there’s enhance growth over Europe anyways, I’m not… I need to see a lot more because if that’s the case then the European equity market should be out performing but you know what? They’re way underperforming the worlds equity market. So I’m not quite buying into that argument yet, but you know I’m going to wait and see first. I just need to see more before I go down that road. You know there are many things in play here which we will see which is why we are getting an increase volatility on a global basis.
FRA: And you’ve written recently on thoughts by commerce secretary Wilbur ross in terms that there will be no trade war… Trading partner of the us will compromise on trade treaty, how would that factor in the US dollar, like the potential US dollar devaluation?
YRA: well you know that’s right, that’s what I call the Kudlow dilemma, Kudlow of course when he got into his post, chairman—chief economic advisor to the president, he said you know (unintelligible) dollar and short gold. Well, not so fast Larry. First of all, be very careful about this because if you have king dollar which Kudlow means a strong dollar. Now we all like a strong dollar if its done—If its effected by good policies, but bad policies and a strong dollar, well that’s not such a good thing. You know—I’m not (unintelligible) grow your way out. You may inflate your way out of your debt problem but you’re not going to grow your way out of the debt problem, so let’s get behind that and if the dollar got too strong then the impotence from the white house would be to have more tariffs because they are hell bent on shrinking this trade deficit so when Kudlow discusses that, he ought to be very careful about where he is going because this white house, Peter Navarro and Wilbert Ross will push for a weaker dollar because a weaker dollar is Mnuchin and Wilbert Ross both said in Davos, is sending soldiers to the ramparts in the trade war that exists every day. So, Kudlow, that’s the Kudlow dilemma. It’s going to be interesting to see how he deals with this. But if, you were to get a dollar rally or even what (unintelligible) said and pretty sure wrote in earlier the week when he talked about a possible rip your face off dollar rally. He was quoting what’s his name (unintelligible name) about that. I’d be very very careful with this administration, they will not tolerate a strong dollar at this point in time.
FRA: And if that were to happen what would be the mechanism to effectuate that through monetary policy with the fed with its independence be compromised?
YRA: Yes! That’s a very good question, we don’t know but you would have the treasury secretary just like he said in Davos talking the dollar down which everybody took great umbrage at, but we’ve had that before, you know—One of my issues with Kudlow—(unintelligible) I respect him for his intelligence, he’s been around a long time. He was a Reagan guy, but you know what the Reagan white house lead the battle through James Baker with the Plaza Accord. The Plaza Accord was an orchestrated attempt to drive the dollar down and how is it done? Really—by sitting everybody down in the plaza hotel and reaching this compromise. We’ll pay because the trade deficit are now going to become an issue for wall street in a way that they haven’t in many many years and they are going to start to effect the movements in the market. Not quite ready yet but these algorithms who think that they have factored in every variable that you need and every headline, they are going to be disrupted themselves by the coming impact if the trade deficit continues to grow. This white house will not sit quietly and they made it an issue, and coming into the election this is going to be an important issue for Trump to hold onto his core constituency.
FRA: And thinking globally—how do you see everything playing out in terms of trade. Will Europe introduce measures to protect against Chinese trade and Chinese investments? So you got Europe Asia the U.S., how do you see it playing out?
YRA: well—we’ve seen that already. There was that article FT (Financial Times) earlier in the week that was talking about how Germany is upset that China is targeting some of the corporate jewels of Germany and… believe me the French are the most protectionists trade orientated going back to— (unintelligible) and I don’t care what Macron says because he inherited that it’s a long standing French tradition—so you know what? As the United States leave the battle, you will see that they will all start tail coating… What the white house is trying to accomplish, so while the white house gets beat up today, it gets beat up today because its easy to beat up on the Trump white house for so many missteps that they made. You watch that the European will follow right on top of this, because they have as much with the Chinese and they run. you know—pretty good trade deficit with the Chinese themselves so lets pay attention to what really is going to take place here.
FRA: And ultimately could we then get global competitive currency devaluation—another round?
YRA: Well I think we already have them. You know even with the yen at 103, 104 or 105, the yen is weak and fairly dramatic especially against the euro currency as we’ve talked about for 3 or 4 years already. That has been an interesting play and even I think that the Europeans, especially the Germans have had enough of the weakness in the yen. If you listen to (unintelligible) again, (unintelligible) very upset in January that Mnuchin and Ross, you know—for the D20 agreed not to target their currencies. Well you know what? Who you fooling? Of course, go read the Swiss statement from the release last week when they held their interest rates at negative 75 basis points. It’s all directed against the currency and the Japanese, every time when you listen to (unintelligible) talk, well—we’re not quite ready we need to see inflation. It’s just a nice way of saying we are going to keep our interest rate policy as it is because it keeps pressure on the currency. Come on, let’s call it what it is. They’re all targeting their currency values by using their interest policies for domestic purposes, but you know what? Many variables are in play here which is what is leading to the heightened increased in volatility. And as we’re talking right now, gold is up 23 or 24 dollars and silver is up 45 cents. This is after a fed increase. The dollar is on its lows, stone cold on its lows. What’s going on here in the market is were going to find out. There’s definitely some significant moves and most importantly is that there are two ten yield curve steepened today. Because… of course they changed the dot plot where it seems that there are going to be three rate rises this year so everybody thinks it’s going to be pushed out further and the feds is not going to be as aggressive as previously thought. So the yield curve, the two ten actually steepened out about 3 or 4 basis points as I’m sitting here.
FRA: Hmm.. Do you see president Donald Trump implementing section 301 of the 1974 trade act where the president can impose duties—If there’s like a perceived violation of trade agreements?
YRA: Yeah… that’s a great piece (unintelligible) last week when they were or two weeks ago when they were discussing 232 on the trade expansion act in 1962 under Kennedy which was interesting when it was passed in October of 1962, that was during the Cuban missile crisis. But they put in these—section 301 of the act in 1974. They put them in just because it was the only way they could get these trade agreements through, is that there is leverage against what they deemed at target as unfair traders so in order to get congress to be able to sign onto it there has to be opt outs based on sort of penalties. So yeah, they’re going to vote. We’ve seen it before with the Japanese in the 80s and the 90s was one of the strengths of the Reagan movement to enact 301. They’re going to use whatever they can—like yesterday we saw them soften some of their demands about 50% car parts in US auto—for NAFTA but they soften on that. Of course, and we saw that the peso. The peso reality and the Canadian dollar was really strong today. There are all types of mechanisms in place where they’re sending messages. Hey you better sit down an pay attention, were serious. We put the seal of tariffs down. (unintelligible) yes we backed off a little bit. We have a lot of tools at our command and we are serious about writing some of the wrongs that we have deemed to taken place in over the last 30 or 40 years. You must pay attention to it because, they have shown that they are serious about this, so they are trying to get better negotiating in so Trump can stand tall and say see. See what I did? I over turned some of these past malpractices and it’s going to help us as business returns to the United States.
FRA: will any of this affect U.S. agricultural exports to china?
YRA: well—It will—there is some rattling, we can see hog prices go down, cattle prices go down, some grain prices are holding up pretty well. Even as we are coming into the Brazilian and Argentinian year grind, the south American harvest will bring a lot of supply into the market. Prices are holding up very well, now that the Chinese may threaten the U.S. agriculture and as you know Wilbert Ross strategically laid out—you have to give them credit because they have done their homework and said look it, they’re still going to be buying our soy beans, I’m not buying it but what Wilbert Ross—I think is timing is wrong on the steel and aluminum because the Chinese, there’s so much—Brazil at a record crop this year. The timing wise is bad, we should of waited about two months for the crop to be harvested and for those to be all distributed somewhat and then laid it out because then the Chinese would have less flexibility. Right now they have flexibility because they can buy more Brazilian beans right now and stick it to the US farmers which could really hurt trump in the November elections, because the American farmers are doing very well. This has been a discussion since the China lobby back in the 1940s. the American heart land wants to do business with china, they always wanted to do business with China and when they embargo China, in the 1940s and 50s when Mao came into power, it hurt the American farmers because it took all those businesses with Taiwan versus the peoples Republic of China stunted American export to a billion people. The Chinese number one have to feed their people, end of story and their growth of Chinese purchases of soybeans which is huge because of the diet changes and more protein base especially with higher grades of protein. You have to feed those animals and a lot of soy meals and the Chinese eat a lot of soybeans. So that demand curve goes ever higher, that’s just not going to change… we’re seeing 10 dollar soybeans which is historically pretty high soybean prices and that’s with record supply. You know—agriculture responds very well to capitalism as prices go higher they produce more, but the demand from china and other countries that have now reach much higher per capita income they consume much more protein so prices remain high no matter how many beans come onto the market.
FRA: Yeah. And the soybean meal needed to feed the chickens, there used to be a saying that they only had chicken on Chinese new years but now they have it every day. Finally, your thoughts on Italy, recently you mentioned the markets are underestimating the importance of current Italian political situation and your reference to Picaso dream.
YRA: The market has fallen asleep, they think that there’s going to be some type of center based coalition that everybody (unintelligible) and that the league are going to get tired of trying to deal with five stars—I think it’s a gigantic mistake because 69% of the popular vote in Italy went to the center right including 5 star and if you try to push them out in order to form a coalition that pleases the eurocrats in brussels and status quo in Italy. Well—(unintelligible) I think you’re going to be running into a major problem and I think that the markets are way underestimating the influence of this. And you get again (unintelligible) I can take or leave most days, but he’s been very good with this. In fact, he’s been writing his warning about what’s taken place and you better pay attention to it. It’s no—Its nothing that is insignificant but the market seems to want to downplay it but we’ll continue to watch this. You know, I laugh because we’ve discussed the European financial institution have a severe problem and if you look at the stocks on the European bank, the deutsche bank—(unintelligible) but all the banks are suffering because the amount of non-performing loans have no been resolved, especially in Italy. So they need to really work this out and yet the 5 star and the (unintelligible) really want to push into… you know what we don’t care where the restrictions are coming from—(unintelligible)—budget deficits, we need to get the economy going and the Italian economy even with these ridiculous low interest rates is not showing enough growth and more importantly with these low interest rates, the debt to GDP ratio, it will be sitting around 132% which is enormous with a much lower borrowing cost, so Italy as you know—major problems facing it. (unintelligible) knows and 5 star knows they’re going to get their way because Italy is not Greece, Italy is far too big… far too big and their impact upon the entire global financial system therefore becomes much greater and as it is how to all work out. This is a very interesting time and yet the market is complacent trying to look past it. But I’d be very skeptical about that.
FRA: Wow. Great insight Yra. How can our listeners learn more about your work?
YRA: Well.. You can certainly go to the financial repression authority, we have a treasure trove of discussion but on a daily and weekly basis. I blog from notes underground which you can get and register for free if you go to YraHarris.com you’ll be able to access it and—as much as I write, respondence to the blog are at such a high level of discourse that, that makes it a must go to place because we really discuss very important things and its done at a very high level I’m proud to say.
FRA: Yeah, excellent. Yeah, great, thank you very much Yra, thank you.
YRA: Richard, thank you as for the opportunity as always, we do get into a good look under the hood as we say.
FRA: Yeap, and we’ll do it again another time. Thank you Yra.
 03/18/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Gordon T Long Talks With Dr. Lacy Hunt
03/18/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Gordon T Long Talks With Dr. Lacy Hunt

 03/04/2018 - Danielle Park: Pensions Are Now Crushing Budgets
03/04/2018 - Danielle Park: Pensions Are Now Crushing Budgets

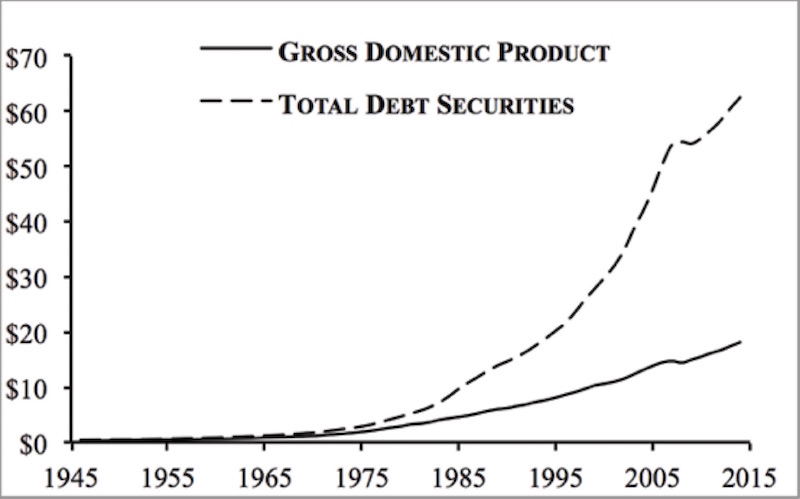
“The elephant of unsustainable pension management has been sitting in the theater of retirement planning for at least two decades. Now it is taking center stage. As obligations have soared, contribution levels have not kept up and management has opted for increasingly risky bets in the hopes of ‘winning’ the funds needed. It’s not working.
Plans that were fully funded 20 years ago, today have maybe two-thirds of the capital needed to cover benefit promises– and that optimistic estimate assumes zero bear markets and fantastical average real returns of 7%+ a year going forward.
The reality of the pension crisis was underlined again last week when the board of the largest $330+ billion US public pension plan, California Public Employees Retirement System (CalLPERS), voted to shorten its period for amortizing future investment losses from 30 years to 20 years. After losing $100 billion in 2008, followed by 10 years of QE-enabled capital markets since, the fund still has not recovered.
The net effect is that state and local governments and agencies will have to further increase mandatory contributions by diverting tax revenues needed for education, health care, roads, environmental protection and other public services.
…
Solutions include lowering benefit payments and indexing, delaying retirement ages, increasing saving/contribution levels, and in some cases expunging obligations in bankruptcy. None of these are popular, but this is reality.”
 03/04/2018 - Martin Armstrong: The Crisis In Pensions
03/04/2018 - Martin Armstrong: The Crisis In Pensions

“The pension crisis at CalPERS is getting closer by the day. The State looks to be totally bankrupt by 2021-2022. CalPERS has just decided to increase the contribution of local governments and cities to their fund. The cities say they are approaching bankruptcy because of rising subsidies, but CalPERS itself is approaching insolvency. The problem is that there really is no real reform in sight. The choice is clear – CUT pension benefits of government employees or RAISE TAXES!. CalPERS simply needs a bailout and very soon.
Board Member Steve Westly even told The Mercury News that a bailout was needed and soon. Currently, CalPERS manages approximately $350 billion of future pension claims of its members. Recently, CalPERS passed an amendment to the statutes, which resulted in higher contributions for the California municipalities. The amount of contributions has been increased several times over the past few years and this time the cities do not appear to be able to handle the increased costs.
Once CalPERS was 100% funded with assets under management. In fact, they had a surplus in the good old days before Quantitative Easing. Right now, the system no longer has more than two-thirds of future claims. CalPERS itself expects an annual return of 7 percent on its financial investments. Most pension funds run by the States are insolvent or on the brink. This is what I have been warning about that the Quantitative Easing set the stage for the next crisis – the Pension Crisis. The Illinois Pension Fund needs to borrow up to $ 107 billion to meet its payment obligations. Promises to state employees are over the top and off the charts. This is why Janet Yellen at the Fed kept trying to raise rates stating that interest rates had to be ‘normalized’ for this was the crisis she knew was coming. And guess what – Europe is even worse and Draghi will not raise rates for fear that government will be unable to fund themselves.
There is NO WAY out of this crisis. The portfolio would have to be completely restructured and benefits reduced. Jerry Brown will do everything in his power to raise taxes and fees to try to hold CalPERS together. That is by no means a long-term solution.”
 03/04/2018 - James Grant: Putting The Cart Of Asset Prices Before The Horse Of Enterprise
03/04/2018 - James Grant: Putting The Cart Of Asset Prices Before The Horse Of Enterprise

Grant’s Interest Rate Observer founder on moving rates from CNBC.
 03/02/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On The Current Conditions In The Financial Markets
03/02/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On The Current Conditions In The Financial Markets

Download the Podcast in MP3 Here
 02/24/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Jim Bianco, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On Investing Implications Of Volatility & Inflation
02/24/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Jim Bianco, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On Investing Implications Of Volatility & Inflation

FRA: Hi, welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight. Today we have Yra Harris, Peter Boockvar and a new guest, Jim Bianco. Jim is President and Macro Strategist at Bianco Research. Since 1990, Jim’s commentary have offered a unique perspective on the global economy and financial markets. Jim’s wide-ranging commentaries have addressed monetary policy, the intersection markets and politics, the role of government in the economy, fund flows and positioning in financial markets. He is a Chartered Market Technician (CMT) and a member of Market Technician’s Association. Yra Harris is an independent trader, successful hedge fund manager, global macro consultant while trading foreign currencies, bonds, commodities and equities for almost 40 years. Yra is also the CME Director from 1997 to 2003. Peter is Chief Investment Officer for the Bleakely Financial Group and Advisory. He has a newsletter product called the Boockreport.com. His great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentlemen!
Jim: Thank you!
Peter: Hey Rich!
Yra: Thank you, Richard!
FRA: Great! I thought we’d begin with a discussion on volatility. We did a podcast recently with Chris Whalen about a week before the volatility began in the financial markets; this year volatility to a significant extent. Jim, have you been seeing that as a trend through your research or what are your thoughts on that?
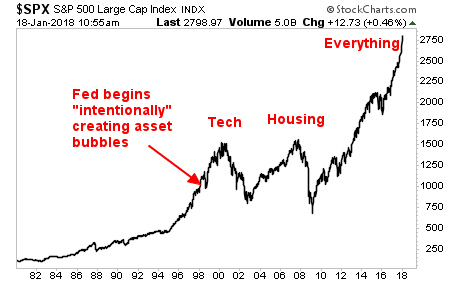
Jim: Not as a trend. Pretty much the opposite. Volatility events like what we’ve seen over the last couple of weeks are not the creation of a trend, they are the exaggeration of a trend. So there was a trend in place already and that trend in place was a turn towards more volatility. The turn towards more volatility was driven by a belief that, for the first time in the post-crisis era, inflation was returning. I’d get technical on you for fifteen seconds. What happened with the volatility event is we caught a short-ball traders on the wrong side of the trade. They did one simple narrow thing; blew up the VIX Market. The volatility measure on the S&P 500 Index option. That’s all they blew up. When we found that that spiked from 12.5 to 50 in two days, we found out how important the VIX is to everybody else. It was their measure of risk. When they saw it go up 400% in two days, they overreacted and the next thing you know, the DOW is down 1600 points. What I want to emphasize is they didn’t create the trend. The trend is towards higher inflation and that higher inflation would bring higher volatility and they got caught in the wrong side of it. All derivative debacles like this are an exaggeration of a new trend that everybody got caught on, not the creation of it.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts on that?
Yra: You can’t say it better.
Peter: In 2017, we saw a hiccup in the US. The Fed decided to raise rates three times instead of one. Let’s start shrinking our balance sheet. That was overwhelmed by the Bank of Japan and ECB. In early 2018, when rates continued to rise, when the inflation pressure started becoming more evident that this is not a short-term bliss. Maybe this is the beginning a more normalized interest rate trend. One of the analogies that I’ve given in the past is when the central banks are full on easing, it gives investors goggles and it makes everything look perfect. When that starts to change, when that liquidity flow starts to slow and rates start to move then those goggles start to clear up a little bit. Monetary policy became more important. Markets are very reactive nowadays. (5:03 – 5:06 would not play. The audio automatically skips it). All of the sudden it woke people up and said,” Uh oh. This is a big deal. This is twice the level of what it was in the summer of 2016. I better start reassessing my positioning. I better start reassessing my leverage. I better start reassessing what valuation I want to place on the S&P 500. VIX and all these other things became a symptom, of what I call now, a disease of rising inflation and rising interest rates that then caused this explosion in volatility.
Yra: There’s been an argument in the market place that inflation is rising but so what. Higher interest rates is not a bad thing. They take the idea that when it comes to inflation, it is either Zimbabwe and it is really bad or it does not matter but there is a middle ground in there which is critically important. I’ve been saying people to stop talking about the Fed. Central banks as a collective, are the easiest they’ve ever been in the post-crisis era. Their balance sheets are the highest they’ve ever been in the post-crisis era this week. If inflation returns, it puts into jeopardy that we’re gradual. Bernanke said,” We are going to get balance sheet back to $2T to 2.5T and it could take until 2026. He wrote it in 2016. It will take 8 or 10 years to get that. If we have inflation, maybe that 8 to 10 years is now 2 years. By the end of the year, you’re going to have a contraction out of the ECB and the BOJ. That’s where inflation matters. It’s going to force central banks to pull in a lot faster than people thought. One last thing. Wall Street runs into this trap all the time. Somebody points out a risk, everybody looks at their watch and says,” Well, we waited eight minutes. The market has not blown up. I guess that risk does not matter.” There’s a risk from all of this money printing. For the first time in nine years, we have an inflation fear and is now putting doubt in central banks. Now, what’s the first thing that markets do? They have a ___ (7:41 inaudible and the podcast skips it) over that. I think that this inflation fear that makes everybody say,” Bring it on! 3.25 is really good in interest rates.” Be careful what you wish for because that is going to cause a reversal especially in the BOJ. If we continue to see global inflation fears rise, the Fed is already tightening right now, that’s why I said do not talk about central banks. This should be a big deal for markets in 2018 and most people continue to dismiss it.
Peter: Just to add on, with respect to what you said, Jim, on balance sheets being at record highs. The analogy we have given out is that yes, they are at record highs but balloon with the air being central banks easing. There’s still air going into that balloon but there’s less air going in. If there’s less air going into that balloon, that balloon is still going to contract. I think it’s the rate of change that is really changing dramatically in terms of central bank (8:41 podcast skips it – inaudible).
FRA: Could the return of inflation force all central banks to accelerate their exit strategy or just some?
YRA: (9:03 – 9:07 inaudible) was just reappointed with a very (9:08 inaudible) group around him. (9:10 – 9:22 podcast skips it). … stand on fiscal policy is used on the sales tax. Draghi dug himself into a hole. (9:25 – 9:52 some are skipped and inaudible). … How do you get out of this? Peter and Jim are both right. Forget about the Feds. Everybody follows the Bernanke book but they’re stuck in a situation here. To me, that’s really dangerous.
Jim: One quick thing about the ECB. Draghi’s term has a little bit more than a year to go before he’s done. The tradition in the ECB is that the next ECB Chairman will probably be German. It does not have to be a German but probably will be a German. That’s code word for a very hard money person. If you’re going to get inflation and you’re going to get a German to run the ECB, you’re going to get a violent reversal in the next eighteen months. Look at two weeks ago. Two Thursdays ago when the DOW was down 1000 points, what was the catalyst story that everybody said? There’s inflation in the UK and the BOE (Bank of England) might have to double the rate hikes that they’re going with. When was the last time the BOE moved the US stock market? That might’ve been the first time. It’s all because of this idea that central banks is maybe peaking soon and starting to reverse. We haven’t had to deal with that possibility until the last two or three months. It was only in the last two or three months that we’ve only really started to see inflation. What Yra said is right that maybe Japan continues to pump money but they might not be enough to do it. If everybody else is going to reverse, then those global central bank balance sheet will peak. These markets will have a digestion problem with that.
Peter: Just to add on to what Jim said, even the Riksbank in Sweden, which is not necessarily relevant for the global economy, experimented with negative interest rates along with others. It’s a good symbolic gesture. They said they’re going to start the process of getting out of negative interest rates well before the ECB starts. Just going back to zero from negative is going to cost an extraordinary amount of loss. The ripple effect that that’s going to have on the world, I don’t think the people will appreciate it. I like to remind people in terms of the concept of risk happening fast. It was 2015 when, the German 10-year went from 6 basis points to 60 in one month and from 60 to 100 points a month later. This is Germany. Not Greece. Not a third-world country. This is a country that went from a 6 basis points to 100 in less than 2 months.
FRA: How could all of this translate onto a change in basic relationship between stocks and bonds? Jim, you mentioned there would likely be a change on that once again?
Jim: First of all, just as a point of emphasis. One of the things that could change it back another way is that if the doubt of inflationary fears go away. There was a mild form of inflation fears about a year ago and then it went away. The difference between now and a year ago is that we’re finding out that the market, collectively, is a bunch of Phillips Curvers. They’re looking at the stimulus from tax cuts, possibility of infrastructure spending, strong growth and that they’re concluding we’re not going to have inflation after we spend thirty years trying to say that the Phillips Curve does not creation inflation. If it is decided that there is inflation, then there is inflation. That’s where it is coming from. To your question about the stocks and bonds relationship, it changes all the time between the way that stocks and bonds trade together. In 1998 to 2000, it changed. What I used to call is under the inflation mindset. In the 1960s to 2000, the starting point of every discussion was, are we having inflation? If the answer was yes, if bond prices went down then stock prices went down. If the answer was no, the 80s and 90s, were not having inflation, then bond prices went up, interest rates went down went up. Bond prices and stock prices move together. Starting around 1998 to 2000, we switched that dynamic because we were worried about deflation. During the middle of that dynamic, we had long-term capitals, the Asian crisis, the tech bubble, sounds like the derivative thing we’ve been talking about the last few weeks as well. Throughout the 2000s until very recently, we worried about deflation. Are we having deflation? If the answer was yes, equity prices struggle. If there was no deflation, then equity prices went up. So now bond and stock prices move opposite of each other. What we’ve seen in the last few weeks is the decline of bond prices and stock prices together since the financial crisis that they both went down together. The day the DOW was down off 300 points. Up until 60 days ago, if you just randomly told me in the last nine years that the DOW was down 300 points, I would’ve said (16:40 – 16:42 inaudible). That’s the way we traded every single time. I think we’re shifting to an inflation mindset. Now where does that matter? In the last nine years, Wall Street has pushed this idea of a 60:40 portfolio. That it’s the optimal way to invest your money; sixty percent in equities and forty percent in bonds because something is always going up. Either there is no deflation and stocks are going up or there is deflation and bonds are going up. But under the new scenario, either they’re all going up or they’re all going down. Both of them have been falling together. So this idea where you can take a lot of risk with a 60:40 portfolio is going to be blowing up on people’s faces. This means that the relationship between stocks and bonds are transitioning right now. It takes around two years to fully transition it. I don’t know if it will take fully two years now but it will take at least months to do it. There will be periods where it does look like they’re transitioning but I do think that we’ve started that process.
FRA: And Yra, do you see that relationship also changing?
Yra: Yes. This whole risk parity. To me, what people don’t understand, is especially on the issue on how you get of out this. Ray Dalio said you’re going to shed tears if you earn cash. Talking about a coming change. That’s in a two week time period. It scared me. Ray Dalio is a great thinker.
Jim: Just to emphasize something on what Yra said that the single hardest thing to do for anybody that’s investing is to recognize the regime that the old rules stopped working. Most people can’t and they keep pounding away with the old rules until they are out of business. The single hardest thing to do in any type of investing is say that we’re now in a regime shift. If you’re wrong, you get wiped out and if there’s no regime shift and you say it is, you also get wiped out. If there is a regime shift and you don’t adapt, you get wiped out. That’s why we have this volatility and blow ups along the way.
Yra: That’s right. And what I think people fail to understand is not just Dalio’s position. It is everybody that has handled this book and tail-coated it. I know a lot of people in banks or foreign exchange traders who made a fortune and have tail-coated George Soros in the BOE. If BOE reacted like the Bank of France and raised interest rates to 100% and said,” We’re just going to do whatever we have to do and you have to pay the cost.” He wasn’t successful in breaking the (2:38 – 2:40 inaudible)… to exit that train would’ve been an enormous pain for all the people who followed them in. So whatever you think Dalio’s positions are, which I think are enormous is tail-coated and recreated the same trades in many other ways. I think that’s what we’re told in the last two weeks. He’s got a lot of company in this low volatility place.
FRA: And Peter, your thoughts also?
Peter: I also think a lot of people lost perspective on the markets. When you turn on the T.V or the radio or when you read the paper, while earnings are great in the economy’s trade and therefore stocks are going to go up and I just want to point out that that’s from the end of 2012. So the calendar year at the beginning of 2013, the January 26th peak at the S&P, the S&P 500 was up 100%. Earnings since then, assuming 2018 assuming $100 to $150 per share, earnings should be up 60%. So the differences is actually multiple (21: 52 Inaudible). When interest rates rise or when people reassess what central banks are doing, why should people pay eighteen times their earnings? All of a sudden, within a week and a half, they decided let’s pay sixteen times with a one dollar change per earnings per share. Every one-term PE is 155 points (22:15 podcast skips, inaudible) while when we’re talking about two-term PEs, that’s 310 points. I think people need to have perspective that the stock market has ran well ahead of the rise in earnings and the difference is PE multiple expansions. It is now compressing because of the new regime change that we were talking about.
FRA: Could the rising interest rates in the U.S. cause us strengthening in the dollar (22:46)… rising defaults in the U.S dollar denominated debt in emerging markets which is estimated approximately $9T? Could that happen or could it also spur a financial crisis in Europe out of the bond markets? Would that mean that international capital flows coming into the U.S. towards U.S. dollar denominated assets? Just some potential scenarios. Jim, your thoughts?
Jim: I would come down on the idea of ‘no’. Let me explain what I mean by ‘no’. There’s this perception in markets that there’s all this money. There is no money heaven. No one ever loses this their money, it just gets allocated around. When the stock market goes down, but all the money from the bond market will come in to replace the stock market money that went down. I do not think you’re going to see some kind of reallocation where everybody is going to come running into the United States and it’s going to (23:53 podcast skips it, inaudible) the U.S. stock market and it is going to hurt them as well. I think the problem with the dollar, and I’ve been wrong with the dollar for several months now, is that the speculative flows are at record highs for some of them. Everybody is selling the dollar or is shorting the dollar right now. This has been keeping it unnaturally strong. If you wanted me to guess why we’re getting a persistent selling of the dollar, foreigners are basing their investments on who the president of the U.S. is. Sell the dollar. Investors have finally realized that it doesn’t matter. Eventually, that’s going to come back to foreigners and make them realize it matters. Your investments in a political idea might see a strengthening in the dollar. But are you going to see some kind of a wholesale run into the dollar that you were suggesting “no, I don’t think I’m going to see that.”
FRA: Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I haven’t (25:12 – 25:13 Inaudible) … since Mark Fields’ comments back in 2017. Now, I’m fairly neutral towards it because it’s been a (25:24 inaudible) for people because interest rates in the United States are going up and (25:28 – 25:38 podcast skips it and inaudible). I’m scratching my head. If the deficit scare is real, I think what they did here by blowing the budget apart and the stimulus is that the people are a bit nervous. I don’t disagree with Jim because I’m really neutral with the dollar. If we go to real yields, Peter wrote about it today, the least positive on the short end of the paper rate I’d say is about 40 basis points based on the number that we have. The dollar would get a kick especially if the other central banks are just sitting there complacently because they would like their currencies to weaken anyway. I think Mario Draghi would like the Euro to weaken. I think the Japanese policies are driven by the desire for a weaker yen with the Trump agenda. People are being conscious and would like to see the dollar strengthen in relative to their own currencies. So, I’m going to wait. I don’t really have a good sense to where we go from here.
FRA: And Peter, your thoughts?
Peter: I’m bearish on the dollar in the short-term but considering the moves it has had, I’m definitely more uncertain about the very short-term move. We went into the year saying they’re going to increase the rates three times but then the markets really doubted it and now have the rising inflation that is probably happening. Higher inflation that’s not met by a rising Fed funds rate is typically dollar bearish. The Fed is going to raise three times this year. Take the Fed’s fund rate to a real rate of zero. That, of course, is well above where it is overseas, especially in Europe and Japan. But there is a reality that people still think it’s jamming around 2.0 even though maybe he’s not. But it’s still going to be on its gradual path. So there’s no way the Fed is getting ahead of the curve. They’re still going to be playing catch-up on top of better overseas economies that’s drawing dollars into other areas of the world. There are secular headwinds to the dollar but I’m less certain. I was very certain when the euro was 1.05 but much less certain when the euro is 1.25 in the short-term. I would not be surprised if, within the next two years, we see the euro at 1.40. It would not surprise me at all if we see the pound at 1.60. That’s were eventually heading within the next couple of years.
FRA: Jim, you mentioned this whole environment could be like the 90s when the markets went down and everything else. Where do investors and traders go to?
Jim: That’s the old 60:40 risk. Something is always going up. Yeah, I guess somebody is going to win the lottery today too. If an asset class is going to be rising, the answer is that they’re going to be small. Commodities might be rising but 95% of the money in the world is not in commodities. We’re creating a new asset class; cryptocurrencies. I, personally, think is an outgrowth of the rejection of policy. Inflation pressures financial markets. They go down. Stocks go down. Bonds go down. That was, ask Yra, that was the 1970s. I’m not saying we’re going to have high levels of inflation but what we’re going to have is that the stimulus will give you an appearance of high levels of inflation. So, I think that it’s going to be very hard to find, other than special situations like in the commodities markets, beyond that is going to be very difficult to find ideas where you can profit while returning to an inflationary environment.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I agree with Jim. What we’re going to see is (31:01 – 31:08 inaudible). Let’s say that the Phillip’s Curve may be able to get it right for a short period of time. We get higher interest rates. And now (31:27 – 31:30 inaudible)… 60:40 because they are both going to go down. I’m not a Phillip’s Curve advocate but if inflation does that. Those are both detrimental for corporate profits because rising wages with rising interest rates (31:42 – 31:53 inaudible). I just don’t see it. I know Peter has looked at this. (31:01 – 32:07). All these companies that borrowed a lot of money (32:09 – 32:15 inaudible). Take the interest rates expense, it is down to a really low level but we know that’s not going to last because for every one percent rise in the cost in borrowing, it’s going to hit discretionary spending levels dramatically. People are in for a shock here. It is really fascinating that (32:39 – 32:52 inaudible). It really does not make any sense. We’re much more worried about inflation. We know how to deal with inflation. In an interview that he did. So, you’re going to get into a feedback where at 60:40, they’re going to be sorry.
FRA: And Peter?
Peter: Just to quantify on what Yra said in terms of profit margins, lower labor costs and lower interest expense are the two biggest contributors for corporate profit growth from the 09 bottom. Just to quantify, there is about $13.5T of total business debt. So for every 100 basis points of interest cost, is $135B. Now, obviously, a lot of companies have turned down debt. But, generically speaking, in terms of labor costs, companies pay about $7T of labor cost every year. Let’s just combine that. (33:50 – 34:00 skips and inaudible)… higher costs that more than offsets the cut in the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%. A lot of the estimates that is out there for earnings per share are all else equal analysis. It does not take into account higher labor cost and higher interest cost. When a lot of (34:23 – 34:24 inaudible) come out with their year-end price targets, it doesn’t include a lower PE ratio. It is static analysis. In terms of where to survive here, I would not be surprised if a two-year T-Bill paying 2.25% interest rate outperforms the equity market in a broad basket of corporate credit over the next few years. I think the commodity space is very interesting. I know a lot of people like to look at the demand side in terms of dictating prices but since that 2011 – 2012 peak in commodities, the (35:03 skipped) collapsed. Not only industrial metals, but also energy and particularly agriculture, which I’ve been very bullish on and on my belief on the dollar, I think gold and silver will outperform most equities and certainly fixed income within the next couple of years.
Jim: There’s $13T worth of debt and most of it has been turned out. This means rates goes up now but I’ve got 3 – 5 years to maturity. So I don’t see risk immediately. In the last ten years or so, there’s been a lot of people that have been turning up their debt through derivatives markets. They have been engaged in floating or fixed payments or receiving to take shorter-term debt and turn it out into longer-term debt. That is when you get a spike in volatility. Even that is going to start to come back to this day. Well I’ve got all of this short-term debt. The Fed is going to raise its rates. What am I going to do? I’m going to engage in swaps contracts in order to it mimic a 5-year note or a 10-year note but now it is more expensive to buy that swap contract because volatility is going up. That’s going to start hitting their bottom line too.
FRA: Great! Thank you very much gentlemen for your great insight. Just wondering, how can our listeners learn your work or go around? Jim?
Jim: Probably the easiest way is to follow us on twitter @BiancoResearch.com or at our website BiancoResearch.com
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: At YraHarris.com and the blog is from underground (36:58 – 37:10 inaudible). Food for thought.
FRA: And Peter?
Peter: My twitter is Pboockvar and subscribe to my daily writings at boockreport.com and my managing business is bleakley.com
FRA: Great! Thank you very much gentlemen.
 02/14/2018 - Danielle DiMartino Booth On Federal Reserve Policy
02/14/2018 - Danielle DiMartino Booth On Federal Reserve Policy

Former analyst at the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas Danielle DiMartino Booth thinks those expecting the Federal Reserve to continue the market support will likely be quite disappointed.
 02/14/2018 - Martin Armstrong: The Sovereign Debt Crisis Is Here
02/14/2018 - Martin Armstrong: The Sovereign Debt Crisis Is Here

“The Romans never even had a national debt. Today, we have government hawking 100-year bonds. We have pension funds that required 8% returns and then governments ordering that the bulk of such funds if not 100% should be ‘conservative’ and invest in only government bonds. We are reaching a crisis point in longer-dated yields because investors are unwilling to lend money at low rates long-term. Smart money is beginning to wake up to the perpetual mismanagement of the long-term trend by the government. The central banks have been backing off of continually buying government debt and the Fed in the USA has announced it will not reinvest when its holdings of government debt mature .. This is the Sovereign Debt Crisis and Monetary Crises we face in the years ahead.”
 02/14/2018 - BIS Chief Sees ‘Strong Case’ For Cryptocurrency Intervention
02/14/2018 - BIS Chief Sees ‘Strong Case’ For Cryptocurrency Intervention

“There is a ‘strong case’ for authorities to rein in digital currencies because of their links to the established financial system, Bank for International Settlements General Manager Agustin Carstens said.
‘If authorities do not act pre-emptively, cryptocurrencies could become more interconnected with the main financial system and become a threat .. Most importantly, the meteoric rise of cryptocurrencies should not make us forget the important role central banks play as stewards of public trust. Private digital tokens masquerading as currencies must not subvert this trust.'”
 01/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Chris Whalen, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On 2018 Trends & The Return Of Volatility
01/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Chris Whalen, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On 2018 Trends & The Return Of Volatility

DOWNLOAD THE PODCAST IN MP3 HERE
FRA: Hi. Welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Yra Harris, Peter Boockvar and a first time guest, Chris Whalen. Yra is an independent trader, a successful hedge fund manager; global macro consultant trading foreign currencies, bonds commodities in equities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997 to 2003. And Peter is the Chief Investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and Advisory at Bleakley and he has a newsletter product called The Boock Report. BoockReport.com. It offers great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Chris Whalen is an investment banker, author and Chairman of Whalen Global Advisors LLC which focuses on financial services, mortgage finance and technology sectors. He was a Co-founder and Principal of Institutional Risk Analytics from 2003-2013. He has held positions in organizations such as the House Republican Conference Committee…
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, talking about that.. (laughs). That’s okay. Most recently I ran and built up the Financial Institutions Group at Kroll Bond Rating Agency which was a lot of fun. Kroll is really an ABS house, first and foremost, commercial real estate and the rest of it. It’s still very small from competing with giants, but it was a lot of fun.
FRA: Great. And also he was on the board of directors for the Global Interdependence Center (GIC) in Philadelphia.
Christopher Whalen: Yes, that was David Kotok’s little project. You know it’s fun to mix business with pleasure. Fishing, central bankers go fishing.
FRA: Yes, I am actually going next month to the GIC conference in Buenos Aires and going fishing before that. There’s also fishing afterwards, sort of the Camp Kotok in Argentina.
Christopher Whalen: Well, some of them go to Maine. Ramiro Lopez Larroy and his kids will just show which is about 15 hours by plane. It’s a lot of fun. They are great people – A very diverse group at GIC. We’re going to Germany this year, the Bundesbank, so if you like monetary policy that would be a very good trip to go on. I would recommend that.
So, what would you like to talk about this morning?
Peter Boockvar: The Bundesbank has disappointed me for the last few years how they give Draghi the license to do what he has done.
Christopher Whalen: Well, they kind of had no choice. I find it amusing that northern Europe is cranking, and my relatives in Holland are having a great year, and yet southern Europe is not. That dichotomy is ultimately going to be very difficult for them to deal with. The Germans look at southern Europe and they just see more checks to be written. The politics of that is slowly undermining Merkel. It’s very interesting to watch. And then Berlusconi coming back in Italy – Isn’t that great?
Everyone: (laughs)
Christopher Whalen: I always tell people to read about Berlusconi and you’ll see where America is headed.
Yra Harris: Draghi will be making trips to Italy.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah. Draghi has been trying to keep Europe on ice by pushing debt cost down to zero, but the debt keeps growing. So, what are we really about here? There’s no fiscal discipline anywhere in the Western world and the Chinese don’t care. It doesn’t matter in China – It’s a political issue. That’s why I was writing about H&A recently because ultimately, whether that company survives or not, will be determined by uncle Xi. That’s how it works in China. There is no church and state, there is just the state.
Peter Boockvar: He may want to set an example though.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, there were a little ostentatious, a little floppy with the parties, pasting their names on the side of office buildings around the world. I think we have 3 of them in New York. It’s quite fascinating.
FRA: A few weeks ago, Chris, you wrote an article, Bank Earnings & Volatility, I thought we could begin with some thoughts there. How have the Federal Reserve and other central banks’ actions affected the credit market, the financial markets and the economy, in general?
Christopher Whalen: Well, what the central banks have done is that they have removed a lot of assets from the market. They’ve gone out with a variety of new money, in the U.S. case: excess bank reserves, and they’ve bought treasury bonds and they’re bought also mortgage bonds. Of recent vintage, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, Ginne Mae paper which have 3, 3 ¼ and 3 ½ coupons with very low pre-payment rates. Those bonds are going to be around for a long time. In fact, one thing I remind people of is that about 30% of the market today is the FHA and Ginnie Mae and those loans are assumable so they will stay with the house. And the house will trade and the loan will be conveyed to the new buyer. It could be very interesting, over time, to see how that affects the portfolio. But essentially, the central banks have taken all of this duration out of the market and since they’re end investors, they are basically buying the paper on credit and they don’t hedge it. So the capital markets activity that you used to see around a lot of these positions when they were held by trading firms, banks and other who were going to trade the assets and cared about mark-to-market every quarter has greatly diminished — There’s no hedging. The Fed’s sought out hedging it’s block and it’s a problem now because the Fed is now illiquid. They can’t sell without creating a loss and they dare not do that because it gets them in trouble with the Republicans and the House who don’t understand monetary policy at all, but have a lot of opinions on it. And so you have this weird situation where the Fed essentially has their hands tied. They’re going to wait for the book to run off which they hope is about $20 billion a month. And I think that they could be wrong. I think that they could too wishful in terms of the runoff rate in terms of the mortgage paper. The mortgage companies are going to be around forever and the pre-payment rate is going to be very low, especially if rates continue to move up. That’s kind of what I see. The trading line on Wall Street, the earning will be greatly diminished by this. Then you have the vote to rule. So all of the books, the investment books that the banks use to trade every day, just the value of the assets are passive now. You put those 2 data points together and you will understand why Goldman Sachs and why all of the banks have seen an enormous reduction in their trading buy-ins.
The other issue is that the mortgage market is down so there is less hedging. The forward market for hedges, what’s called the TBA market, has a lot less activity. We’ll do a $1.5 trillion in mortgages this year which is down. The peak was $4.5 trillion during the 2000’s; we don’t want to do that.
Peter Boockvar: Yes and why aren’t we seeing an CNI loan growth?
Christopher Whalen: The banks had to slow down. They had a pretty good run in 2015/2016. We had a little scare from oil which didn’t really materialize. Most U.S. banks did fine on oil credits. There was some restructuring, but the banks we follow like Cadence, which is a small lender that was built to do energy – They have no problems. But now a lot of banks have run up to a regulatory limit on commercial real estate loans, multi-family…there’s a big shtick now for the smaller banks. They’ve essentially run out of customers in certain markets too. The OCC, for example, is forcing regionals to peel back their multi-family exposure because the prices have gone up so much. They just look at that go whoa, wait a minute. And they’re right. Loss rate on these assets, multi-family assets, are negative. So if the loan defaults, you’re going to sell the property for a lot more than the loan and that’s reflected in the ABS numbers too. It’s an interesting time in terms of different asset classes, but I don’t see a lot of growth in the book. I really don’t. BA had a really good quarter at year end, but that was the exception. Most of the big guys were not growing. And of course PMC had a very good quarter and had a nice tax number. I think overall, don’t look for alpha in the banking industry. Between the regulatory changes and just the tenure of the economy you would be in the bond market, right? Anybody could raise money in the bond market in 2016 and part of 2017. So, we had a bull market in fixed income which has driven a lot of strategies and I’m sure Yra has some thoughts on that.
Yra Harris: Let me ask a question in regards to that. I was really taken by it because it was such a good point. With the ECB, BoJ and certainly the Feds, the dynamic hedges are missing from the market, but they are going to resurrect themselves as more paper winds up in the hands of private holdings whether it be by pension funds or insurance companies. But do you think that Jerome Powell…You know I go back and read some of his earlier stuff and of course his initial position as a Fed governor, he had a lot of issues with the massive build-up of the balance sheet. Do you think that he might be quicker to say that we can hold the rate at 2%…Do you think that it’s a possibility?
Christopher Whalen: I think that the snippets from the minutes that have sudden found people’s attention…which is very funny, right? We only pay attention to chairmen. It’s a cult of personality. So here you have Powell saying some very interesting things, very forthright, not an economist, he’s a financial guy, and I’m told he’s fairly decisive although he’s quiet and he listens. He knows how to make decisions. On this he’s got politics because the congress, if you remember years ago, they confiscated the Fed’s surplus to pay for a highway bill. And the idiots in congress, I wrote about this for the American Conservative, keep permittences from the Fed as revenue. They don’t understand that it’s an expense foregone. It’s not revenue. You’re just making the debt go away. Every year they look at this money coming in and the CBO and everyone else say: Oh look, it’s revenue. But it’s a snake eating its tail because the Fed and the treasury are one. It’s like a Hindu god, but in economic terms they are the same. And Bob Eisenbeis, who I interviewed, is wonderful on this issue – He is very funny. I think that Powell is going to be a lot more straight-talking then the others have been and I fault Yellen and Bernanke on this because they should’ve gone out and said to the congress: “No, you can behave like this. This is ridiculous. You don’t go confiscating our surplus.” It was just part of Washington politics, but the Fed didn’t respond. If Paul Volcker was there he would have been up on the hill kicking the shit out of them. And the problem is, these are bureaucrats, they come from academia. They have no money and so they don’t know how to behave in big league politics – It’s a tragedy. I think Powell will be much better. I am very hopeful about his 10-year as chairman. It desperately needed change. We got to get the economists out of the temple, I’m sorry. I love them, but they can’t make financial decisions. You want them on the staff, Yra, you don’t want them trading.
Peter Boockvar: We wish that was the case 10 years ago and now Powell gets to clean up the mess.
Christopher Whalen: Exactly and you know, Volcker cleaned up a lot of messes too. They always clean up other peoples’ messes so it’s a public service.
Peter Boockvar: And this is the biggest mess the world has ever seen.
Christopher Whalen: Oh yeah. No question.
Yra Harris: And with Bernanke he had the courage not to act.
Peter Boockvar: Right. Bailing out people doesn’t take courage. It’s not bailing them out what is courageous.
Christopher Whalen: Well precisely. And the Fed has not said no in a long time. They haven’t said no to accommodating treasury options and they haven’t said no most recently with this lunacy of QE. I mean the first one was fine. They had to reliquify the banking system as Walker Todd put it out to me a while back, but the rest of it was crazy. Selling all the short-dated stuff and loading up the book with long-dated treasuries so they own mortgage backs with an average life of around 12 years now. They have extended a lot, by the way, over the last 18 months. Even if the portfolio gets smaller, the duration has got to go up.
(laughs) How about that?
Peter Boockvar: Chris, what was their thinking in their models with operation twist to say okay, in their models, let’s flatten yield curve and that will be good for growth. And then today they express worries over the flattening yield curve.
Christopher Whalen: Well I know, but this is the point. When you have central banks take all this duration out of the market, nobody is hedging the position; well obviously it’s going to be hard to get those maturities to back up. There is just nobody selling euro/dollars, nobody doing swaps or anything – There’s nothing. So there is market is in stasis and they’re going to push up the short end, but there’s nobody pushing up the long end. So it’s gone up a bit, but I keep wondering…I wrote about it this week. I’m kind of hedged on my bull market 10-year trade, right? But, there is still nobody out there selling it. So I do think you have a flat curve in prospect, I agree. It’s bond market basics. It’s got to be somebody at that table in Washington who understands the bond market and I think Powell does – There’s hope.
Yra Harris: But in understanding the bond market, Chris, do you think that he will move to try and steepen the curve by maybe holding the front end, by saying hey, we don’t have to raise rates. If I get it to 1.75 on the Feds’ fund rate or 2%, I’m basically in a neutral real yield. That’s where I am. That’s probably about neutral on the front end. Maybe the real yield on the front end goes to 50 basis points positive, but I don’t think he goes there. Would it not be in his optimal mindset to say let’s start shrinking the, as Peter would say, quantitative tightening on the longer end on the duration. If the yield curve steepens out to 120-150 basis points it’s not necessarily a bad thing.
Christopher Whalen: I totally agree with you. If the Fed were acting rationally they would be doing all of that. They would have even been hedging a bit of the buck. Just trade it. Go out and hedge on the duration.
Peter Boockvar: Definitely afraid of affecting its bubbling asset prices.
Christopher Whalen: That’s part of it – True.
Peter Boockvar: That’s behind their entire thinking.
Christopher Whalen: But bureaucratically in Washington terms, they don’t want to take a loss because then the remittance to treasury goes away. And believe it or not, in the small minded world of some of these Fed people, that’s what they worry about. So, vector that into your thinking too because he’s absolutely right – They should be trading the book. They should have been doing a lot of things, but they’re not thinking like market people. They are thinking like Keynesian and academic economists and that’s scary — It really is.
FRA: In your article you mention also that this is likely going to result in a volatility returning to the markets that were all short volatility – Can you elaborate on that?
Christopher Whalen: Well that was the comment from Powell. He said at the end of that snippet from 2012 that they were going to unwind their short volatility position. In classical terms, if you buy a portfolio of RMBS it should give you a relatively short position, but in this case I think the other part of it is our perspective, the market. We’re sitting here and he’s got all the duration and we’re buying. Now, all of a sudden, he says that we aren’t going to buy anymore and we’re going to let it run off. So eventually private market participants are going to take up that duration, think of it as the weight that they have to support with capital, and they’ll have to hedge. So you will see market activity return. I think that the Fed has missed an opportunity to get a little bit more of this done quickly and figure out how much the street is willing to support. That’s the thing that we don’t know. The Fed has been supporting everything.
Peter Boockvar: The Fed lost their opportunity. The Fed had a chance to raise 3 times in 2015, 3 times in 2016, now they’re entering a situation where maybe the Fed fund rate tops out at 2-2 ¼. And they have now an issue with this falling dollar and bubbling inflation pressures. Just imagine when we do hit a wall and they start to cut rates and what the dollar is going to do in that scenario.
Christopher Whalen: I think it’s a lot simpler than you put forward which is: go ahead and keep your little quarter point march and if you see spreads start to widen, you stop. It’s the basic Irving Fisher test, right? That was the playbook for Bernanke.
Peter Boockvar: That is too much of a free lunch for me. I think that there is no free lunch in reversing this policy that they have implemented.
Christopher Whalen: So, you think we go to 6%? That’s what Yellen said years ago.
Peter Boockvar: We don’t need to go to 6% to cause a major problem. All the 10-year has to do is go to 3.5%/4% and you’ve got, I believe, a recession on your hands. I think the sensitivity to changes in interest rates is dramatic, as it’s been. You’ve got duration levels that are as high as they’ve ever been globally – That’s where the risk is.
Christopher Whalen: Well you’ll certainly see defaults go up because we’re hiding a lot of defaults with the artificial manipulation.
Peter Boockvar: And it’s not just that. Well you need a zero interest rate to go back to zero and $9 trillion of paper is going to lose a lot of money mark-to-market
Christopher Whalen: Hey, I know that’s why…
Peter Boockvar: Actually, I take that back. It’s more than mark-to-market — It’s real life losses.
Yra Harris: From a trader’s point of view…That position is enormous that they are carrying and more people have synthetically created that. Now you’ve got to realize that all of this volatility selling is all from people who are mimicking that risk parity trick. You can mimic it whatever way…You can recreate this trade synthetically in a million different ways. So when you have to actually start unwinding it, it’s almost like the long-term capital of 1998, we’re not going to be able to get out of that door because a lot of people are going to be racing out that door at the exact same time that you want to go because they have the same position whether you realize it or not.
Christopher Whalen: Well of course. And the VIX is just a popularity contest – There’s no basis for that contract. It’s just a matter of supply and demand. It’s like CDS. There is no basis on the underlying credit anymore.
Peter Boockvar: Well sure, but the VIX is still being determined by a lot of participants placing their bets and puts and calls.
Christopher Whalen: Absolutely. A lot of them weren’t hedging the past few years. Everyone was leaning in one direction.
Peter Boockvar: Of course.
Christopher Whalen: You would see default rates double in Peter’s scenario, easily. I think that’s from latency in the system. If we see the 10-year go up to like 3%, I think the windows will be shaking.
Peter Boockvar: And I read a stat over the weekend that of the roughly 2,000 companies, 40% of the debt is floating rate. And that cost goes up every single day with what LIBOR is doing. Even the 2-year note yield today is up to 2.12.
Christopher Whalen: That’s what I’ve been wondering about is to imagine the reissuance of equity that was bought in by these guys as they desperately try and pay off this debt. That could be a lot of fun.
Peter Boockvar: Yeah. The 1-year bill today is now where the S&P 500 is.
Christopher Whalen: We’ve had 4 years of amazing record bond market activity of each year in terms of new issuance and I would say 1/3 or ½ of it was to fund stock repurchases. It’s been quite something.
Yra Harris: And you know what, there’s another part…When the BoJ and ECB are busy buying corporate assets, there’s no hedging that goes on there either. And there’s also no stock re-lending. Another issue that I’ve raised…
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, that’s true. They may not lend the assets. That’s right. The Asian central banks are very, very conservative on that stuff. They won’t re-hypop.
Yra Harris: Yeah. There’s no rehypothecation of anything so now all of a sudden the game gets even more interesting and the question becomes: Do all the ETFs rehypothecate? Or does that result then with everything in that basket we get way late off the market and make it even more expensive for short sellers. So we’re not getting any short selling for some of these companies that are involved in ETFs are really miserable companies. So the whole dynamic here is shifted. And I don’t know that the players have really shifted.
Christopher Whalen: I don’t know about the ETFs. I would suspect those assets are available, but the central banks are the big thing. When they buy all of this paper and just put it away, you’re right, it doesn’t come out. It doesn’t get loaned. It reduces liquidity – That is, to me, the key thing.
The fascinating part is to look at the Swiss. Swiss National Bank is now buying stocks. Why? Because if they don’t, the currency will appreciate. That is their chronic problem. They just can’t keep the money out and even with penalty rates, they still can’t manage it. So if they stop, it will go up.
Peter Boockvar: That’s what one of the interesting central bank comments this week was from the deputy governor of the Swiss bank in Sweden, who has also gone down that rat hole of negative interest rates, and she said that they are not going to wait for the ECB to start raising rates. They’re going to probably start doing it this year. So I think that there is an end in sight to this negative interest rate experience over the next 2 years.
Christopher Whalen: Well, the whole system has way too much debt and a lot of debt that is mispriced. So like I said, you’ll see the banks start to lean into this too. I think you’ll see provisions gently go up from where they are. I was surprised to see the credit cards up this much this quarter.
The mortgages are still real quiet. And commercial is still really quiet because the collateral values have gone up so much. A loan you made 2 or 3 years ago, the building will get sold easily for the principle on the loan which is typically a 50 LTV (loan-to-value) loan. Look at the equity that has been created in multi-family and commercial real estate over the past 4 or 5 years – It’s ridiculous. And it was all levered up again.
Look at New York. New York is going to be a lot of fun. We have compression underway right now.
Yra Harris: Will the balance bring back foreign buyers to the U.S. market to hold this mark up a little longer?
Christopher Whalen: I don’t know. I’ve been trying to get some good data on that because it depends on a lot of things. There was certainly a gold rush for a while, but then the Chinese shut the door. They changed the rules rather significantly. That’s what H&A is about. I think that for Europeans too, things have calmed down a bit so you don’t have that crazy flight capital that we saw in New York in 2015 and 2016. But the bid for high-end condos, that foreign big is definitely waned. I know a couple of brokers who just do that market and there’s a lot of stuff for sale.
Peter Boockvar: There are a lot of signs that commercial real estate has peaked out in this cycle.
Christopher Whalen: Oh yeah — Definitely. But you know a lot of markets are completely on fire, just look at Denver, downtown Denver…
Peter Boockvar: Yeah, with certain demographics.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah and they’re leasing them.
Peter Boockvar: A lot of population growth.
Christopher Whalen: Yes. That city has exploded. The city has almost reached the airport. And for those of us who remembered when the airport opened, it was really far away.
Peter Boockvar: Yeah, I was at that airport 2 weekends ago.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, and now (highway) 70 has expanded to the airport. It’s about a 40 minute run. That whole area with Colorado Springs and everything else has just completed exploded in terms of development.
Yra Harris: When they built that airport I said: Why are they taking away the old stable that said, “Stupid”. What vision I had.
Christopher Whalen: Now people are going to start expanding east away from the airport. That’s already happening.
Yra Harris: Wow. It will be in Nebraska.
Christopher Whalen: Exactly. But anyway, markets are going to be very interesting. I think that the fact that the dollar has been trading off the way that it has been is going to make for a very interesting year…
Peter Boockvar: And what we’re seeing in front of our eyes is the air leaking out of the bond bubble. Whether it’s here, whether it’s in Europe with the German 10-year breaking out above this multi-year range. I don’t necessarily know the pace of it from here, but things are changing before our eyes with interest and currencies. If there was going to be a major risk to this whole tranquil environment that it’s perceived to be, it’s the rise in interest rates and certainly a big draw down in the U.S. dollar. I mean commodity prices are at multi-year highs, the CRB printing 200 yesterday and holding them today. I think things are changing and there’s still a lot of nonchalance in the face of that.
Christopher Whalen: Of course. Markets sometime just sort of trade around numbers for a while for no particular reason and then you have an event that wakes everybody up and it moves, like the election. If you look at most charts for the bond market, there’s this big discontinuity around November 2016 and what do you do? Now it’s moved. And it moved again for a variety of reasons. China used to be the excuse, but I don’t think we’ll have that now. It will be a fairly boring inward look at China.
FRA: Chris, on your article you mentioned there could be downward pressure on long-term bond yields as the U.S. treasury concentrates future debt issuance on the short-term majorities.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, that the schedule. And again, going back to our earlier conversation, you’re the Fed and you see treasury in the market with huge issuance. I can put a lot of pressure on short rates such that they may blow past the targets and keep going. Imagine that. Meanwhile the Fed isn’t going to sell anything outright and they’re not doing anything on the long end. They should be selling the futures at least. You don’t want to sell the cash positions? Fine, but do something because otherwise we’ll flatten just like Peter said. I totally agree with that. And it may happen quickly. It could happen in weeks – Imagine that (laughs).
Peter Boockvar: I still expect a creep higher in long rates.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, it will bounce up, but it could easily rally. You want to be careful because there is so little paper. If they reopen the old issues which they can do, then you’ll know that somebody is yelling in that building saying, “Hey! You should be issuing longer dated paper.” The pit was planning to take their runoff and invest in the short end stuff the treasury is issuing, right? But their runoff may be so slow that they might not have that much net cash if they want to keep up with that $20 billion decline in the overall portfolio. So, I think it’s a funny situation. It goes to what Peter was saying. We could have a really nasty market environment because the Fed can’t help, the banks can’t help, they’re not allowed to anymore. So the street has no strong hands here that come in and push out a bad auction or push on the dollar if it gets messy. They would just have to intervene.
Yra Harris: And if they were to actually start…If Powell says, “I want to sell off…” to go back to your first point Chris, is that they are going to incur losses. And then they’re going to say, “Hey, we’ve got losses on our books this year because we’re actually taking some losses on the long end stuff that we bought.” So they’re kind of locked in that situation. And the situation on the front end has gotten so interesting that I actually called someone at the CME and said that I think it’s time for them to dust off the old contract and bring it back because it may become useful besides with the euro/dollar.
Christopher Whalen: Well no, this is the thing, the Fed economists in Washington were bragging about the fact that they made money on QE and they don’t understand. To your point though, Yra, what Powell has to do is get up and say, “We’re going to be selling some bits of the portfolio to help accommodate the treasury’s issuance and to rebalance because it’s far too long.” And they can do that in a variety of ways, but then he’s got to look at them square in the eye and say, “By the way, this going to reduce remittances for years.” They have a little account called the negative asset; they came up with it, where they put the losses. The congress capped the Fed’s capital at $40 billion when they confiscated the surplus for highways. So this is the situation you have and they don’t want to be insolvent. If there’s a big number in this contra account and they have $40 billion in equity, people can do the math. That’s the politics of this. It’s very strange. You got to realize that they are central bankers, they are very funny and it’s a big factor.
So, if Powell will change that? That’s a big deal.
Peter Boockvar: I think also a key factor is how much control these central banks can have over their external environment. I am of the belief that markets are going to force their hands. I still believe that cyclical inflation pressures are going to force their hands whether it’s commodity prices, wages or supply chains. I read an article yesterday on the front of the Wall Street Journal on how it’s almost impossible to find a truck to deliver your goods and people are paying hand-over-fist to just try and find drivers. I don’t think it’s necessarily fully in their hands. I mean Powell is going to have to start watching the German 10-year yield every day. Behind the scenes, obviously, a liquidity flow is turning into more of a drip and that all of these central bankers have to look at each other because what one does is really going to influence what the others do both on the upside and downside. When you think about this rise in interest rates, as some of these banks start raising, it gives other central banks cover. So, you’re less inclined to keep rates low if other people are doing it on the upside just as we saw the reverse. Peer pressure cut the rates to nothing and it’s going to do the reverse on the upside. I think that also feeds on itself. I am just amazed at people believing that this is going to be a smooth process and historically it never is.
Christopher Whalen: It’s even worse now because they took cash flow out of the system by forcing rates down. Forcing rates down is a debtor-friendly policy. It’s meant to transfer value from savers to debtors. So now, you have more volatility in the system because it’s less cash flow. People also have very little fat. There’s not a lot of embedded savings in the system from carry because your assets don’t throw off that much cash flow. It’s stunning when you look at Bank of America and the gross yield on their book is 4% — They’re not making money. The whole industry has got a negative risk-adjusted return because the return on assets is so low. In fact, I think that the number for the industry now if 0.75% on earning assets across the board. It used to be over 1.00%. And so the central banks by constantly forcing rates down, they’re taking carry out of the system and it’s not good – It’s deflationary, ultimately.
But I looked at the debt thing, Peter, and I totally agree on it. I’m going to have a lot of fun watching this. I was doing comments today for one of the regulators on whether or not they should allow different credit scores for underwriting loans – What do you guys think? Do you think that’s a good idea to have more than one way of measuring something like that?
Peter Boockvar: It makes sense.
Yra Harris: Yes, it would. I think the whole cycle from a private perspective, you know having my kids go through this stuff, and honestly it’s ridiculous. It’s truly ridiculous in the way that they measure it and they hold everyone accountable to the same standard. I know, it made the banks comfortable with time and there was a need for it, but if I ran a small community bank I would never do business like that. And I know they saddle with them. That’s not how you properly do business.
Christopher Whalen: Well, that’s what I’m telling them Yra. Like you said, the government shouldn’t be in the business of picking one. You let the people who underwrite loans figure this out and then the markets are going to tell them whether they like it or not because they’ll price the pools accordingly. So, I think we can figure this out real fast.
FRA: Just as a final question if you can go around to give your thoughts on where central bank: monetary policy and government fiscal policy is going this year in 2018.
Your thoughts, Chris?
Christopher Whalen: Well, for monetary policy I think that they are going to try and stay on the program as far as rate increases. But you get the 10-year stuck and it keeps moving Fed funds up – You’ll have a flat curve. And I think they’ll have to stop at that point.
Fiscal side: I don’t see any inclination of discipline in Washington – It’s a train wreck. They’re going to have to figure out a way to raise some revenue otherwise we’re staring at some pretty scary deficits. And I think eventually the credibility of the United States will suffer.
FRA: And Peter?
Peter Boockvar: Well, I think the weakness in the dollar is beginning to reflect the worries of those depths and deficits. That maybe we do have a $1 trillion budget deficit again in 2019. Obviously fiscal policies, in terms of tax cuts, are in place. Everyone’s got their fingers crossed that it actually improves economic growth as opposed to just improving earnings per share. We are seeing some wage growth which is a good thing, but one thing that we’ve seen is that the assumption on Wall Street was that the tax cuts all that would flow to the bottom line and we’re seeing that not all that will flow to the bottom line.
Christopher Whalen: Oh yeah. And the repatriation narrative is infantile. I cannot believe that people with PhDs in economics can sit there and go on and on about how cash is going to be brought back and invested in the United States. That’s not the way corporate finance works.
Peter Boockvar: Yeah, and a lot of that cash has been spoken for anyway with all the debt accumulation to buy back stock. So companies have already frontloaded the repatriation by taking on all this debt.
Christopher Whalen: Of course. But if you look at tax shelters like you saw they hit the Goldman because they are the great tax shelter shop. And a lot of that stuff is not going to come to light. You think everybody is going to go to the IRS and turn themselves in? The case with Dow last year that the Supreme Court declined to hear was a big deal. Donald Trump has the same tax lawyers as Dow. Trust me, the IRS now, any corporate they go to sham partnerships with as tax shelters, they basically just have to write a check. They have no appeal. There’s trillions of dollars at stake here. Trust me, these corporates are not going to come forward and say we did this wrong. Nope.
Peter Boockvar: I continue to believe that the other side of the easing mountain is upon and that creates the biggest risk for markets and the economy. People say that we’re not going to have a bear market until the economy goes into a recession and I argue that it’s going to be the rise in interest rates that leads to a decline in stocks that then leads to the recession. A trillion dollars of liquidity coming out from the Fed just in a loan is going to be a big deal as we deeper into the year. That’s what we have to look forward to over the next 2 years. The Fed taking out a trillion in loan the next 2 years after beginning that last year, the ECB ending QE, and that’s a $600 billion reduction in their run rate in 2018. And then the elimination of negative interest rates. So that’s what we have to look forward to over the next 2 years in terms of interest rates and I don’t see risk assets just whistling past that.
Christopher Whalen: Oh no. Look, everything is compressed. The whole curve is going to expand. Yra?
Yra Harris: Yeah, everything that was talked about and then you throw in the infrastructure spending package Trump is going to get through. I mean he’s not only selling the world today. You should watch how he probably hijacked Davos because they couldn’t lick his boots fast enough and he’s disruptive…So he’s got all this more debt coming on. He’s got really got discussions going on, in the United States of course, about financing debt. We are going to find out if his interest rates are going higher. We know the answer to it, but the rate of the world is going to have to find out. You have the ECB who took the Bernanke model and did everything they could to explode it with the amount that he could buy and he’s still…Peter and I know, he’s going to end in September, but it’s going to have a massive amount of assets on that balance sheet in the ECB and with the Germans breathing down their neck…There is nothing good going on there. There is nothing good and it’s going to come back to haunt. Now we have Joe from China and he’s reminding us about Minsky. The Chinese are reminding us about Minsky so we know we are in a very difficult situation and the world is just sleeping through it because you wake up in the morning and you see your stock portfolio is doing a whole lot better so you go, “What’s the difference. We’re all good here.” And they carry on. So, I think it’s going to be this year. I don’t think it’s going to wait for 2019. Some of these issues that people have chosen to pretend don’t exist. And it’s all bound to, we always know it. I think the 3 of us would agree that all crises come up from the debt market. Credit and debt markets determine everything and we’re there. It’s just what’s going to be the actual start that sets it off. I am not sure. I do agree with Peter that it’s going to be central bank oriented and it’s going to come as a change of direction. I think, Christ, you would agree with that too, it’s just how they do it. And Jerome Powell is going to be an interesting guy to see how he reacts to it.
Peter Boockvar: I think a very important question is: Where is the out-of-the-money put strike price right now on the Fed? What level, what percent decline, tells Jerome Powell that he needs to stop his tightening or reverse it? I think that’s going to be an important question.
What’s his tolerance level if these asset markets reverse themselves?
Christopher Whalen: But that’s an important question you’re asking because the tolerance level was very low. In other words, they wouldn’t tolerate any market upset. With Powell, it may be a little different.
Peter Boockvar: Because Powell has more tolerance.
Christopher Whalen: Yeah, I think he does.
Peter Boockvar: I agree.
Yra Harris: …Selloff in the equity markets? I don’t know.
Christopher Whalen: That’s the question Yra.
Yra Harris: Yeah.
Peter Boockvar: The irony is that you get a 20% correction then you’re just back to where you were last year.
Christopher Whalen: Oh, Powell has an easy button on his desk. The question is: Does he push it?
Peter Boockvar: Right.
Yra Harris: Yep, I think that’s absolutely right.
Peter Boockvar: As we speak, interest rates are breaking out today. The 10-year is up to 2.67% now. The 3-year is approaching 2.13%.
Yra Harris: And the Europeans…Today they’re not the catalyst; other times they are the catalysts. I’m interested to see it.
Peter Boockvar: Yeah, the dollar rallied for a couple hours after Trump tried to defend it and went straight back down again.
Yra Harris: And you know what? We didn’t even get into our discussion with the Swiss because they get the alchemy award of the last millennium. The game that they played here and pulled off is unbelievable to me. It tells you about the state of the world…
Christopher Whalen: Well, Peter’s right. They could take a loss on all that corporate exposure that they have. That would be a lot of fun.
Yra Harris: You know what, Richard, they finally admitted now that they are going to be the cryptocurrency capital of the world. They have been the currency capital of the world. But I think that is absolutely right. And it’s interesting, Peter, that is the Yen that turned when Kuroda was speaking at Davos today. The Yen turned very hard.
Peter Boockvar: Yep, it did. He said he’s getting more comfortable as inflation is going to their target.
Yra Harris: Yeah, and I think the Japanese are waking up that the Trump administration is not too happy with the Yen being so relatively weak. And Draghi and Kuroda can pretend all they want…And what was that comment yesterday from that one guy, and I know that they went back to that damn G20 meeting in Washington, which I kind of thought that they would, but he said, “Monetary policies that have a negative effect on currencies, that’s just an effect, that’s not a targeted currency.” Right…And that’s why every central bank when they release the statement about their interest rate intentions cites the level of the currency. Everybody in the United States, that is. Everybody talks about the level of the currency. Everyone discusses the level of their currency as being one variable in determining how they’re going to set interest rates.
FRA: Interesting times and great insight on the credit markets, financial markets and the economy. Thank you very much gentlemen for being on the podcast programmed show.
Great discussion.
Yra Harris: I’d love to do this again. This is great.
FRA: Just as a final word for our interested listeners. How can they find more information about your work, Chris?
Christopher Whalen: Just go to my website: www.RCWhalen.com. It’s the same handle on Twitter. And the Institutional Risk Analytics which is a free newsletter.
Peter Boockvar: Go to www.BoockReport.com and look at the asset management business: www.Bleakley.com.
FRA: Great. And finally, Yra?
Yra Harris: You can find my blog at www.YraGHarris.com and sign up for Notes From Underground which is also free. Whenever I write which is sometimes 4 times a week or sometimes 1 time a week will be sent you. And listen to the FRA podcasts. I think that they are very informative.
FRA: Great, thank you guys and maybe we can all do this together sometime.
Great discussion.
Yra, Peter, Chris: Thank you.
Transcript posted by Daniel Valentin
 01/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris And Peter Boockvar On The 2018 Trends In The Financial Markets
01/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris And Peter Boockvar On The 2018 Trends In The Financial Markets

Download the Podcast in MP3 Here
FRA: Hi welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight. Today we have Yra Harris and Peter Boockvar. Yra is an independent trader, a successful hedge fund manager; global macro consultant trading foreign currencies, bonds commodities in equities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997 to 2003. And Peter is the Chief Investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and Advisory and he has a newsletter product called The Boock Report. BoockReport.com. It offers great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentlemen.
Yra Harris and Peter Boockvar: Thanks, Richard.
FRA: Great! I thought we’d do a view on your thoughts on 2018 in general; where markets are heading, what the trends are, if you see any geopolitical events happening; effects on financial markets and the economy. And so, maybe we begin with the current rally in equities. Do you think it is sustainable? What are causes of this? Where do you see it going? Maybe start with Peter?
Peter Boockvar: So, what we have is enthusiasm, of course, post-US tax reform combined with optimism about global growth. Generally speaking, that is overwhelmed any concerns with central banks and the tightening or less easing of monetary policy. We went from “Don’t fight the FEDs, don’t fight Central Banks” to “who cares about Central Banks” because everything is fine in the economy and there is disbelief that we’re making the transition from a reliance on monetary policy to the benefits of a fiscal policy and synchronized growth. That is what the market currently believes. I think, this year, that thesis will be tested as monetary policy usually dominates fiscal policy in terms of its impact on markets and the economy because interest rates are such a strong lever and in a highly indebted global economy, that becomes even more so the case.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I have to stop and say that things Peter and I have done a lot with you Richard and so much of what we discuss is really coming to fruition. In fact, today is the most important day coming out of Davos (World Economic Forum) I hate this time of the year because I’m just not a big fan of what goes on in Davos. I found it, actually, kind of despicable to tell you the truth that these people gather and there’s so many political powerful people that are from central bankers to treasury secretaries to finance ministers discussing things and it’s an expensive ticket. I think its $650,000 to $700,000 and just what are you paying for? And it’s only going to be my problem and of course, there’s a day like today. We got a double blast; from Wilbur Ross and Steve Mnuchin. Mnuchin is a secretary and was talking about “if the dollar goes down, it’s actually good for U.S trade and Wilbur Ross, found to be more incendiary because he said,” …well, there’s trade wars every day. What was the exact phrase that he used? “Now we’re sending soldiers to the rampart”. Well, that’s a very, very incendiary phrase and I was truly bothered by that. So, everything we just talked about, everything Peter speaks to, this is going on. You know, Richard, I think that the 10-year will close out the year at 3.4%. I heard Richard Fisher today pushing about poor rate increases. Maybe. The more I hear what these people or what this administration are talking about, the more concerned I get as to where this is all going. I think I understand why Mnuchin and why they chose Davos to make these statements. That’ll be an issue for other people to think about. It’s very problematic and it does raise some serious issues for the Fed. It’s going to put Jerome Powell in a very difficult position especially if they keep the dollar down. I think we’d probably agree. The reason they keep it down. If you’re going to attack the Trump administration for starting a trade war, the only other alternative is to mark the dollar down. So, it now becomes open season, as far as I am concerned, on the dollar. So, why not? Richard, today you’re talking to two people. I know Peter has certainly been bearish, for what, $1.08 on the euro?
Peter: Yeah, $1.05.
Yra: Yeah, at $1.05 for sure. So I know these discussions have been going on for almost a year. And, Richard you know the many conversations that we’ve had in fact, I know Peter and I totally found commonalities when Mark Fields came out of the White House and talked about currency manipulation being the mother of all trade barriers. So it’s almost like this administration has adopted to that and said,” Hey, you want to go this route? We can play this game too,” and that’s where that leaves us to today.
Peter: It’s a very dangerous slippery slope. Steve Mnuchin is obviously trying to help the manufacturing sector but that’s 10% of the U.S economy. We are a consumer-based economy. So, damaging the purchasing power of a consumer-based economy is very dangerous. You have potential for rising input prices and certainly higher interest rates and I think that will swamp any benefit to multi-nationals. You have commodity prices, say CRB index, which is at the highest level in about two and a half years have rising inflationary pressure, generally speaking, particularly in wages. Now you have the threat of rising interest rates that will only be exacerbated by a weaker dollar. We import more than we export; highly inflationary. Foreigners own a lot more of our assets than we own of their assets and we rely heavily, particularly in the U.S treasury market on foreign buying of our bonds. If you look at last year, one year ago, a European buyer that wanted to pick up some yield bought a U.S treasury; 10-yr at 2.45%. A year later, not only did they lose some principal, since prices are lower, but they lost 15% by owning the dollar. So this is a very dangerous game. The administration should be focused more on currency and dollar stability, not the basement. There’s a very negative slippery slope.
FRA: Could other central banks, outside of the Federal Reserve, take reaction to this? Could there be currency depreciation intentionally done by other central banks? Do you see that?
Peter: We’ll find out tomorrow when we hear from Draghi.
Yra: There’s a lot of people short Yen or long dollar/Yen here who have been comfortable. That is not a comfortable position that you should be in because if there is somebody out there with a target on their back, it’s the Japanese. The BoJ (Bank of Japan) should’ve ended this policy. That doesn’t mean you have to start tightening and I know they’re not buying as much as they say and as the market thinks that they are because they don’t have to. There’s not that much to sell so whatever you have to clean up to keep that yield curve at that position is certainly not nearly as much as it was a year ago. You don’t really know the full amount of buying but with whatever they want to do they step into the equity market anyway people are buying but whatever they want to do. They step into the equity market anyway. It’s a very slippery slope and I think we’re going to hear from Peter’s executive director or from ECB (European Central Bank) about the strength in the euro. Now in some ways, the strength of the euro helps Draghi because it keeps the Germans at bay. It’s interesting that Jens Weidmann, now all of a sudden started talking more and more. So it does give Draghi some leverage. He could certainly go,” Well, we can afford to be more patient.” It’ll be interesting to see in his press conference how much he discusses the recent strength of the euro.
Peter: I actually think in this counter-intuitive that the strength in the euro actually gives Draghi some license to back away from his policy because inflation pressures are building in Europe as well. What the central bankers want, they have to be very careful as with, because if they achieve the inflation they want, interest rates are not going to be where they are. If Draghi gets us 2% inflation, the German 10-yr is not going to be a basis point, it’s going to be multiples of that. We saw in the market data today, talking about prices pressures intensifying. I want to bring up Japan and I’m going to quote Reid from this press release today from market on Japanese manufacturing. It said,” Strikingly output price inflation accelerated to the fastest rate since October 2008 an inch sharper rise to input cost. With a low rate in unemployment and sustained growth in official GDP data, inflation pressures should continue to mount.” Just imagine if they get the inflation they are hoping for, what’s going to happen to these bond markets? So, by having a little rebound in our currency, they can maybe moderate the inflation pressures. At the same time, giving the central banks an out. Now, of course central banks won’t look at it that way. I’m sure Draghi is going to whine about the stronger dollar is making it difficult for him but I think this is a window that’ll give them the opportunity to back away from their policies because I have to believe that they see the same inflation pressures that we do, particularly in the commodity side, with prices continuing to go up every day seemingly.
FRA: So, for this year, do you see a trend towards quantitative tightening by major central banks?
Peter: Well, the Fed is certainly initiating that. The ECB (European Central Bank) and the BoJ are just buying less but buying less is still a form of tightening. If you blow less air in a balloon, there’s still air going in but less air means a contraction of that balloon.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: Peter and I have little bit of a different view on this because I still think that Draghi is operating, not just prior to his mandate, his self-declared mandate; is of course the preservation of the euro. I still think that his end game is to put so much debt on those books. Not that he doesn’t have it already, he does. He’s going to push for the creation of a Euro bond. Merkel (Angela Merkel), I can’t tell you what she’s thinking right now. She has got some serious issues. She was chirping about some stuff today about globalization, what they need to get done are they going to divide banking authority. There’s a lot of things in the platter in Europe. It’s just not a straight path and I really think that if inflation takes off in Germany, Draghi and a lot of bosses will be happy because it’s a way for them to punish the Germans for being so intransigent towards Greece, Spain and Portugal. And pushing for fiscal austerity even when unemployment is over 20%. You’re going to have to endure this because right now, the most ridiculously priced asset in the world is certainly German debt. It’s preposterous. Peter keeps pushing it and he’s a 100% right. Right now, the interest by any practical measure, the interest should be about 4 %.
Peter: Yeah
Yra: Right.
Peter: Which should be in line with nominal GDP there.
Yra: Yeah. Maybe 4.5%. It is so preposterous. Let alone all the others but nobody acknowledges that. They all look for reasons. Germany is a land of savers. Every bit as much as the Chinese savers. That’s why the current account surplus is so huge. It’s the largest in the world because Germany saves. They save a lot of money and these savers are being punished because the people who are wrong are not Germans who are investing in the DAX or anything, it’s German pension funds and insurance companies but it’s not individual Germans. They got beat up so bad in the market back in 1999 and 2000. They’re not that invested here. So, most of their money is in fixed income type of instruments — they’re getting killed. We’re speaking on the Financial Repression Authority (FRA), nobody is being as much financially repressed as the German population and that has political notifications.
FRA: Will interest rates tend to rise this year necessarily at different points in the yield curve for yield curves across the major economies? Peter?
Peter: I believe that’s where we’re headed. In the U.S, they keep talking about rising commodity prices and rising wage pressures that are clearly evident everywhere will see whether productivity can offset that or not. The Fed is obviously going to be buying less. You have an enormous amount of supply coming our way as debts and deficits continue to rise. We could have a trillion dollar budget deficit next year. Now, I know the relationships between deficits and interest rates that are somewhat squishy but that was the case in a bull market in bonds. If we’re no longer a bull market in bonds, then the U.S treasury market maybe become more sensitive to U.S debts and deficits. Then you throw in the weaker dollar which can impact foreign purchasing of U.S assets. So I think that interest rates here will continue higher. I think they’ll surprise to the upside. In Europe, I think, interest rates there have only one way to go and that is higher as the ECB will likely end QE (quantitative easing) in September. As they’re currently buying less, or 50% of what they were buying in December and Japan is obviously the wildcard. Actually, before I get to Japan, let’s get back to Europe because this is what bondholders in Europe have to look forward to. Not only do we have a situation where QE is shrinking and going away, but after that they have the end of negative interest rates to look forward to afterwards. So, you had the Riksbank today saying that we’re going to start the path out of negative interest rates even before the ECB starts doing it. So, we are now looking at the barrel of the end of negative interest rates over the next two years. With seven or eight trillion of negative yielding interest rates, there’s going to be a lot of money lost in just getting negative interest rates back to zero. I see only higher interest rates under many different scenarios out of the next couple of years globally.
Yra: I agree wholeheartedly with Peter. I think the 10-yr yield, Peter and I have not discussed targets and I hate choosing targets but when I got pinned down I said,” The 10-yr will be at 3.4% at the end of December of this year. I think I’m going to be low. I think the curve will be back between 130 and 150. I really believe that. If they keep bringing the dollar down, it’s going to come harder and faster as Peter talked about that slippery slope. So, I’m a 100% in agreement and at 2.63 on the 10-year it’s a nice technical level. We could go a lot farther, especially if we have the central bank step back and are not there buying as much.
FRA: Now, one of the economists at Davos we mentioned earlier is Bill White, the former Chief Economist for BIS (Bank for International Settlements). He is now the Head of OECD Review Board. Just wondering on your thoughts, he mentioned because of this rising trend in interest rates, there could be some problems on the horizon due to the problems in servicing debt. So there could be a Central Bank debt trap if you will. Your thoughts on that, Peter?
Peter: Over the last few years, the average duration of credit around the world has gotten to record highs. Which means we’re hugely sensitive to small changes in interest rates. I would have to agree with that. I’ve read some chart from Deutsche Bank saying that,” considering the amount of global debt for every hundred basis points of rise in interest expense or in interest rates, can lead to a loss of 1.2 trillion dollars on paper. We’ve been addicted and accustomed to extraordinarily low interest rates that has dictated behaviour whether it’s the behavior of lending money to a junk credit with almost no covenance to keeping zombie companies alive to buying expensive paintings and hundred million apartments in New York City or buying the S&P 500 at historic valuations compared to 1929 and 2000. Changes in interest rates are higher and it doesn’t have to be a lot higher. It could have dramatic effects on the pricing of a lot of different things because the cost of money is the important price in input to a lot of these things. I think the markets are way too nonchalant with this move in interest rates and this change in behaviour with respect to central banks.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: You can’t say it better than that. Bill White, whom I have great respect for, as I call him Mr. Lean or Clean because in 2006, he wrote that wonderful paper for BIS talking about the role of central banks and should they be in the business of leaning into spectated bubbles or should they just wait and just clean. He was warning what was coming. We are addicted to this. We’re so addicted to just taking on more debt, more debt, and more debt. What are they using the debt for? To buy back stocks and pay dividends. This is so classic. Ray Dalio, whom I certainly respect as a thinker. I’ve been reading him for almost 35 years and Jeremy Grant also. But it seems to me they’re doing a lot of what I call “chirping” on issues that ought not be discussing such as: if you’re holding cash, you’re going to be sorry. Ok, maybe. But as I think by the time I was down with you, I did something a few weeks ago that I haven’t done in nine years. I took the free cash which is out of my trading account and bought T-bills (Treasury Bills) as my security. My daughter called me and said,” Dad, ninety-day T-bills are 138 basis points.” What am I thinking about? I’m moving and I’m not the only one because Warren Buffett said he’s got a one hundred million in T-bills. These are interesting moments here. I’m not as convinced of this great melt-up as everybody else. I think Peter is getting to where, as usual, things started getting called. We’re very sorry you own a $150 million dollar painting.
FRA: Could there be a slow-down in asset inflation due to the quantitative tightening trend?
Peter: It should. It certainly hasn’t happened yet. The sixty-four thousand dollar question is “when does it matter” and none of us know but I think we’re more confident that it will definitely will matter. I just have to be able to understand that risks are dramatically rising when you have such extreme valuations at the same time you have rising interest rates and a tightening of monetary policy. But again, the question is when does it matter and we won’t know until it does.
Yra: Yeah, and that’s right. People say, if they listen to Peter and I talk, you guys are just crying because you missed it. I have more money in stocks than I ever had. Before the market was at its highest, just by good fortune, started peeling back more. So I’m peeling back into this because I missed the last five percent. I’m not going to be upset because when the break comes, it’s not going to be a five percent break. It may be 15 or even a 20% break. Everybody says,” well that puts you in a bear market.” I don’t know that these rules people really hold in the realm of these Bernanke terminology; zero bond interest rates. I don’t know if any of these old rules hold but we’re going to find out.
FRA: Yeah, exactly.
Peter: We will find out.
FRA: Yeah. If this would’ve happened if they were a significant and fast fall in asset values of asset pricing, could there be a reverse in course by central banks from tightening back to quantitative easing?
Peter: Here is where it gets really difficult for the Fed because they went so extreme and were so slow in removing that accommodation, they left themselves with very little wiggle room. So in the past recessions, they obviously have a lot of bulls to respond. If this selloff is precipitated by higher interest rates, weaker dollar and higher inflation and the Fed decided to start cutting rates that would be a further mess for the U.S dollar and potentially even more inflationary and could lead to even higher long-term interest rates. So then what the Fed is going to do is, they’re potentially really screwed and it also ties hands with QE that could weaken the dollar even more. That gets back to the original discussion on the dollar and the administration wanting a weaker one. It really creates a difficult situation for the Fed if the dollar weakness continues because it completely ties their hands in responding to the next down term here. Because imagine them cutting interest rates with and already weaker dollar, that would be a real mess.
Yra: You know what, if you look at the last the curve steepened out over 180 or 200 baseline, I’m talking about the 210, that was when the second QE2 and everybody was convinced. Now we’re really going to get inflation. So the Fed, of course, wasn’t moving on the long end even though they were buying more. People were selling thinking inflation was really going to take hold. People are smug about the stock market breaking or possibly being negative. The other side of the coin has been where people say,” Where is the inflation?” They started talking about gold but gold is not going to go up because of inflation. Gold is going to go up because the central banks in the world capitulate to the deflationary scare because that is when gold went up the first time. There was no inflation. They would do anything and I mean anything to prevent deflation setting in and that’s what Peter was talking about. If they had to back track here now, look out!
FRA: Did that prompt them to go into extreme negative nominal interest rates so we get real nominal interest rates going into negative territory to an extreme level as if they’re cutting the interest rates on the low end to the same extent they did on the first financial crisis?
Yra: No, that view will certainly have “good friend” on the Fed.
Peter: Yes, no pun intended.
Yra: Pun totally intended. Thank you, Peter
Peter: I’m not convinced we go to negative interest rates. I think you’d blow up the U.S money market industry. I think the banks would go bananas so I don’t see that being a possibility in there. I think that the experiment with Japan and Europe with what they did to the profitability of the banks there. I think there’s a part of negative interest rates that’s been repudiated as a good policy. As the reserve currency of the world, having a negative interest rates, what a disaster that potentially could be.
Yra: I totally agree. I think that point was so well taken. I think Japanese stocks is a safe hiding place for many years. I still hold them. They’re finally starting to move now and they’ve been terrible. It’s like the European banks. Every time I hear people talk about European banks, what Deutsche Bank is trading 19.50? Big deal. They haven’t really responded well. Yeah, they’re well off their lows but that was because there was a question of their sovereignty. Now we’ve got beyond sovereignty at least for a minute until one of the European countries who really have a lot of sovereign debt becomes an issue and our sovereign bond is going to be zero risk rating forever but we’ll get to that question later.
FRA: What are your thoughts on geopolitical risk to the financial markets in the economy, Peter?
Peter: I’m less worried about geopolitical risk. It’s usually more news worthy than economic or market worthy. I don’t think we’re going to war with North Korea. I put that on the backburner, it may happen a day here or a day there. I’m less worried the geopolitics than I am of central banks really screwing this thing up.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: I couldn’t agree more. To me North Korea, I had trip of my own to North Korea because my son who really knows Japan well. He said,” Look it, as long as the United States isn’t sending air transports and take people out of Seoul, you don’t have to worry about anything because there’s 150,000 Americans living and working in Seoul. We know what happens if the United States were to bomb North Korea. I’m just talking about bunker busters that the retaliation upon Seoul would be so great. There’s nothing going on there. To me, the most dangerous place right now politically is Europe because we have the Italian election coming up and there’s a lot more possible impact coming from there. You can’t show that on television. You can’t take a picture of what’s going on politically in Europe. You can talk about it but it doesn’t have that dramatic effect. The only thing is the Saudi-Russian connection and possibly Turkey but that’s with us at all times. The Mid-East is the Mid-East unfortunately. I don’t see much else.
FRA: What about your thoughts, Peter you recently mentioned, Europe could be the epicentre of the next financial crisis coming out of the European bond market. Do you still feel that way?
Peter: Yeah, we need to remember that the bubble this time around was in central banks and interest rates. Just by having a conversation about negative interest rates tells you the bubble ran because, you know, that’s the epitome of a hot potato market. With Europe flooded with negative interest rates and the ECB reversing themselves, that’s where I think there’s a major, major risk. I think people have to really focus on that. Plenty of risks that could emanate from the U.S but a blow up of the European bond market will have global market interest rate reverberations.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts on that?
Yra: That says it all. There’s nothing I could possibly add to that.
FRA: Given this view on the horizon, how can investors protect themselves or what asset classes, generically, do you see as making sense in this environment? Peter?
Peter: I remain positive on commodities. Not just initially on the weaker dollar but we’ve seen years of underinvestment. Gold and silver is the way I’m playing the weaker dollar directly. I think that will continue to be a good place to be and I expect much higher prices. I think shorts from bonds, now all of a sudden, pay you something. As Yra said earlier, owning T-bills, you actually get paid in a coupon that is at or above the dividend yield on the S&P 500. Those are two places that is a way to protect yourselves, so to speak, in this kind of environment.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: Here we are, three sophisticated money people and we’re going to park on T-bills and that’s what I’m doing. We know that real yields are still negative on the short-end but it is far better than where we’ve been. I’m moving more to cash every day. This to me, is one of the greatest gifts we’ve seen. Could it be more rational? Sure, you can. We know that. When the S&P 500 came under pressure today, the break was severe and it actually held at a huge technical level but we still have twenty minutes left and while the S&P’s are hovering at unchanged on the date, it wouldn’t surprise me to see some pressure. Especially Mnuchin and Wilbur Ross, as Peter said, they are on a slippery slope and they are playing in a very dangerous arena here and this isn’t good for equities. The equity markets are much higher ready and as Peter talked about the double-edged sword of a weaker dollar and the impact on corporate properties. It’s not as clear and easy as some people think it is because there is going to be a push back and all you’re going to do is wind up with more uncertainty and disruptions. These are serious disruptions. When you start playing and trying to manipulate financial instruments like currencies, you open up the door to a lot of unintended consequences and we saw it this morning. The first reaction was for the DOW Jones to go up because it’s a large multinational corporation they have been reading this for so long. They see a weaker dollar. “Oh that’s good for you European markets Of course, the European markets never could get up off their behind. In fact, I’m buying DAX this afternoon because they have the DAX under severe pressure but where else are you going to go in Germany? What am I going to buy? Whether the euro goes higher or not, really to me, unless it goes another ten or fifteen percent higher, would I really start to get concerned about it for European corporations. Nothing is going on here. They are playing with, not even dynamite, something that is far more volatile and I’m getting very cautious.
FRA: Great words of wisdom. Thank you very much Yra and Peter. How can I listen more about your work? Peter?
Peter: You can go to BoockReport.com and if you want to learn more about Bleakley, go to www.Bleakley.com
FRA: Great. And Yra?
Yra: Turn into Financial Repression Authority or check out my blog www.YraGHarris.com. It’s a good place where you can get thinking. The good thing is people can really do get some trade ideas that you can really act upon. Peter and I are not offering theoretical analysis. I think there’s really bonafide proof to act upon.
FRA: Thank you very much gentlemen. We’ll end it right here and we’ll do it another time as well in another session.
Peter: Thanks guys. We’ll talk in a few days
Yra: Yeah. See you Friday. Thank you.
Karl De La Cruz
Karl.delacruz@ryerson.ca
 01/24/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Graham Summers On The Everything Bubble
01/24/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Graham Summers On The Everything Bubble

DOWNLOAD THE PODCAST in MP3 format
FRA: Hi welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Graham Summers. He’s current president and chief market strategist of Phoenix Capital Research, a global investment research firm located in Washington D.C. He’s a graduate MBA of Duke University. With over 15 years’ experience in business strategy investment research, global consulting and business development.
Welcome, Graham.
Graham Summers: Hi Richard it’s nice to be here.
FRA: Great having you on the show. Today we’d like to focus on your new book The Everything Bubble: The Endgame For Central Bank Policy and you got the book divided into two parts; how we got here and what is to come. So maybe we can base the discussion on that if you want to give us some insight into how we got here.
Graham Summers: Sure absolutely. So the idea for the book hit me when I saw that central banks, particularly the Federal Reserve in the United States, because I’m based in the US and most of my clients are, so my focus tends to be on that financial system. But I noticed that central banks were intentionally creating a bubble in sovereign bonds, which in the US we call them treasuries and they did this in response to the 2008 crisis. When I saw that happening it was cause for severe concern because in our current way that our financial system is set up, these bonds are actually the bedrock of the financial system. They’re the most senior asset class that there is. And if you look at what’s happened the last 20 years, we’ve had this kind of period of serial bubbles. In the late 90s, we had a bubble in technology stocks. They called that the “tech bubble”. Then when that burst, the Federal Reserve intentionally created a bubble in housing that was the housing bubble which led to the Great Financial Crisis of ’08. The significance of that is that housing is a more senior asset class than stocks. Then when the Great Financial Crisis hit in ’08, they dealt with that by intentionally creating a bubble in bond. So this is what actually gave me the idea for the title of the book The Everything Bubble because if you create a bubble in the interest rate against which all risk assets are measured, you’re going to end up creating a bubble in everything. It’s like raising the tide of the ocean, every ship going to rise as well. So I started writing the book and essentially what I quickly realized was that in trying to describe these things most people were probably not going to have a good idea of what I was talking about. And they were also probably going to ask why are things this way. So I divided the book into two parts: how we got here and what’s to come. The first half how we got here essentially started with the creation of a Federal Reserve and runs all the way up to about 2016. And I wrote with using a very simple plain language because a personal pet peeve of mine is that finances intentionally kept kind of opaque and confusing because I think it’s meant to keep most people ignorant of how the system actually works. So my goal was to write at least a hundred pages that anybody in the world could read and would instantly be brought up to speed on how did the United States financial system come into being. Why was the Fed created? How does the Fed work? You know, how did we get off the gold standard? And eventually leading up to the current era which is: how did we get into this mess? Where basically every 10 years we’re having these massive financial crises. And why is that the Central Banks are getting away with policies that really are completely insane and which none of us voted for?
I guess that answers your question.
FRA: Yeah that’s interesting. So can you walk us through in terms of the era of serial bubbles beginning, the Fed crossing the financial Rubicon, and leading up to the Everything Bubble?
Graham Summers: Sure I’d be happy to. The easiest thing to do by the way is to just if you really want to know about the things, buy the book. It is on Amazon I think they’re running a 10 percent discount. So the stuff you’re interested in, by all means, check the book out. But the kind of the bullet point way I’d run through this would be when the U.S. completely severed from the gold standard in 1971. It did two things. Number one is: it opened the door to endless money printing because up until that point if the Fed chose to print a ton of currency, central banks and foreign governments could still convert their dollars into gold if they wanted to via the Fed. So up until that point while the Gold Standard had technically been ended for most of us in 1933 by Franklin Delano Roosevelt, it wasn’t until 1971 that the gold standard really was rendered moot for everyone including central banks. So when that happened, suddenly the US Federal Reserve and the United States would be paying any and all debt using U.S. dollars. And of course, these are U.S. dollars that the Federal Reserve can print. So what happened at that time was you see a sudden ballooning of debt relative to the actual economy in the United States.
And there’s a chart in the book which shows basically GDP, which is the gross domestic product, which is the annual economic output of the U.S. and the second line is the total debt securities and the financial system. And what do you see in that chart is that starting around in the 70s these two lines are pretty close together, but after 1971 when the world was removed from the gold standard, the trajectory of the deadline was almost parabolic and just keep going up and up and up. Meanwhile, GDP continues kind of in a linear fashion growing. This was that suddenly the system flooded with debt because the debt is paid for by dollars which the Fed can print at any time so there’s no limit to any of that. What this did was it got us to a point where in the late 90’s the amount of debt relative to the economy was so massive that if ever there was a serious period of debt deflation, which is basically a time in which debt prices are falling which means they’re starting to go insolvent, which means that people are going bankrupt. You’re going to have to restructure debt. As soon as that started to happen the Federal Reserve would panic and flood the system with liquidity because the dirty secret for central bankers is that the thing they fear most is debt deflation. When debt deflation hit, which is when debt falls in value, which means its yield goes up. It means it becomes more and more expensive to issue debt. And if most governments in the world have been financing their budgets with debt, the minute the debt deflation hit, that’s essentially the bond market saying, “hold on now it’s going to cost you a lot more if you want to continue financing your budget”. So this is always the focal point for the Federal Reserve, which is why starting in the late 90s. The Fed switched to a policy of intentionally creating asset bubbles because the alternative would be to let the financial system reset by allowing the debt to clear. Nobody is going to go for that because first of all, it is political and career suicide and second of all it’s the complete systemic reset. So Greenspan then Bernanke and ultimately Yellen all engaged in the same policy, which would then create asset bubble and any time that the asset bubble burst and a crisis hit, it will simply flood the system with more money and create another bubble.
FRA: This is quite interesting also in light of the cryptocurrency developments you mentioned the central bank power of printing money, fiat money, this whole monopoly power. Do you think that governments will give up this monopoly power to private-based cryptocurrencies? That this would be something that would not allow them to print money at will.
Graham Summers: No, they won’t endorse that in any way. Cryptocurrency is the result of two things. One is the fact that central banks are basically trashing their currencies by printing so much money and money capital flows to where it’s treated well. And if your alternatives are Swiss Francs or Euros or dollars all of which are being printed by hundreds of billion, you’re going to seek something else. So I view cryptocurrency as the natural kind of reaction to the system being set up the way it is essentially an individual saying well I want to get out of there somehow and I’m going to create an alternative. The secondary effect is capital flight from China, which is that hundreds of billions of dollars are fleeing China and they’re using Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to get the money out. We know that 80 percent of the trading volume of Bitcoin is actually in China, but that’s sort of a topic for another time. But no to answer your question the Fed will never endorse cryptocurrencies. What the Fed will most likely do is try to create its own. And we know from an interview that the New York Fed President William Dudley gave back in November that the Fed has actually been examining that and looking into creating their own alternative to Bitcoin and the Fed would love that. Because if the Fed could somehow get the system to go completely electronic meaning physical cash no longer exists, it would allow the regulators to monitor every single transaction that occurs. And it would also remove the systemic risk of cash because physical cash only represents about 1 percent of the actual wealth within the system. And another dirty secret is that if enough people ever went to the bank and demanded their money in physical cash the whole system would blow up, the money is just not there. You know 99 percent of the so-called wealth is just electrons stored on bank servers and none of the banks actually have the money on hand, which is why a big goal for central banks is to get rid of physical cash in the next 10 years or so.
FRA: Yes, I agree with you fully and that gets us into your other section on what is to come. So you do talk about that the war on cash and also I would say it ties into negative interest rate policy because with the abolishing of cash it would allow central banks to more easily implement monetary policy especially if it goes into negative interest rates. Would you agree?
Graham Summers: Absolutely. So if you look at what I call the period of serial bubbles which is the late 90s till today. The Fed’s response to every crisis has been more and more extraordinary. When tech stocks blew up and we had the tech crash, Alan Greenspan kept interest rates down at 1 percent and he kept them there for like three years more than he should have which is what created the bubble in housing. Because if the rate of interest held by the Federal Reserve is lower than the growth rate of economic activity, money is essentially free because you can borrow money at the interest rate investing almost anything in the economy and you’re going to pocket the spread. So that was how the Fed dealt with the tech crash. Then the housing crash happened and the Fed cut interest rates to actual zero, keep them there for 7 years and does something like 3 trillion dollars in quantitative easing, which is basically printing money and then using that new money to buy assets from the banks which is the kind of backdoor bailout essentially the Fed doing a kind of cash for trash for the Wall Street banks. So that’s what happened last time around and we now have a bubble in sovereign bond and those are the most senior asset class in the financial system. The natural logical conclusion would be that when this bubble burst we’re going to have to see even more extreme policies. And the Fed has already hinted that in research papers and in speeches what those policies would be. They would most likely be negative interest rates meaning the rate of interest the bankers and the Fed is charging on the system is negative three or maybe even negative five. We’d also have that combined with nuclear levels of quantitative easing, so quantitative easing of like 100 billion or more per month. And then at the same time they try to ban cash. The way all of this would work is implement negative interest rate. Well that makes it difficult to sit on cash, so you banned cash so that people can get their money out of the banking system and in faith because of banks trying to charge you 3 percent on your deposit. Well heck just put your money in a safe. You don’t have to pay that interest anymore. So the Fed’s going to want to close the loophole that physical cash present. Than nuclear quantitative easing, the goal here is to just buy as much debt as possible to try and stop the debt bubble from deflating in an attempt to reflate it. And then the final policy will probably be some combination of wealth taxes, bail in and capital grab. Then what basically the way I would describe this is think of it this way, if the problem is that there’s too much debt, your goal is going to be to get as much capital as possible. So any money that’s lying around whether it’s in physical cash or in say, a payroll check you haven’t cashed for a couple of years and you just forgot about it. Or perhaps a CD, a certificate deposit, lying around or even savings deposit that you have in a bank. Government regulators are going to want to get their hands on it, much of that is possible because at the end of the day the issue is there’s too much debt. Most of the large entities in the system are financially insolvent as soon as interest rate normalized. And so they’re going to try and seize as much capital as they can.
FRA: Yeah exactly. And the NIRP, the negative interest rate policy, could also be in light of inflation or rising inflation if you have real interest rates as being negative, so nominal minus interest equals real. What exactly do you see playing out in terms of negative nominal interest rates or just negative real interest rates with rising inflation?
Graham Summers: I think we’ll see actual negative interest rates meaning the interest rate is in the negative like negative three in nominal terms. If you look at the history of the Federal Reserve, typically, when they react to a crisis or a recession on average they cut interest rates about five percent from their prior peak. Which following that line, if interest rates are three percent or the next crisis hit, they’re going to cut them five percent. That’s going to get you to negative two. If interest rates are around one, that gets you down to negative four, so this is how it’s been every time for the last 70 years. So I do think we’ll see nominal interest rates. We have them in Japan, we have them in Europe. Both cases demonstrated that nobody who implements them actually gets kicked out of office which is the ultimate fear for politicians and the central banking class. So no one gets kicked out of office for doing it and for whatever reason the system goes along with it. The reason the system goes along with it is if your option is to pay a little bit of money in NIRP and I end up losing that money, but the bond bubble stays intact and the system continues to function. Versus I don’t pay NIRP, I dump my bond. The bond bubble blows up and everything goes systemic reset, you’re obviously going to choose the first one. So this is why Central Banks have been allowed to get away with policies that just defy logic. If the alternative is everything blows up you’re going to go along with it no matter what. And we saw this with NIRP in Europe, we saw with bail-ins, which is when your savings deposits are actually raided by the bank and used to keep the bank afloat. We saw that in Cyprus, they got away with it there. So, currently there’s not really any indication that there’s going to be enough societal unrest to actually stop central banks from doing that. So, obviously they’re going to do it.
FRA: And do you see the Everything Bubble as bursting at some point or will it be more off of a situation where these measures as you mention the financial repression of war on cash, bank bail-ins, and wealth taxes. Do you see those measures as ongoing within Everything Bubble continuing to expand?
Graham Summers: Yes. The second option, they’re continuing. It’s very complicated to answer that because if you have an Everything Bubble, you’re going to have small asset classes blowing up. The real question is what happens when the sovereign bond markets finally blow up. That’s when you get the actual sort of systemic crisis. So if you look at the debt market as different sectors. For instance, the subprime auto loan sector is currently under a lot of duress. So there are little areas in the economy that are already blowing up here and there. My view currently and what we’ve been telling our clients is that we think central banks are going to have to taper and withdraw liquidity this year because inflation is beginning to threaten the bond bubble. What I mean by that, is bonds trade based on inflation. Inflation is rising, and then bond yields will rise to match it. If bond yields rise, then bond prices fall. If bond prices fall enough, then you start to have a debt deflationary collapse. And while we’re starting to see is that the bond yields on the German, Japanese and United States government bonds are beginning to all rise. So the bond market, the sovereign bond market, is beginning to react to a fear of inflation. Now if central banks have a choice: pool liquidity and let stocks drop or continue with the liquidity, let the inflation genie out of the bottle and blow up the bond. They’re going to choose number one. So my current view is that in the near future like the next six months, you’re going to see a lot of central banks pulling back and getting more hawkish and they’re going to let stocks correct in some way to try and keep the Everything Bubble, the bond bubble, intact. Whether or not that works, I don’t know because once inflation starts rising it’s very hard to get it under control.
So that’s where we are right now, but actually timing the Everything Bubble bursting and thing on this day it’s going to blow up. That is impossible. You know what you can do is you can look at what’s developing in the market. That’s what I do in my financial newsletters and assess where we are in things. Currently, we’re starting to get into dangerous territory. And what matters now is to see how central banks react to it. You know if they pull back and get hawkish, they probably can get away with keeping the show going a little longer, but if they just keep printing money, particularly the ECB and the Bank of Japan, and funnelling it into the financial system by tens of billions of dollars. Inflation’s really going to become a major problem and that’s going to really crash the bond market.
So that’s where we are right now.
FRA: What about longer term. How you see that playing out?
Graham Summers: Well longer term at some point the whole thing is going to blow up just like it did in ’08. Timing exactly how that happens, you’re going to have to look for key things. You know what triggered ’08 was the underlying asset class, which the bubble was based on, in that case housing, those prices peaked and began to drop. So that started to happen with sovereign bonds recently. The question is: does that continue to happen? And then you start to see the derivatives markets and the credit markets locking up. Because if you look at ’08, the crisis, in terms of the progression you had housing peak in ’06. Then you had some of the investment funds that were investing in subprime mortgages, which is the riskiest component of the bubble blowing up that was in ’07. In ’08, the derivatives and credit markets were locked up that’s how got the great financial crisis. So if you view that as a kind of template for where we are now. The underlying asset class, in this case sovereign bonds, has peaked and is beginning to turn. The question is: Does it continue to do that and then we start to see investment funds, bond funds, and then the credit markets blow up? We’ve yet to see that and that’s the key thing I’m looking for right now. If that starts to happen that means we’re in late 2007 area of the timing of the next crisis, which would mean the next one would be insane in the next 12 18 months. But again these are the things we’re all looking for. I haven’t seen them yet. There are no definitive signs that the crisis is beginning right now. The only definitive thing is we’re seeing that the bond yields are rising and this is going to start to concern central bankers very shortly.
FRA: Could the sovereign bond debt crisis be catalyzed through Europe? If we look at Europe, what’s happening in terms of a withdrawal of some of the quantitative easing from 60 billion Euro per month to 30 billion Euro per month — Could the actual crisis come out of Europe rather than the US or Japan?
Graham Summers: It could come out of Europe for sure, it could also come out of China. In terms of Europe, the issue there is that you’ve got a lot of distinct countries with their own individual central banks none of which can print the currency anymore. The only bank that can print Euros is the European Central Bank, which is overarching all of the European Union. You know Germany has its own central bank, so does Italy, but they can’t go and print Euros. That’s what actually led to the crisis with Greece and these other countries. Well, let me back up what led to the crisis for those countries have they had too much debt relative to tax receipts. The reason why those crises actually accelerated and became systemic in nature was their central bank could not print currency or engage in bailouts directly to try and prop the system up. They had to go to the European Union and if you go the European Union then you have issues where countries like Germany and France are saying, well why are we bailing you out when we don’t have a crisis ourselves? So Europe is a kind of a weird case of mutually assured destruction. You know on the one hand if a country leaves the Eurozone, and not like Britain did but like an actual country that’s located directly in it like Italy or France, then the whole thing blows up because suddenly the credit markets go because at that point the credit rating for the European Union is different. You start seeing interest rates rising and that will render these countries insolvent. So, Europe is kind of strange case where they’ve sort of cobbled this thing along. A lot longer actually than I thought they would. I thought they were actually a serious risk of going under in 2012-2013, but again it comes back to that original issue, which is if the option is: Do I go along with this insane policy and assist the main is kept the float or do I reject it and the system blows up? Everybody in a position of power whether it’s a politician, large-scale financial firms, and the central banks is going to go number one. But absolutely if you want to look at countries that are at risk of blowing up Europe would be top of the list along with Japan and China. The U.S., while its debt situation is also catastrophic, has the benefit of having the reserve currency of the world and a more diverse and liquid economy. The way I like to put it is the U.S. is kind of the least dirty shirt in the bunch, but the reality is every single one of them is in serious trouble the minute rates normalize and when that happens then it’s anyone’s guess exactly how it goes down.
FRA: And finally, how do investors invest in this environment? How can they protect themselves in what you’re saying is likely to happen just from a generic asset classes point of view?
Graham Summers: You know everyone’s risk profile is different. If you’re looking for sort of active investment advice and sort of being steered through the financial markets on a week by week basis I write a financial product called “Private Wealth Advisory”. That’s the sort of actively involved we’re buying commodities now or selling bonds now kind of thing. That’s more for people who are actively in the market, who want to have their capital directed in a way that they’re going to continue to profit no matter what happens. If you’re someone who’s more just concerned, what do I do in the next crisis hits, you know, how do I prepare? I’m not really looking to invest actively. The best bet is probably to invest in actual hard assets, things like gold, real estate things that you actually can touch with your hand. Things that actually in the case of hard assets real estate produces some cash flows as there are benefits there. But really think of it this way if the whole world is based on paper debt, then actually owning something outright particularly something that has some sort of financial stability and a less volatile price movement that’s probably going to be one of the safer places probably to be. Does that mean that if you put all your money in real estate you’re not going to lose anything when the crisis hit? Absolutely not. Everything will get hit. The question is: how do I preserve my capital in the way that it’s hit less and I emerge from the situation with as much of my wealth intact? The only real way to go about that would be somewhere in the hard asset class is: gold, precious metals, real estate, businesses that have operating cash flow, and stable demand things. I mean there’s a big reason why Warren Buffett’s been loading up on things like Kraft and other businesses that no matter what happens, you know people will continue to eat cheese or continue to drink beer, and Budweiser awhile back. And that’s sort of the way I’d look at it that way. So it really depends on your risk profile I can’t say hey everyone go do X because everyone has a different risk profile. Everyone has a different interest, but the reality is if the big picture way of looking at things is hey there’s too much debt then central banks are going to be forced to devalue their currency to finance that that you’re probably going to want your money in something of tangible value as opposed to something based on that currency which is going to be devaluing.
FRA: Wow that’s great insight, Graham. Thank you very much for being on the Program Show. We will post a link and information on the book on the website as well. And do have a website that our listeners can learn more about your work.
Graham Summers: Sure we have two websites. One is phoenixcapitalresearch.com. That’s our website for our products where if you’re looking to be actively involved in the market you want someone actually directing you to buy and sell a different thing to tell you what symbols to buy and what price to pay. That’s where you want to go. If you’re looking just to get sort of more familiar with our work. You can do two things one is you can buy the book “The Everything Bubble: The Endgame For Central Bank Policy” on Amazon right now. Or you can go to our free e-letter. That’s called gainspainscapital.com. That’s totally free. I send out a daily briefing on what’s happening in the market and assessing some of the big picture things that are going on in the system. And finally we’re on Twitter gainspainscapital, but the Twitter handle is the @GainsPainsCapit ending with the T. And you can find us on Twitter and I am on there most days commenting on what’s happening in the world.
So those are a lot of different ways you can get a hold of us.
FRA: Also we will interweave some slides that you’ll send within the body of the transcript of this podcast on our website as well. That would be great.
Graham Summers: I’m sure they’ve done based on the conversation. I’ve got a couple of charts in mind that should help illustrate some of the things we talked about.
FRA: Thank you very much, Graham, for being on the show.
Graham Summers: Thank you. My pleasure, Richard.
“The Everything Bubble: The Endgame For Central Bank Policy” on Amazon right now. <https://www.amazon.com/Everything-Bubble-Endgame-Central-Policy/dp/197463406X>;
Transcript submitted by Boheira Manochehrzadeh.<bmanoche@ryerson.ca> and Daniel Valentin
 01/20/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: FRA Co-Founder Gordon T Long On The New World Order In 2018
01/20/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: FRA Co-Founder Gordon T Long On The New World Order In 2018

FULL TRANSCRIPT:
FRA: Today we have a very special guest, Gordon T. Long. He is the co-founder of the Financial Repression Authority. He and I started it up. He has been publicly offering his financial and economic riding since 2010 following an international career in technology, senior management and investment finance. He brings a unique perspective to macroeconomic analysis because of his broad background which is not typically found or available to the public. Gordon was Senior Group Executive with IBM and Motorola for over 20 years. He founded the LCM Groupe in Paris, France to specialize in the rapidly emerging internet venue capital and private equity industry. He is a graduate Engineer at the University of Waterloo (Canada) with graduate business studies at the prestigious business school, University of Western Ontario (Canada).
Welcome Gord!
GORDON T LONG: Thank you Richard! That’s the Ivey School down at UWO.
FRA: Yeah. A great background just in all areas to give you that deep insight from different perspectives as you’ve always had.
GORDON T LONG: Well thank you, but it makes me feel like I’m an awfully old man, but I am…But Richard it’s nice to be on this end of a speaker because of all of the videos we did for FRA together…Videos versus the podcast we are now currently doing so it’s nice to be talking from this end.
FRA: You have done an incredible amount of the videos that we started off with over many years.
I thought today we’d look at the 2018 perspective. Over the last several years you have done a yearly analysis of what the risk are in the economy and the financial markets and put it all together, tying all the dots together, in a sort of thesis that you see happening. And you’ve graciously provided a number of slides that we’ll make available on the website and also as a part of the transcript we will write for this podcast. I thought that we would begin there by using that as a basis for our discussion.
The first slide you illustrate a number of risks — Do you want to elaborate on those?
GORDON T LONG: Yeah, absolutely. As you’ve said I have been doing these every year. I started in 2010 where I actually started circulating it to my subscribers and into the public domain and it’s not where I chose a subject to write about. It starts with a process that I refer to as a “process of abstraction”. And the first part of that process is listing all of the tipping points that need to be tracked and watched without drawing any conclusions. In the first chart we are showing here are showing the risks which are grouped in from high to low risk in segments here. We had just over 34 last year which some of them are shown right here on this chart. This year going in we have 44 that we are following and tracking very closely. And when we take those risks and we start to follow them in a process of abstraction which I will show you how we come up with the thesis…But over on the right hand side of this chart you will notice a red box with 11, those are the new ones of the 44. This is the top 11. Quite a number of them have been there for a year, some of them for a couple years now…the bond bubble, China’s hard landing, Japan’s deflation, but what’s really showing up this year and has been moving into this hierarchy is the stock market valuations you see at number 2 as a tipping point. It hasn’t been up this high before, just maybe barely breaking the top 10 as it has grown. But also down at number 11, flows in liquidity and that is the magnitude of what the normalization by the Federal Reserve, effectively the taper program at the ECB and even the reductions in the rate of growth of money supply at the Bank of Japan. The “flows of liquidity”, which is still very high 135 billion a month, is falling and is mapped out to fall. These are some of the destabilizing factors that we see growing, not that the others here aren’t going away. And another one here is number 8, “credit contraction”. We are at the end of an extended expansionary period, one of the longest in history. We are going into our 9th year and we see signals that the business cycle and credit cycle has reversed and has started to fall off — With that is backdrop. The second chart here is really the process we flow. You see the coloured boxes on the left and then we start to abstract those and group them into themes and then from those themes we try and synthesize them and ask, “What are they trying to tell us?” as we move to the right. At the bottom you can see the kinds of things we track over at a site I have with my son called: Matasii.com. And we track all those and they’re in the public domain if you want to follow them or look at them. But it leads to these conclusions and that is the subject and you can see where it’s led us in previous years as they keep shifting around and the thesis papers that we wrote. What we find too is that we’re always at least 18 months to 2 years ahead of things before they really come into the fray and become major front and centre. When you really recognized financial repression back in 2012, it was pointing us earlier 2 years before that that it was going to be a major movement and that was as quantitative easing was starting to unfold in the United States. But this year it has forced us to talk about something called: “The New World Order” and I need to state right off the bat that it is not what the conspiracy buffs have been talking about for years. It just happens to be the same name. The new world order is basically a social change that is happening right now because of: the advent of networking and networking communications, the degree of inequality that is starting to surface across the developed worlds, the richer getting richer and the poorer getting poorer, and a number of other factors that we’ll get into, but it’s changing the forms governance, it is going to change the forms of institutions that haven’t changed since the Breton Woods at the end of the Second World War which were predominantly US-based institutions if you would: IMF, World Bank in Washington, the United Nations in New York. But these institutions haven’t really changed and the new world is going to force these changes. Governance, the whole idea of a sovereign state is changing. So in the paper we lay out what those changes are going to look like and how they’ll unfold.
Any questions on that, Richard?
FRA: Yes – Does this include also the network for blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies?
GORDON T LONG: Without question. It’s very central because one of the major changes we believe is going to be an exchange in trading around the world. And I’m not proposing that people should go out and buy Bitcoin, but I am saying that it and other factors like that are going to be with us in a massive way, and more importantly, the technology underlying it, the blockchain technology. So it’s going to and is already reinventing banking and you’ll that accelerating in a bigger way because it’s reflective of the sovereign state and borders are going away. Once you’re on the network…That’s the beauty of a product like Bitcoin and how many are there…a thousand different types now? But it says you can go anywhere in the world and do these transactions so how do you police it, tax it, regulate it? That’s the whole beauty of it – It’s self-regulating and self-policed, you don’t need governments and you don’t have the cost that goes with it. And that’s the model. I’m not trying to talk about Bitcoin; I am talking about blockchain and that model. One of the driving forces is that it will allow us to do away in some ways with a nation state. It doesn’t mean that we are getting rid of governance, but the governance of populations is going to change. We have a centralized approach to government, its top-down right? Well our forefathers never designed it that way. At least in the United States it was supposed to be the bottom-up, but it’s changed. And the technology and the network will allow that reverse and bring the control down to the bottom slowly because it’s not like the status quo is suddenly going to rollover, but these social changes are so big and so powerful and there will be some crisis in here that will force this change to happen.
FRA: On one of the slides you have: “The network is the instrument to control the governments or the governments will use it to control us.” Which way do you think it will go or do you think it will be a combination of both?
GORDON T LONG: It will be a war, that’s for sure. The governments will see it as taking away their power and their control and I don’t mean that negatively because they feel they need to have it to manage, but the reality is that they can be managed differently. You mention in the introductory that I had 20 years in corporate life so I was well acquainted with trying to run large scale organizations on a global basis. Back in the 80’s, the corporations were called international and they were just really beginning to grow. Growth internationally was far bigger than domestic and the problems that went with trying to do that and what came out of it with technology was that we had to decentralize. We were forced to decentralize and push it to the lowest level. It allowed us to downsize, right size, outsource, but to flatten organizations so that we could be more responsive and we could operate in more countries effectively. I’m kind of netting that out. Well our governments are actually in the same boat today. They need to be decentralized, but you can’t decentralize over a border though you can decentralize in the United States by pushing more control and power to the towns, but it’s going to be across borders. And we are seeing that really in effectively trade blocks today. That is where they are trying to work together in a coordinated fashion where they are trying to decentralize and have the power of a group, but they haven’t harnessed the technology to do it and that’s going to be a big part of the changes. So from a sovereignty standpoint at top-down, we are going to go to bottom-up. We’ve got inequality between nations within nations. What we’re going to have is equality across nations. These are going to be some of the changes we are going to start to see. Where we have country laws right now we are going to see international laws because globalization was never planned, it happened. Consequently, we never put institutions and laws in place to handle that. Yes, we have the international courts and the United Nations, but they’re not proactive. As Ronald Reagan said, “The government isn’t the solution. The government is the problem.” So they’re standing in the way of the degree and the speed of the change must have right now.
FRA: Yes, I can see the power of blockchain technology as providing decentralized platform to address some of those challenges of inequality by eliminating the middleman, for example, in transactions or services. But what about on cryptocurrency as one of those applications of blockchain — Do you think that governments will allow private-based cryptocurrencies to coexist with the monopoly power of fiat money that they have today?
GORDON T LONG: It depends on what government you’re referring to. I think our listeners are aware of the SWIFT system (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication), we really have two sets of governments in the world, the developed countries and countries that I will simply refer to as the “bricks”. We have Russia, we have China and we have Brazil, we have India, we have countries that are outside of the formal developed countries with their currencies where they are debasing it, that is the developed countries. So when, for example, we pass sanctions against Russia, the way we impose them is ways through the SWIFT system and various forms. Well obviously there is a tremendous conflict and it leads into this whole concept of de-dollarization which is going to be one of the major changes in the next 24 months — It’s huge. The whole discussion that we should have on here is on de-dollarization, but the conflict that’s going on right now and part of the answer out of that is what’s going to happen to cryptocurrencies because it’s a way of getting around the controls that the central banks really have on the creation of money, the value of that money and the debasements of those currencies. Ever since Bernanke came in with his, “Enrich thy neighbour” and we have rotating debasement that is when we stop debasing, the ECB, and the BoJ. I have referred to them as the currency cartel, the four currencies, the big debtor nations, the USD, Euro, Pound and the Yen. That’s 95% of the currencies that are exchanged in the world and they’re the ones that are the primary debasement on the other side, which I was referring to, of the bricks. They are not debasing, but in many ways are trying to use gold-backing. So there is a fight that is going on and cryptocurrencies really bring that to the floor. Now Russia and China their problem with it is allowing money to flee out of China right now as capital flight. As it shakes itself out we’ve got these huge geopolitical issues that are facing us, but the cryptocurrencies are not going away. I’m not saying that Bitcoin won’t fail and something takes it place, I’m not saying for one moment that the government banks aren’t going to endorse it. But by endorsing it I’m referring it to controls and trying to use it as competitive advantages as opposed to it being a free open-sourced product like Microsoft Edge. If you go to Firefox, its open technology, there’s no charge and it’s open. It’s like Wikipedia. Once you open up that Pandora’s Box, you allow all the people in the world to participate in a really free democracy.
I’m not sure if I’m making any sense there, Richard, but this is how powerful the concept and the reality of the blockchain currency are because it takes it down to how you can vote. I actually lay out in the thesis paper examples and links to videos, which I encourage listeners to go and get the links, of people who have shown how you can take this technology and put it into democratic organizations from the ground up that can actually grow itself into a world organization…How voting would happen, how policies would be set, how individuals would participate in it at a town level, a state level, a regional level, right up through a global basis where you get a really participative democracy and it works in a much faster period. It sounds impossible, but there are just some brilliant people that are showing how to do it just as brilliant people that showed how blockchain and cryptocurrencies could work.
FRA: And do you see this evolution as being a part of a movement towards the fiat currency cycle failure as one of your slides indicates. Are we going to have a coming currency crisis?
GORDON T LONG: I don’t know if we’re not already in it, Richard, and have been for a while, but yes, absolutely. This chart that we have here which is labelled, “Fiat Currency a Failure” really shows how we’re evolving. There is a little star in the middle in the red pointing to whereabouts we are in this cycle. I put out a chart, that’s included in the thesis paper, back at the time of the financial crisis called, “The Fiat Currency Failure” and the cycle that we would go through. This is a very simplified version of it. Once you get off sound money, you put yourself on a road map that nobody has ever retraced themselves from and has always ended in a fiat currency failure because at that point you’ve entered a fiat currency. But it starts at the top right here with growth and debt. Once you start growing your debt, in the case of the United States, when you consume more than you produce and you become a debtor nation and then all of a sudden you balance your trades out there is a lack of savings going on. You get stagnant productivity and what it does is it forces you into a fiat currency which we did officially in August of 1971. But now what starts to happen is you really get stagnant and falling standards of living because savings, which are typically in a capitalist system, invested into productive assets is what in fact improves your standard of living. That’s what allows a standard of living to increase and when that doesn’t happen, investments start to slow and you get falling capital expenditure and a falling velocity of money. You just had Lacy Hunt on and he’s very strong on what the issues of falling velocity of money are. But then it leads to what we’ve had for a long time, financialization of the economy which we now have. When you get the financialization of the economy all of these issues that you and I have talked about for years now associated with financial repression have become front and centre of the government trying to manage the economy at the best that it can do. But it leads to extreme leverage which we have now, unprecedented degrees of leverage, but it creates policy crises – Fiscal, monetary, public, that kind of disruption is where we are at right now. Before we get to the currency failure, the whole leverage itself has to start correcting and what happens then is really collapsing collateral values. There’s insufficient new savings and insufficient profits. And I’m talking about real profits which are coming from productive assets that are creating new profits which is new collateral, new value that underpins our society. We have $230 trillion of debt right now and you don’t lend money out without collateral. So what happens is all the money that has been lent out, the collateral has been repledged so many times, something called rehypothecation, across the global world within the Euro/Dollar system that the issue now is a shortage of collateral. Now if the collateral falls in value, let’s say that interest rates go up on bonds which means the bond price goes down, the collateral against those bonds is being reduced because what we do in our world right now is we’re making debt and asset. So we’re taking bonds and making it an asset and we’re pledging it as an asset. So when it goes down in price because interest rates are going up, you have to produce and pledge more collateral. Where’s that collateral going to come from if you don’t have new savings. That’s the era that we’re entering right now. Then, of course, we’ll have the governments forcing new kinds of systems or policy changes such as helicopter money to push more money into our society and that’s when we start to get into hyperinflation. We’re not there yet. We are still finishing a deflationary cycle because of the globalization, which is starting to peak. When I say peak, the rate of growth is what is beginning to peak. Once we get into fiat currency beginning to fail, we have the social strife and then we get these forced changes into these institutions and forms of government which I talked about earlier.
Didn’t mean to be long winded, Richard, because there’s a lot in that and we lay that out in the paper.
FRA: That’s great. There is a lot going on. On the next slide you mention where we are and that appears to be past the Minsky moment – Can you elaborate?
GORDON T LONG: Yeah Richard. You know governments aren’t going to roll over and quit on us. And I’m not about to say that markets are about to plummet because what governments are very good at doing is changing the rules. When they change the rules they allow things to accelerate. I can give you all sorts of examples of that. Remember the last financial crisis at the bottom of it we had a concept called “mark-to-market”. That was that all the books were so full of derivatives that they had to price them in a way that would price them to market. But to save the market, besides the 13 facilities that the bank came out with, the regulators changed it where they didn’t have to mark-to-market. They marked to fantasy. All of a sudden the bottom was in and the stock market took off and it was running ever since not because of that but it is an example of how they changed the rules. They could’ve never changed that rule is crises never hit, but we do that. So every time we get into a problem we change the regulations so that we change something else. Right now, even if the mark could start to fall, we have such a huge entitlement program, I think in the United States we are at least $10 trillion underfunded in total pensions at all levels – You can’t have that kind of collapse. So it says you got to keep the equities up. As you and I both know, the Bank of Japan is already buying equities. It owns 5% of the Nikkei, north of 70% of all ETFs. The Swiss National Bank buys $65 billion almost every quarter that we know about. A lot of the central banks, even the Norwegian central bank have been buying. So they are buying equities already. Apparently the Fed is not and the ECB is not and the Bank of England is not, but if we get into a crisis you can expect them to start buying equities in some fashion. I’m not saying that’s definitely going to happen, I’m just trying to give you an example that this is not over. They have not run out of tricks that they will bring forward to keep this thing going into this Minsky melt up. It goes back to that cycle we were talking about. You can keep doing it unless there is collateral somewhere and there is just not enough unpledged collateral out there right now unless they just print the money. Then what happens is you just print it without collateral, which is called helicopter money because that the basic derivative of helicopter money, then immediately you get hyperinflation. Whether that’s this year in 2018 or 2019, I don’t know, but I do know that over the next 3 years this big reversal that we talk about in the paper is going to unfold and is going to take away all the options from the governments that have fiat currencies.
FRA: Can you elaborate on how you see that happening and what the reversal may be?
GORDON T LONG: Yeah, absolutely. It is not my concept. This was actually a paper put out by the Bank of International Settlements in Switzerland. They were very clear that it is the most important paper they have put out in years. They were warning the central banks to say look, you’ve got to get off this paper money and you’ve got to start normalizing and you’ve got to do it now. And they’ve got the gun to do it. What they’re saying and what they argue is that the issue is that the demographics which are changing dramatically…You know the baby boomers aren’t buying as much, the Millennial’s don’t have as much money, at least in the United States, but around the world even in China where we’ve had a dramatic reduction in the growth in population, we don’t have the youth that’s coming on in relationship with the accumulation of wealth that the previous generations have had. So what we’ve seeing is that the rate of savings, and savings goes back to this building of collateral and underpinning debt and the rollover of the debt, is growing but at a certain rate which is a much slower rate. It is slower than the investment capital that is needed to sustain the debt levels and the growth levels we have right now. The delta, its difference, is growing at a significant rate. That is going to force yields to rise steadily because of supply and demand and not necessarily in a big spike, but consistently. As yields go out, it lowers the collateral value of the bonds and as we were saying earlier before we began the show, Richard, the global swaps marketplace is over $600 trillion and at least $400 trillion of that is in bonds. So a 1%/2% increase in rates is just a staggering reduction in the collateral value which has to be shored up. It’s like a giant margin call. For those who have had a margin call, you know it’s not a very good day. So that’s the problem and it’s like a glacier, it’s coming and we stop this. We can’t create the babies and the people to do it. And now we’ve got so much leverage in the system and they’ll try and stop it using pension plans, buying the market, printing the money and that’s what will eventually lead to a fiat currency failure.
I hope I explained that easily.
FRA: Yes and it’s quite interesting.
GORDON T LONG: It’s a 70 page paper. I tried to summarize it in less than 70 words.
FRA: And with the pension crisis, how do you see that unfolding? What will pension funds be doing given this view that you see unfolding.
GORDON T LONG: Well, I think the pension plans right now are in the middle of a lot of changes that they know they have to do. I think they see a large amount of this pretty clearly, at least the better ones. They have been moving out of the stock market. I think they see a bigger run up, but they’re moving into private equities and exchange traded products. They are not looking for liquidity; they are looking for long-term investments. I think they are also counting on the government to come in and start to guarantee investments. I think you’ll see the governments come in and guarantee investments with payouts on it even if it’s with fiat currencies. I think that they are speculating that the major central banks will enter into buying the equity markets. If that’s the case they will stay in and start going heavily into the equity markets. I don’t think that they have bought into that quite yet – I have. I believe that’s where the central banks are pointed. There was a paper out that showed we have $400 million in pensions around the world globally, all totaled. Right now in the United States we have an $84 trillion underfunded pension entitlement – Where is that money going to come from? They just can’t print it. They have to make sure that it’s created through the financial markets and a big part of that is either in the debt market (bonds) or in the equities.
I’m getting a little off-track here, but it is an important point that right now as we talk here today, they are talking about funding the government’s debt and you know we got a $20 trillion thereabouts U.S. federal debt. And the tax plan on what it’s going to do and how it’s going to increase it. But we are squabbling over nothing because the United States debt is not $20 trillion; it is $84 trillion because of the unfunded liabilities associated with Medicare, Medicaid and other social programs that we’ve made commitments to that are coming due. We have 10,000 baby boomers a day that are retiring and we’ll have a 1,000,000 a year turning 70 years old next year. The rate at which they are now claiming and a number of people who don’t have the money to pay into it, the youth, is significantly out of line. But as bad as that is, that’s still not our debt. This is why this cycle is going to unfold because this debt is actually $220 trillion and you ask how I got this number and that’s what is called the fiscal gap. We’ve had Kotlikoff on a couple times and he’s even laid it out before congress – They know it. What the fiscal gap is let’s say we lend money to Puerto Rico. The U.S. doesn’t lend money to Puerto Rico, the banks do. What we do is we guarantee it and we guarantee it in what is called in accounting lingo, a contingent liability. So the banks lend the money, Puerto Rico pays the banks and by the way they couldn’t pay 6% when bankrupt, but now the banks want 12% or 14% because they are not worried about it. They gouge them because they know if they default we’re going to anti. We pay, if in fact, somebody goes broke. Well we have got $220 trillion because we’ve been bankrolling everyone in the world with “government aid” for whatever country and we have these contingent liabilities. Let’s say the U.S. economy actually suffered a recession or a slowdown and let’s just say 2% defaulted. Now we’re talking close to $5 trillion on $25 trillion
Am I making sense here?
FRA: Yes, absolutely.
GORDON T LONG: And that’s why this is a given. The question is just the timing of it. That’s why we’ve going to see a new world order because out of this crisis, it’s not all bad news. Out of this crisis is the natural set of changes that need to happen and there’s a better world on the other side of it.
FRA: Given this view of a potential unfolding, as you’ve indicated, what are your thoughts on the financial markets short-term, medium-term, long-term and the investment markets in general? How do you see that unfolding for the various asset classes like commodities, equities, bonds and currencies?
GORDON T LONG: Well it really gets bound to what you price it in and that is the U.S. dollar. Gold could be going up or down depending on what is happening to the U.S. dollar, right? So it’s really what’s going to happen in the shorter term — What kind of strength we’re going to see or weakness in the U.S. dollar. A big part of what you see with the U.S. dollar is often it is a flight to safety. If we have geopolitical problems, people tend to flow to the least ugly at the party, if you would. So the money will flow to the U.S. dollar which strengthens the dollar which has a certain behaviour in the asset markets. So we’re facing significant numbers of tipping points (opening slide) right now. Which one of these might create a shock that impacts the U.S. dollar and the various crosses right now? Because the moment we have this is what happens is that Japan takes home their money into the Yen because it’s been a safe currency for them despite the debasement of it and then the carry trade starts to contract. So that’s what you need
to watch. You need to watch what’s going to happen to the dollar. I personally think we’re going to have some pretty significant freights, in the next 6 months, in the financial markets because we’re at such levels it’s only natural. We haven’t had a 5% correction in historical lengths of time. 15%, 20% is perfectly normal in a market, but the leverage couldn’t handle that right now. As we see some of these normal adjustments in the market it’s going to be how we react to them. And whether the policies, which I was eluding to earlier, forces the central banks to reverse course of normalization and taper, whether it forces them to put into things such as helicopter money – Time will tell. These crises are going to happen and it depends on how people are going to react in the market.
I am not sure this is the time you want to be speculating in the markets. That last 5% or 10% can often be the most expensive. There’s a lot of places to invest right now besides the stock and the bond market.
FRA: What would be your suggestions for investors, generically, in terms of asset classes? Where can they protect themselves and get yield?
GORDON T LONG: The best advice I can give is to get out of the currencies and get into hard assets because real wealth, the real collateral we talked about, is hard assets. Money is something where you have to grow it, mine or build it and those are the hard assets. So put your money into those real items. Gold and silver have always been the epitome of a hard asset, but to be frank they are right now a manipulated paper market. I think that is pretty evident, but that doesn’t mean that you don’t have some level of those kinds of hard assets. There are a lot of various commodities. Look what’s happening with cobalt, nickel and lithium right now. There is no better performing hard assets then them; They are right off the charts. Why? Because off electric bolts, our cars and it’s not because I think there are going to be a lot of electric cars in Canada and the United States, but because that’s where they are going in China and India. There is no question. There are 50 new models coming out next year. As a Canadian, just go up to Cobalt, Ontario. They are blowing off their lids. Now that game has already happened, but the point is that those are the kinds of areas that are continuously being needed to be looked into. The reason they move is because people say, hey there is some real value here. I know junior gold mining stocks have restarted to move to. But I am not saying to do that. I am saying to look for hard assets.
FRA: You mention also private equity as a potential investment?
GORDON T LONG: For those who can participate in private equity. More typically in the United States you have to be an accredited investor, so you’re limited, but I do know there are new laws changed in Canada that allow you to have a certain percentage in private equity. They aren’t as liquid; they are longer term. But sometimes in a crisis you are just glad to have your money in a safe place.
FRA: Perhaps to end our discussion today we can go to your last slide on, “What All Politicians Can Be Expected to Do” with a quote from President Donald Trump.
GORDON T LONG: I put him up just to say he’s just like all the rest. No matter what, they are going to print the money. It’s not because they are bad people, it’s the only solution that they can agree on because it’s not their money. And Trump was quite clear before he became president he said we can’t go broke because we can print the money. And he said he was the king of debt and I’m not picking on Trump in the least in my comments. He’s a right-wing conservative and he believes this is the solution. So you can bet that as these events unfold, and they will unfold, that that’s the tact they will take. Once you know that then investing becomes relatively easy because once you understand the policies that the government is likely to take, your investment becomes a little bit easier.
FRA: Great insight as always, Gord. This has been a fascinating discussion. We’ll put up those slides.
How can our listeners learn more about your work?
GORDON T LONG: Right now I am pretty well restricted to my work because I am retired, I’m an investor, I just manage my own money and I do this work to really narrow in on where my investing should be, but I publish and put all of this at www.matasii.com and there’s a subscription service for it depending on what kind of detail you want to go down to, but a lot of it is right out on a public page. That’s www.matasii.com. If you sign up for the newsletter, we’ll send you a various list of things if you’re interested.
FRA: Well great. Thank you very much for being on the show. It would be great to do it in the near future again.
GORDON T LONG: Talk to you again, Richard.
< Transcript written by Daniel Valentin >
 01/18/2018 - Danielle DiMartino Booth: The Consequences Of Rising Interest Rates
01/18/2018 - Danielle DiMartino Booth: The Consequences Of Rising Interest Rates

Danielle DiMartino Booth Economic and Market Consequences of Rising Interest Rates
Jay Taylor Media, Released on 1/17/18
Danielle DiMartino Booth, former advisor to Dallas Fed Richard Fisher, talks about how rising interest rates could impact the economy.