Blog
 06/19/2019 - Will Italy’s new “mini-BOT” be the mechanism for it to leave the Euro Zone?
06/19/2019 - Will Italy’s new “mini-BOT” be the mechanism for it to leave the Euro Zone?

 06/19/2019 - Yra Harris: Investors are leery of central bank desires to keep downward pressure on interest rates
06/19/2019 - Yra Harris: Investors are leery of central bank desires to keep downward pressure on interest rates

“As I wrote last week, Trump is weaponizing the dollar, especially as he got a tweet response from President Draghi: ‘WE are not Targeting Specific FX Rate.’ This is not what Trump accused Draghi of. He just said a weaker currency, not a specific rate. Regardless, the GOLD/euro, gold/Swiss and other gold crosses have made new highs as investors continue to be leery of central bank desires to keep downward pressure on interest rates. Can Chairman Powell remain sanguine and patient in a world where Draghi and others are so dovish?”
– Yra Harris
 06/18/2019 - RALLC: Beware of MMT and how MMT could affect investing and trading
06/18/2019 - RALLC: Beware of MMT and how MMT could affect investing and trading

“Don’t dismiss Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) as unlikely to influence policy. This heterodox economic doctrine advocates sharply increased fiscal expenditures backed by money creation. An alluring promise of MMT is that it directly confronts a perceived flaw in today’s conduct of monetary policy: pumping liquidity into financial markets as the standard response to stock market and economic turbulence inflates asset price bubbles and thereby exacerbates income inequality …
Real assets provide a measure of inflation protection. TIPS, commodities, and REITs may appreciate as and when investors attempt to reposition for an inflationary regime. Unfortunately, today TIPS provide real yields below 1%, commodities pay no real yield at all, and REIT prices are highly correlated with the US stock market.
Repositioning portfolios to hold capital assets domiciled in countries with more conservative policies provides an alternative approach to protecting portfolios from inflation. Such protection comes at a cost. The premium the wealthy are willing to pay to protect real purchasing power at least partly explains the current negative real interest rates charged on Swiss bank deposits.
One way or the other, a return to high and volatile inflation can be expected to depress future capital market returns. Informed investors can prepare by paring back positions in mainstream stocks and bonds, diversifying into real assets, and revising down future real return expectations.”
 06/13/2019 - Yra Harris – Consider the Dollar has been Weaponized
06/13/2019 - Yra Harris – Consider the Dollar has been Weaponized

“It was former Ford CEO Mark Fields who said in February 2017 that ‘currency intervention is the mother of all trade barriers.’ The judge of that barrier is now Secretary Ross. Now, if you are certain that the U.S. DOLLAR is heading higher it is time for a reassessment of that trade. As the Chinese said in a white paper last week, YOU HAVE BEEN WARNED. It didn’t take long for President Trump to involve himself in the the currency manipulation discussion as he tweeted on Tuesday that ‘the euro and other currencies are devalued against the dollar, putting the U.S. at a big disadvantage. The FED Interest Rate way too high, added to the ridiculous quantitative tightening! They don’t have a clue!’
Consider the DOLLAR has been WEAPONIZED. Make no mistake about it.” – Yra Harris
Notes From Underground: Trump Has Weaponized The Dollar. Do the Longs Know?
 06/13/2019 - Martin Armstrong: The Federal Reserve may try to peg Interest Rates
06/13/2019 - Martin Armstrong: The Federal Reserve may try to peg Interest Rates

“The Fed realizes that QE has been a complete failure. What they are looking at is the 1942-1951 period when the Treasury ordered the Fed to create a peg and support the bond market at benchmark rates of interest thereby installing caps. This is slightly different than QE which buys in debt on a wholesale basis. The Fed may try the peg and this will result in a bifurcation of interest rates where private sector rates will rise and public rates will become fixed even on the 2 to 10-year paper. I believe they will come under pressure to try to prevent the national debts from exploding, which will introduce yet another crisis of inflation. By trying to peg the rates, when the market smells a rat, they will end up in a position of having to monetize the entire debt. We have some very interesting times ahead.” – Martin Armstrong
 05/29/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Daniel Lacalle and Yra Harris on the Eurozone’s Monetary, Fiscal and Bond Nightmare
05/29/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Daniel Lacalle and Yra Harris on the Eurozone’s Monetary, Fiscal and Bond Nightmare

FRA: Hi, welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. today we have Yra Harris and Daniel Lacalle. Yra is an independent trader, successful hedge fund manager, global macro-consultant trading foreign currencies, bonds, commodities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997-2003. And Daniel is an investment manager and has been a professor of economics. He has a PhD in economics, author of “Escape from the Central Bank Trap”, “Life in the Financial Markets” and “The Energy World is Flat”. He writes frequently at the Mises Institute. Welcome Gentlemen!
Daniel: Thank you so much! Always a pleasure.
FRA: Great, today I thought we would do a focus on Europe, what’s happening in Europe, the parliamentary elections and tying that in to some recent writings that both of you have done. We can also touch upon the Chinese-US trade frictions. So maybe to begin with, we get your views on all of the elections that have been happening this past week. Looking like a strong move to nationalist based parties and what your thoughts are on the effects of what this means towards the economies in Europe as well as the financial markets. Yra, would you like to begin?
Yra: Well, in discussing the elections, I think the biggest part of the election story now comes of course, you know I’ll talk about the horse trading. But from my perspective, most important element should be and I’m not sure how Daniel, whether he will agree with this or not, but Jens Weidmann should become the ECB president and my view on that hasn’t changed in several years. But I believe the same back in 2011 that Merkel succumbed to the charms of Sarkozy and settled. It was a mistake because I think it’s important for Europe that a German were to head the ECB now. Because you have to get the German populace to buy in full force into everything that the European Union wants to accomplish. And if you don’t have a German I think running the bank, it will be bad for German domestic political politics. So better to have somebody, especially of the caliber of Jens Weidmann and that will be a very important element because if we look at the flawed of how this all ends, Mario Draghi has built with Angela Merkel’s blessings and others, a massive balance sheet is whatever it takes scenario. What happens to that balance sheet? I think the highest probability is going to be that it gets folded into a euro bond which is what the main stage of the European project want anyway so you may as well have the German at the head, and I will stop there.
Daniel: I actually quite agree with what you are saying. I think that what these elections have shown is two things I believe.
One is that there is an important rise in the number of seats taken by euro-skeptic or nationalistic parties and that is I think very evident in countries that have seen very, very weak growth and the constant erosion of purchasing power from the monetary policy. You see there in Italy, you see it in France, you seen it also in Germany, even in Spain. So, I think that the first take is obviously that there has been a very significant rise in the populace. I don’t like to call it populace- the nationalistic parties.
The second point is that these elections have been about everything except monetary policy. There has been varying interests in the debates that there has been very few comments in the debates about monetary policy, about the role of the European central bank. And you’re very right, looking at the central balance sheet right now is about 40% of the GDP of the Eurozone at the peak of the QE. The US, the federal reserve, central bank was less than 26% of the GDP of the US.
So, it is very important that as you very well said, that the next president of the European Central Bank is a German official. And the reason for it is because the European central bank is already moving to some form of monetization or Euro bond. Because it cannot buy more sovereign debt but it’s buying every maturity and therefore it’s putting a lot of pressure on sovereign bond yields and on spreads. As such, if the Germans who are not very keen on full monetization of debt etc. See (6:14-6:16 Inaudible) European Central Bank under somebody that is not a German it can definitely create some tension in the euro and Europe.
FRA: And you’ve recently written an article called “ECB’s Monetary Trap” Daniel. In which you describe what’s happening in Europe in general and as far as what the objective is, you see that the ECB is looking to make public spending cheap to finance in a sort of financial repression. Can you elaborate on that?
Daniel: Yes, the ECB launched the quantitative (7:03 Inaudible) program as a tool to improve the possibilities of a government going to take structural reforms. However, in this process what has happened is that governments have grown accustomed to very low interest rates and cheap debt. What they have done is the opposite. If you look at the general results of the European elections, with the main parties that have won are demanding is more deficit and then more government spending. So, the ECB funds themselves monetary prep (7:42-7:45 Inaudible) it’s policy, it stops the low rate purchasing of maturities program that they have right now. What ends up happening is that you see massive rise of spread yields in the eurozone that could rock the economy very quickly. On the other hand, if it doesn’t stop and it continues to do what it is doing, instead of buying or telling the governments to undertake structural reform, what it is actually doing is whitewashing the populist agenda. Which is that government spending should be fully monetized and that there is no problem with massive deficit spending.
FRA: And you mention a lot of this basis is that there is no apparent inflation. As you point out, there has been a lot of inflation since 2000. Can you elaborate?
Daniel: This is actually quite humorous, because if you think about it the European Central Bank, most of the economists, most of the censuses is telling us that there is no inflation in the eurozone. As such, monetary policy can be as (8:59-9:01 Inaudible) as needed for as long as it’s needed. However, at the same time, you have every (9:06 Inaudible) France, demonstrations of the Yellow Vests. And what are they demonstrating against? The rise in prices. The rise in consumer prices, the cost of labor and in the polls undertaken by the eurozone, the second biggest concern of households after unemployment is the cost of living. It is a complete fallacy that there is no inflation in the eurozone. And more importantly there is quite a substantial amount of inflation. Prices has risen as I mentioned in my article, 40% since 2000 whilst productivity and salaries have barely risen.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra on ECB’s monetary trap and the perspective of Daniel?
Yra: I couldn’t agree more, and that’s my point about why they need a German to head up the bank. And I see that Daniel seems to have come out of it the same way. I had a conversation yesterday, first time I ever talked to him but I respected him for 40 years, 35 years, Mr. Zulauf. We had a nice long conversation and I raised the same issue with him and we’re having this discussion and I said “Look, if you follow the work of Carmen Reinhart, which I think is very important on financial oppression, which of course is who sponsors this podcast; Financial Repression Authority, nobody in the world has been as financially repressed as the German citizen because of their culture of saving”. That’s just the way it is, they really don’t. When the Germans did step up to speculate in stock markets, they ran right headfirst into the (11:19 Inaudible) market back in 1999, 2000, 2001. They had the lowest housing purchasing ownership because they don’t borrow. They don’t borrow to buy houses.
It’s just not as common so here you have: If I’m a German saver, and let’s say I’m in short money. I’m getting negative 50 basis points, 40 basis points, 30 basis- whatever, it’s negative. And inflation in Germany, I don’t care what it is in the rest of Europe, I live in Germany and we know that’s where it manifested itself and with Merkel’s ridiculous energy program which has driven up energy costs. I have suffered tremendously in order to bail out everybody else. So, the fact that I’ve been so financially oppressed as I feel as a Bavarian burgher and I’ve not been able to vote for any of this. Nobody has ever asked me even (12:27 Inaudible) received piece in the Financial Times talking about taxation, we got representation and of course financial oppression is certainly a form of taxation. So I need to see Jens Weidmann, I want Jens Weidmann because I have to feel that somebody is actually looking out for me. Right now, nobody is looking out for me. Yes, I know Germany has benefited from a weaker currency to the Deutschmark would have been very, very strong. But that’s an asset as well as a liability.
So, this is- Daniel, 100% and I can’t agree with it more; it’s a monetary trap and Draghi following more importantly Bernanke and the Japanese, whether it’s Kuroda or Shirakawa, has walked into this and he has no exit. So, the exit has to be to create the folding of the entire ECB balance sheet into a euro bond. I’ve looked at this and I’m sure Daniel there’s no other way out of this and it builds every day and now of course they’re buying corporate bonds which who Jim Grant did a wonderful piece in Barron’s over the weekend about it. That the ECB has been an enabler of French corporate takeovers because money’s so cheap and that is exactly right. And I will end on that because one thing the Brits are not doing intelligently is they can get the ECB to fund the entire Hinkley Point nuclear project and basically zero interest rates by just selling the damn bonds to the ECB, you know the French would never get it because the EDF would love for that to happen and the Brits ought to do that before they leave and saddle them with the entire cost of it.
FRA: Your thoughts on that, Daniel?
Daniel: That is actually a very, very good point. You mentioned this concept of German benefiting from a weaker euro which has been used quite extensively by consensus as a main benefit for Germany in the monetary union. However, you’re absolutely right. Who has been the other side of the trade and who has (15:08-15:09 Inaudible). And one side, the German savers have been massively and negatively impacted by a weaker currency and the low interest rates. But also, the household consumers have seen a very important rise in consumer prices, the energy (15:31-15:34 Inaudible) power prices more than double for households and as you already said they don’t (15:44 Inaudible) massively like the Spaniards or like the Italians to buy property and what ended up happening as well is that you have riots- well not riots but demonstrations in Berlin because rental prices are going through the roof.
So, the way out for the ECB is evidently some form of rolling the balance sheet into an euro bond, absolutely it is. There is very little else that can be done. However, how do you sell this to a European Union in which the level of its trust between nations has increased when you have the peripheral countries trying to go back to 2008 and have large deficits, even break the European Union. You have had even as recently as a year ago you had the president of the- current vice president of (16:50 Inaudible) talking about the possibility of breaking of the Euro. A euro bond on one side is a solution and the other side is a massive time bomb because if it is successfully launched, what would happen would be that peripheral countries would be screaming for that euro bond to be extended to current deficit. And on the other hand, if it doesn’t it would be entirely a liability for the German household. It is not an option and I think that is why you need to find a way in which with the new president of the ECB, you implement some sort of process in which responsibility and shared responsibility comes also with some form of guarantee that’s going to be effectively implemented.
FRA: You mention also Daniel, that there are 16, ten-year sovereign bonds in Europe now showing negative real yields. Do you see that condition as persisting or maybe getting worse?
Daniel: I think it will get worse, I personally think it will get worse because as we were mentioning before, the problem is it’s very easy to enter into progressive (18:27 Inaudible) monetary policy, very easy to print money. It’s very difficult to get out. And it’s very difficult to get out when you have three factors in the eurozone that differentiate real economy, for example the US. Now in the eurozone, 80% of the real economy is financed by the banking system. In the US it’s 20%. Therefore, shocks in banking system have massive impact on unemployment, on growth, on credit for SMEs, you name it.
The second factor is the level of government spending at a country in the European Union level. Government spending and government liabilities is very, very high and the reason why it’s so very high is also because you have a massive and growing liability on the pension side. So, one side you have the banking system which is still very fragile and financing a large part of the real economy. On the other side, you have very high levels of government spending and governments that- basically, a 1% increase in government debt expense in the eurozone would mean that deficits would balloon in (20:00 Inaudible) 16, 17 countries.
But the third factor is also very important, is that 80% of gross capital formation in the eurozone is recycling of capital. Therefore, you’re not having a dynamic capital expenditure that is driving new technologies, new (20:20-20:23 Inaudible) etc. Productivity growth is very poor, and overcapacity remains very high. That third factor that leads to a very, let’s say perverse incentive from both governments and the ECB to Japanize the economy, to sort of keep it stagnant but let’s say, painless.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra, on negative real yields in Europe?
Yra: Well, I think that’s absolutely right. You see how it’s crushing the banking industry in Europe. The worst performing stocks for 30 years have been the Japanese banks. And that’s been with a lot of the banks being destroyed in Japan, so you think based on the concept of an oligopoly at least, that the profit margins would be great. But of course, the central banks have destroyed that and as Daniel points out, of course Europe has a much more banking sensitive base economy. Not corporate bonds although the issue being is to their benevolent actions creating more corporate bonds causing the incentives of corporations to entertain that.
But you look at the banks, listen. The crown jewel of European banking was Deutsche Bank, that doesn’t even bring a laugh, the Spanish banks have recovered somewhat from the terrible situation they were in, the Italian banks we will never know what the real story is there because especially under Fazio. This is one of the great feedback loops of all time is because Fazio rules sovereign debt is zero-risk weighted. So, unit credit or Sienna whatever I’m loading up on Italian sovereign debt because I earn a decent return relative to everything else. And I don’t have to reserve (22:42 Inaudible) so it’s a beautiful relationship Bob. In fact, I actually asked (22:48 Inaudible) that question. I say when he was at the Bank of Spain, of course he was in favor of zero-risk weightings, but I ask, well I said “now that you’re at the BIS do you have a different viewpoint on that” and he started laughing, the answer of course is self-evident.
This is a giant, giant mistake but it’s more part of what Daniel calls “the money trap” and it is a money trap. And of course, Draghi can’t really get out of there fast enough. You know, October 31st can’t come quick enough because it’s going to be very difficult just like it was for Yellen and now certainly for Jerome Powell in trying to exit from the strategy that is very difficult to exit and then they really had no exit plan. So, I think it’s really worse for Europe and that what’s they’re caught in and if you look at Europe, nothing says it better than of course the stock valuations of European debt.
FRA: And Yra, you frequently made reference to the book by Bernard Connolly called “The Rotten Heart of Europe”. Bernard Connolly used to be a senior economist with the Brussels Commission. How do you see what he foresaw in that book to what’s happening now in Europe?
Yra: As I say, all you have to do is read the fore, he wrote the book in 1995, he updated it with a new foreword in 2012, 2013. If you read that you have to go, get a nice scotch and sit back and think about this through because everything he has talked about has come to fruition. Unfortunately, he is not proud of it, by the way because I know Bernard well. So, he’s not proud of that and it’s always worried him, and this is where it sits. And you know everybody points out ridiculous things. What they worry about, ridiculous things because the Financial Times which used to be a good newspaper has become a joke because they just sit there and nod in agreement with whatever comes out of Brussels and don’t challenge it. The fact that this election is the biggest issue, of course what they wanted to make the biggest issue was nationalism and anti-immigration. I would vehemently at rise of the Alternative for Deutschland and it’s actually at its beginning in 2013 in response to what the ECB actions were.
And this is going to get worse because these are pocket book issues, and nobody has an answer for it. And fiscal, you know as long as the Germans remain (25:59 Inaudible) about fiscal austerity or at least fiscal- I’m going to say more importantly fiscal responsibility. I mean, you see it as we’re sitting here right now Rome and Brussels are going back and forth and I’m willing to bet that as much you know, people think that Brussels is going to place a fine upon Rome, it’ll never happen. It can’t happen because the Italians, you got to give Salvini his due cause he understands. He gives power to the old saying: If you owe the bank a hundred dollars, they own you. If you owe the bank a billion dollars, you own the bank. So that’s exactly what’s going on there and the Italians are not foolish. They understand. And I really think that Salvini must meet all the time with Yanis Varoufakis. He explains to him because he was very upset when Alexis Tsipras sold out the entire movement to get whatever he could out of Brussels but Salvini is going “There is nothing you can do to us” and they’re going to run a much bigger deficit, they have to. They’ve got no choice. So that’s where it lies and going back to Bernard Connolly “The Rotten Heart of Europe” which is still the most important book, I’m sorry if I hurt anybody’s feelings about Europe, it still has relevance and the players he talks about 20 years ago, 25 years ago, are still heavily involved in this now. So the book still has great relevance.
FRA: And your thoughts Daniel?
Daniel: I completely agree with what Salvini is doing. I was in Italy recently, there was a TV debate about this whole to and fro between Brussels and Italian government and one of the members in the league was saying “Hold on a second, you mean that we’re going to get a 4 billion euro fine for having the same deficit as Spain?” It’s become a system of perverse incentives because on one side is (28:25 Inaudible) we cannot exceed the deficit and we cannot break the rules agreed at (28:32 Inaudible) etc. However France has missed those same targets 11 times, Germany itself as well and France for example has not had a balanced budget since the late 70s.
The problem of the eurozone has nothing to do with the lack of government spending. The problem of the eurozone’s very poor productivity, very undynamic growth and very weak levels of employment, comes from the excess of government spending. And obviously yes, they will run larger deficits as you very well said there is no other option because Italy has been stagnant for two decades, France as well. But ultimately the issue here is, is that going to solve anything? And the Germans will finance that deficit at the end of the day, it’s a bit of, sort of a bender-financing type of situation. But if you think about it, from the perspective of whether that is going to help the eurozone countries economies improve in productivity and therefore salaries improve in competitiveness and improve in growth, unfortunately it won’t. Yes you will have deficit spending, more current spending in subsidies and in malinvestment but fortunately that is not the solution. The point that you mentioned before, is at least you will sort of hide the risk of European banks under the rug of the ECB, that is as much as you do. But unfortunately, I don’t think that it’s (30:37 Inaudible) large deficit is going to move the country into growth because it’s been running a massive deficit for many, many years and it hasn’t.
FRA: And finally, a question on the global trade. How do you see the US-China trade frictions and their effects on the financial markets and the global economy and also do you see intensifying US-European trade frictions as well… Daniel?
Daniel: How do I see, I was explaining this to my students the other day. If you have a company and you have the biggest supplier of your company, how do you treat your supplier? You treat your biggest supplier with a little bit of tightening. You demand discounts, and if somebody is your biggest client, you take them for dinner, you treat them nice, you send them presents for Christmas and so what is happening right now is exactly that, is the negotiation between the largest customer and the largest supplier. And what I see is that the rhetoric of consensus is blaming the global slowdown and the problems of the eurozone, the problems of different economies on something that has absolutely nothing to do with it. Which is this trade dispute between the US and China.
The first reason is because people perceive that the trade dispute the US and China is something that is hindering the growth of the rest of the world, and it is not. There is absolutely zero evidence that China is importing less than the rest of the world than what it needs. Actually, there is all the evidence that it is importing a lot more. China has a trade deficit with most of the rest of the world.
The second thing is that there is this perception if there was this agreement with the US and China, it would be an agreement that would sort of kick back growth and the growth mode in the global economy. We tend to forget that if there is an agreement between the US and China, it is a zero-sum game. If China starts importing more soda from the US, it means importing less from Argentina, because there is no evidence that China is importing less than what they need. Actually, there is all the evidence that they’re importing more than what they need in order to boost GDP and it’s evident in the (33:26 Inaudible) bill. The same with natural gas, if China imports more natural gas from the US, that will mean less natural gas imported from Qatar.
So, what I’m trying to get to is that this dispute is a negotiation, and that this negotiation, there will be an agreement reached. However, a lot of Europe, a lot of the excess valuations in the market, excess risk taken of the market etc. Was predicated on the idea that an agreement between the US and China would sort of change the global trend of growth. I think it’s not going to do it. The impact on it right now, we are seeing right now is obviously, you get (34:16 Inaudible) you get very low 10-year sovereign yields. So, you have flight to safety and I think that basically just the trade war has been use as a subterfuge because either we have been in a trade war since the early 2000s. Remember all of us here remember for example, the aluminum war between the Bush administration and what Obama did with for example, solar panels, all these things. Either we have been in a trade war since 2000 or we are not in a trade war now. What we have now is let’s say a less diplomatic negotiation. Will the US go after some of the imbalance afterwards, after reaching an agreement with (35:10 Inaudible), you bet they will, you bet it will. And the reason for it is the reason I always explain to everyone. You go down the street here in Madrid or in London or in Germany, any city in Germany, any city in France, tell me how many US cars you see.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra?
Yra: We are very much in agreement. You know I think this issue is far more of course than trade and it’s long overdue. You have to let the (35:47 Inaudible) whose been screaming about China’s entry into WTO which of course was all laid out by the Clinton administration and the way they were done and the rules that were crafted. In the way that China has skirted around what the WTO’s true intentions were on certain issues and it’s been long overdue. But American corporations and American businesses are not just like European businesses by the way, is not without some liability in this because they are willing to quote-on-quote sell their souls for access to a billion .3 consumers. Anything to get into that market.
So, they knew what the rules were going in, they just didn’t believe them. And I always harken back to 2009 when Jeffrey Immelt was then CEO and Chairman of GE. You know GE started pulling out of some business because they realized they couldn’t make any money in China. It was very difficult, you have to give a lot in the partnerships. So, they realized then it was not working out. These are things that some have been corrected but everybody went into China knowing what the rules were or not, what the rules were not. And the Chinese has been very astute so let me pick up more Daniel, which is I keep saying to people. If you’re right about the outcomes of China, then you should be buying Mexico. And as bad as Mexico can be with all it’s corruption, the whole concept of NAFTA which we are revisiting too was that they were going to build a North American behemoth of Canada, US and Mexico, big population and it would ensure that there would be wage pressure on US unions to keep America somewhat competitive on that basis and the Chinese disrupted it because January 1st in 1994 when NAFTA began, that’s the Chinese devalued the yuan from 5.8 to 8.7. They knew full well what the intentions were and of course that’s created the Asian contagion because you had all this capacity built in Thailand, in Malaysia, Indonesia, Hong Kong, Taiwan. Massive amounts of capacity and now the Chinese were doing their best to disrupt the whole thing anyway, which they did.
And they created what came four years later and of course Mexico suffered immediately with the- what do they call it, the tequila crisis. But if you believe that this has staying power and you’re a large global corporation, a multi-national corporation if we still use that word. When I was in school, the essence of my research was multi-national corporations, that was the 70s. Then it’s time for NAFTA investments into Mexico and actually AMLO, who is from the political left, he understands what’s going on. Can you get the corruption under control? Hopefully he can because he has a huge popular mandate, but I would look to Mexico, Mexico would tell me more about what people really think than anything else. Because there it is, (39:41 Inaudible) that sit on the northern border of Mexico, southern border of the US were built to be the key focal point of the global supply chains which China basically uprooted by design.
So, there are things we don’t have to guess at this, if we watch to see what is going on, we will have a pretty good idea. Right now, it’s not telling me. I look at the peso, I look at what’s going on in Mexico, it wants to happen. But you’re not seeing it yet. I think some people are pulling out of China because they’re fearful so they’re moving some factories across to Vietnam and Thailand and Malaysia again, but we’ll see what happens. But if you look at the value of the peso relative to when the yuan was devalued by 50%, the peso then was I think about 3.3 to the dollar is of course is 19 to the dollar so all kinds of advantages. But let’s see if they work out. I think it’s a little early to make that decision, but it is worth watching and it will tell us more about global trade because Daniel’s point about (40:53-40:56 Inaudible) so what it means is if you don’t buy soybeans from the US, you buy from Argentina, someone will buy the US soybeans. But it’s the same again with LNG but of course in the LNG issue a lot of those long-term contrasts there’s a lot of Asian financing that went to building those huge complexes down on the gulf coast. So, with that comes contractual agreements, a lot of that LNG has to go to Asia, it’s not like Trump will say we are going to sell it to Europe, no you’re not. There are long term structural agreements you will have to adhere to. There’s a lot of things going on and they’re really worth watching and now I have to go and read Daniel’s work because I’m not familiar with it, but this conversation has really elevated that for me so thank you.
Daniel: And thank you!
FRA: Great, this has been great insight and fascinating discussion, how can our listeners learn more about your work, Daniel?
Daniel: Well, the easiest way is to go to my website DLacalle.com. And obviously you can find my books on Amazon and you can also follow me on Twitter at DLacalle_IA.
FRA: Great, and Yra?
Yra: Where I’m writing as usual is at “Notes from Underground” but you can go to YraHarris.com and register for, it’s free. There’s a lot of great discussion that comes from people all over the world, it’s all about discourse and ideas and of course we’re, Daniel in the classroom, I’m in the training arena and investment arena so we try to beat the concepts around and try to create very profitable opportunities for training and investing and that’s what our goal is, again there’s no political agenda, there’s nothing else but trying to generate profitable trades and if that’s what your designs are then it’s the right place for you to come and join the discussion.
FRA: Great, thank you very much gentlemen.
 05/23/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on the U.S.-China Trade War
05/23/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on the U.S.-China Trade War

 05/06/2019 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith on the Loss of Confidence in Institutions
05/06/2019 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith on the Loss of Confidence in Institutions

FRA: Hi, welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Charles Hugh Smith: Author, leading global finance blogger and America’s philosopher we call him. He’s the author of 9 books on our economy and society including “A Radically Beneficial World: Automation, Technology and Creating Jobs for All”, “Resistance, Revolution, Liberation: A Model for Positive Change” and “The Nearly Free University and the Emerging Economy”. His blog OfTwoMinds.com has logged millions of page views and is in the top 10 of CNBC’s Top Alternative Finance Sites. Welcome Charles!
Charles Hugh Smith: Thank you Richard, it’s always my pleasure to be on the program.
FRA: Great, I thought today we would do a focus on what many are seeing as a of loss of faith in government institutions. In particular government in general and the thesis behind this: what is driving this and what are the implications to the economy and to the financial markets.
Charles: Sounds like a great topic! I know before we started recording you were explaining that this is one of Martin Armstrong’s core theses about the next few years and so maybe you can take the lead and summarize Armstrong’s perspective on loss of faith in institutions.
FRA: Yes, he’s one of the most vocal people that are mentioning this thesis and so he sees it as stemming from a number of sources and we will explore those. But importantly also he looks at the implications of this two (Inaudible 2:01) economy, two of the financial markets and in particular movement away from public assets towards private assets. Public assets meaning anything government makes or produces like in terms of currencies, bonds whereas private assets would be equities and also things like precious metals.
Yeah, let’s take a look at what is driving this. We can break it down into a number of categories. We got growing political dysfunction, discontent, polarization at the political front that’s driving this loss of faith in government institutions. We also got economic factors in terms of purchasing power loss and you’ve got a number of charts to share on that. We’ve got also the limits of what central banks have been doing and how they painted themselves into a corner. So, we got dysfunction at the central banking point, we have also got dysfunction in government pensions. We see this happening especially in jurisdictions like Chicago or the state of Illinois, other states where municipalities are running into problems with unfunded liabilities and emerging government pension crisis in many jurisdictions of the western world. If you’d like to start off with some of your charts that you’ve shared and how you see the (Inaudible 3:54) pushing the loss of faith in government institutions?
Charles: Great, I think I’ll start out by setting two kind of contexts that seem to be global in their reach. In other words, we can look at every place from China to Japan to the EU to the US to emerging markets and find the same elements or characteristics of the relationship between the public and government. There’s a general sense of the loss of trust in the government’s narrative. In other words, the governments around the world in general are saying “everything’s fine, the status quo is working. Great for everyone and there’s very low inflation, wages are rising, and the economy is doing very well for everybody”. And we get the feeling they’re adjusting these statistics to support their narrative rather than really giving us the truth, which is probably considerably less rosy. So, we feel like we’re being either manipulated or being lied to as a means of supporting those few who are benefiting from the status quo.
Also, to kind of mask the reality that the general public has been politically disenfranchised. In other words, you go to the polls and in a democracy and you vote for somebody else, but the status quo never changes. And so, there’s that sense that we’re politically disenfranchised so if you feel that you really have lost your political voice and your financial voting power as well then you are going to lose faith in those institutions.
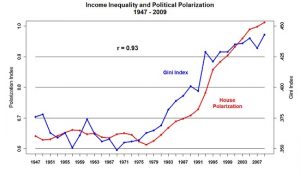
And so, I’m going to start with this chart of political polarization and income inequality:
We can see that the two track each other very closely. In other words, political polarization is highly correlated to the rise in income inequality. Which I think we can conclude that political polarization is just one indicator of the stress that occurs when people lose confidence in governance in general. They start trying to vote for someone on the extremes because voting for people in the middle of the spectrum hasn’t changed anything.
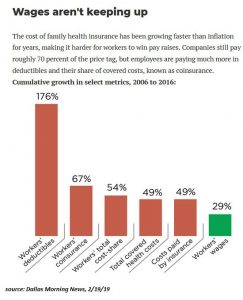
I have a chart here about wages and health care costs which are unique to the United States.
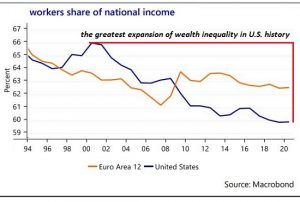
But I think in general this loss of purchasing power of earned income is global. In other words, globally governments are understating the loss of purchasing power and the stagnation of wages and we can see this in the worker’s share of national income which has really plummeted in the US but it’s declined even in Europe.
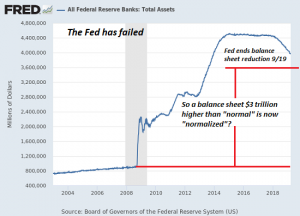
We’re constantly being told that everything is normal and like the federal reserve here in the US has added almost over 3 trillion dollars to its balance sheet and then it reduced it rather modestly. And it already declared that it’s going to end that reduction in its balance sheet and then call it normal.
But it’s clearly not normal so once again we have a sense that we are not really being told the truth. We’re being told what’s politically expedient to support the idea that the status quo is functioning and doing a great job for everyone evolved.
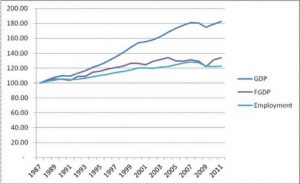
There’s the chart here I have of Financial GDP and GDP and employment.
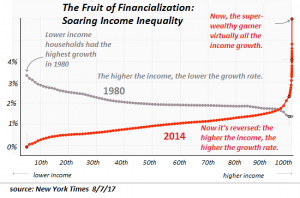
The basic idea here is if you subtract out the financial sector, most of which flows to the top 1/10th of 1%, then GDP is in the US has actually been flat. In fact, it tracks employment which has also been flat. So once again, we’re told this statistic of GDP is up 42% in the last decade which would sort of make us believe that we’re 42% better off but in actual fact most people are worse off. Their earning are stagnant and they are not 42% better off. That there’s all the gains that have been registered are in the financial manipulation sector and those flow to the top of the wealth power pyramid and we see that in this chart of The Fruits of Financialization.
Most of the income gains over the last decade flowed to the very top of the wealth pyramid, the top 1/10th of 1%. So, is there any wonder why people have lost faith in institutions when you look at all the things that are going on in the real economy that the government is attempting to mask or hide or massage to fit a simplistic and false narrative.
FRA: That’s a great chart and you got some others as well that shows at the same time the overall loss in purchasing power and how income is just not keeping up with rising expenses.
Charles: Right, and so when I hear you describe Martin Armstrong’s thesis, then it includes this idea that the loss of faith and institutional failure is going to occur first in Europe and possibly Japan and that would trigger a massive capital flow into the US, which despite its own loss of public faith is still in better shape economically than Europe or Japan. Maybe you could describe that, how loss of institutional functionality and loss of public faith is going to drive capital flows going forward.
FRA: Sure, so what he is saying is that the highest level is just a movement from public assets to private assets. The idea that if you’re into government bonds or government-based currencies, there will be a movement out of that, away from that and more into equities and into things like tangible assets, precious metals. As you mentioned, with the US being relatively OK compared to other countries due to the fact that they’re willing to kick the can down the road with more money printing, more quantitative using. They could be the last to go in terms of an emerging financial crisis phase 2.
So, what he sees as a scenario of developing where things happen first out of Europe. Europe especially by the problems with the euro currency, there is no fiscal union there. The European central bank has reached its limits of anything it can do. A lot of countries have borrowed from each other. There is a significant amount of debt, emerging pension crisis there as well at a significantly worse state than even with the situation in the US and so what he sees is an emerging euro crisis in Europe, in the European monetary union resulting in overall movement away from the euro and towards the US dollar. Also, this is being driven by a strengthening US dollar due to US dollar denominated debt internationally, so that’s likely to make things worse. We saw today emerging market currencies breaking down different countries as well so it’s all happening quite rapidly now. The end result as you see is an international capital flows towards US markets, US equity markets as well as non-European monetary union markets. So, Switzerland, Scandinavia, Norway, as well. There’s some movement there but generally overall to the US equity market.
Charles: I think that’s fascinating and you know I’ve been a dollar bull for many years which was often an unpopular view. Because people look at the problems in the US and they kind of extrapolate those problems and then they declare that the dollar should collapse right, and in actual fact I think it’s the opposite as you’re describing. I think we can quantify this a little bit in a couple of ways and I’d like to talk to that if we could. If we look at the yields on government bonds, of course the US’ is really up there. You could get almost 3% still compared to getting a quarter of a percent or half a percent elsewhere so it’s just makes financial sense to lock in a higher yield if you can right, if you’re a global money manager.
If you see what you described, which is the US dollar shortage. A scarcity since there’s so much money has been borrowed, denominated in dollars so there’s a global demand for dollars. It’s simply not there for the euro, yen or yuan. It’s just- none of those currencies have been borrowed basically, as heavily as US denominated debt so you’re actually getting a double benefit here if you buy a US treasury because you’re going to pick up any gains in the dollar as the dollar appreciates against other currencies and you’re going to pick up the higher yield. So, there’s that and then if you look at just some of the really basic measures of US central bank leverage and like for instance if you take the balance sheets of the central banks and you compare them with the GDP. You know the US is relatively low, the GDP is 20 trillion and the Feds balance sheet is 3.5 trillion or so. By any measure of generalized security of the economy and the banking system in the US is definitely less leveraged and has more buffer if you will, compared to these other economies. For instance, even China where everybody is feeling very confident that China is growing again and so on but they have over 40 trillion in debt and their GDP by some measure is still smaller than the US so they’re really leveraged out there.
And the other thing we talked about really quickly before we started recording which is that the eurozone is one mechanism right, the shared cross-border trade and employment flows and that kind of thing, the reduction of tariffs and so on. But the euro as a currency is another structure and that many of us have felt for years is flawed because it extends this currency to completely different and diverse nations and there is no fiscal controls over that currency. So, it strips away the power from individual nations to adjust their economy by letting their currency weaken. And it really doesn’t seem to work on a fundamental level. So maybe we can say in a way what many of us have been talking about since 2011-12 crisis in the eurozone. That it’s finally getting to the point where stuff is going to start breaking.
FRA: So, this all is contributing to central banks dysfunction to the point of coming out towards a loss of faith in government institution all of the result of going in that direction. The bond market, especially in Europe is just totally dysfunctional from the European central bank. They have gone to negative interest rates and the limits of what they can do by a quantity of using the same thing in Japan. Those two areas in particular seem to be problem points. At the moment, much worse than what the US situation is.
Charles: Right, and you know I think this is a great comment you just made about the limits of monetary easing policy, of lowering interest rates and buying assets. And so, then the other way that governments attempt to solve problems is through fiscal stimulus. They try to borrow 5% of the GDP or something and flood their economies with government spending. But if your bond market is dysfunctional then you’re not able to sell bonds and support this kind of very high fiscal deficit spending to boost your economy that way. If the bond market stops functioning then governments wouldn’t be able to spend so how do we call it, so generously by borrowing money in the bond market. So that I think could be a real problem and of course people are always looking at interest rates but if nobody wants to buy the bonds and then the central banks is having to monetized the bonds for the government to spend on fiscal stimulus, where is the limit there and of course many of us have looked to Japan and said, well is there any limit on how much money the central bank can monetize government debt. So, we may be running into those limits as well.
FRA: Exactly, and there’s one chart I’d like to contribute as well. It’s from Gallup done a little bit earlier this year, where they did a poll of Americans trying to name what the greatest problem facing the US.
https://news.gallup.com/poll/246800/record-high-name-government-important-problem.aspx
35% of Americans named the government, poor leadership or politicians as the greatest problem facing the US. This number has been increasing over time, there’s a great chart they have from their poll that we will have available on the website. We chose how in the early 2000s that number was only around 8%, 9% range, 10% and it’s just steadily gotten worse over the years, increasing to about 15% in 2010-2011 up to about 20% in 2013, 2015 and then more recently going much higher so from 25 to 30 to 35 currently. And Martin Armstrong also made a point of this, that it was back I believe in the Civil War that once the number gets up to 45% (Inaudible 20:54) or say the revolutionary war against the British. For revolutions to happen, the number gets about to the 45% range, that’s when things happen so we are not that far away from there, between 35%-45%.
Charles: I just want to mention antidotally that this loss of faith in institutions, I think arguably is extending even beyond government. In the sense that say higher education, admission scandal in the US, where private institutions as well as public universities have been caught up basically in this corruption scandal. I think people are looking at even private institutions and feeling that they are no longer trustworthy and so It’s like an erosion of the entire social contract.
One other quick comment about government, loss of faith in government is: I live part-time in California and you know California has very high taxes on virtually everything. I mean it’s got one of the highest sales taxes, really high property tax, really high-income tax and very expensive fees for everything having to do with the state and at the local government. And yet, they’re throwing billions of dollars at things like traffic congestion and public education and homelessness and yet none of these things ever seem to get better. And people’s day-to-day real-world life, they look at that. They’re sitting in tremendous traffic congestion, they’re standing on the subway, they’re seeing all this public infrastructure crumble or decay or simply not work very well and yet they’ve cast billions and billions of dollars’ worth of bonds, taxes keep going up.
And so, there’s a sense I think that’s growing that the government is incapable of solving the problems whether it’s from corruption or incompetence or the problems are simply unsolvable. Whatever the nature of it, people are now saying the government is no longer functioning. So, when you use the word dysfunctional, I think we can apply that extremely broadly. Like people don’t really care if it’s not dysfunctional from personal corruption of the insiders, they knew about that. Or some other insider sweetheart deals or whether it’s just general incompetence. And so whatever the cost people are no longer believing the government can do what it’s supposed to be doing for them and they don’t have a representative voice. They feel like in many states like California, it’s a one-party state right, it’s basically like the equivalent of the Soviet Union or some other communist regime. There’s one party that rules and even in other states that supposedly have two-party representation, whoever you vote for nothing ever gets better. And I think that sense is very wide spread. Which is why these outsiders have won elections in France like Macron, the Ukraine and Italy, around the world people are sort of desperate for representation that they are voting for complete outsiders, people that are outside the party system and so on. We are seeing I think lots of signs of that loss of public faith.
FRA: Exactly, this is a global phenomenon resulting in throwing the encumbrance out everywhere so it’s politicians that have not been career politicians but maybe candidates like in Italy, in the Ukraine that are actually getting elected now so it’s actually a global phenomenon. In your recent book “Pathfinding Our Destiny”, you actually highlight also how government is captive to special interests in big money, threatening the democracy so there is a lot of issues there where it’s driving that disenfranchisement feeling amongst the citizenry.
Charles: Absolutely, we see just example after example of some wealthy, Silicon Valley type or corporation pouring millions of dollars into some lobbying and hiring hot-shot attorneys and so on to basically change the regulatory structure in Washington to basically let them continue to do whatever they need to do to maximize their personal profit at the expense of the public interests. People are obviously- it’s like how you can look at this and not lose faith in these institutions. And a lot of people say the government has always been corrupt and there’s always been private money and it’s a little obvious, but I think the average person is unaware of the explosion. That it’s like an order of magnitude increase in lobbying and money pouring into these politicians’ campaigns and into lobbying. And so there used to be I believe, I don’t recall the exact numbers, but you’ve probably seen the same statistic that there used to be several hundred lobbyists in Washington D.C. and now I believe there’s something like 12,000. And you know they are all just giving away millions and millions of dollars and so something we touched on and I’ve touched on in my book is the system is breaking down because centralization itself is the problem.
If you aggregate all the power and capital into the hands of a few people at the top, where there be government or government private, then they are very liable to corruption and policy errors because you are not drawing upon the expertise you get if the system is decentralized. Where local communities and smaller banks and so on can solve their own problems by being flexible and adjusting and adapting to their local realities. I don’t think that you can say, and this is my personal opinion, I don’t think you can say “oh if only we elected a comedian here or something that the problem is going to be solved. I think that the government is too powerful and has too many controls over capital to be anything other than dysfunctional.” And I think people are starting to awaken to that that it’s the government’s structure, it’s not just who we elected that really just turns out to not really matter that much. Whether you call it the deep state or central state or whatever. So, I think what we are really talking about is a structural problem that has not yet been recognized.
FRA: And in your book you mention that to find that way to a better destiny we must create new localized structures, optimized for resilience and adaptability. As you just mentioned, something that is more flexible, decentralized, sustainable, democratic, opportunity for all, type of characteristics. How can we do the transition from where we are today towards that?
Charles: I don’t want to be cheating here but I want to mention that you and I are going to be talking about agile technologies in our next program next month. But I tend to think that there is going to have to be a disruption of the centralized status quo to kind of open up some room for other solutions. So, you know this crisis we are talking about where people just lose faith in the bond market and then that breaks down and then government funding breaks down. That when these large-scale centralized structures break down, then people are going to be more open to trying some other solution because you know human nature being what it is, if you can just kind of stick with what you know. The devil you know is better than the devil you don’t know. So, people would stick with the dysfunctional system until it breaks down so it’s like too bad, that’s probably the way it’s going to be. But we may need to have a financial and governmental crisis which will open up peoples minds really and willingness to take a look at some more decentralized solutions.
FRA: That’s the way forward as you conclude in your book, that better options are available if we are willing to explore.
Charles: Yes, that’s right.
FRA: Well it’s been a great discussion Charles, and how can our listeners learn more about your work?
Charles: Please visit me at OfTwoMinds.com, there’s free sample chapters of my book and extensive archives. Take a look, it’s all free!
FRA: Excellent, as you mentioned for our next discussion we will go into more detail on actual solutions, technologies that are happening that can be put in place to help meet your vision of a more decentralized, sustainable and democratic institution where there can be an increase of faith in those institutions.
Charles: Terrific summary for next month. Well, thank you very much Richard!
FRA: Great, thank you Charles!
 04/01/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on the End Game for Monetary and Fiscal Policies
04/01/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith on the End Game for Monetary and Fiscal Policies

FRA: Hi! Welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Charles Hugh Smith: Author, leading global finance blogger and America’s philosopher we call him. He’s the author of 9 books on our economy and society including “A Radically Beneficial World: Automation, Technology and Creating Jobs for All”, “Resistance, Revolution, Liberation: A Model for Positive Change” and “The Nearly Free University and the Emerging Economy”. His blog “OfTwoMinds.com” has logged millions of page views and is number 7 on CNBC’s “Top Alternative Finance Sites”. Welcome Charles!
Charles: Thank you Richard, always a pleasure!
FRA: Great, I thought today we’d discuss a couple of topics that are currently on your mind, based on your recent blog writings. In particular there is two. One is called “Politics has failed, now central banks are failing” and the other is “The coming crisis the FED can’t fix: credit exhaustion”. And they’re very much related so I would like to explore that, what’s going on, why are these trends happening, potential implications for the political landscape and the investment landscape. So Charles, can you give an introduction on these two blog posts and how you see them relating?
Charles: Ok, to me these are timely topics as we look around the world, we see that politics is failing in Britain with the whole controversy- convoluted controversy over Brexit. Then we see in France, we see the yellow vest movement and here in the US we have seen Russiagate and all sorts of manifestations of a failed political system.
And so, I think my key point that I want to start with is: If our politics was able to fix what was broken in our economies, then we wouldn’t be relying so much on central banks. But you know, so what’s happened is our political system is dysfunctional and incapable for a variety of reasons of actually solving the problems that are systemic in our economy and society. And so, the politicians have kind of punted- you know, they passed the baton to the central banks and said, ok now you guys fix it with monetary policy and the problem there is twofold: Monetary policy is only at two levers. You can buy assets, and then you can use that mechanism to adjust interest rates.
But you really can’t affect social policy or how money is spent in the economy. It’s a very simplistic limited model and so the central banks have responded to this political pressure, like do something to fix the economy, especially in the great global financial meltdown of 2008-2009. So the central banks did what they could, which was drop interest rates to near zero and then flood the financial systems with liquidity and credit and we have to remember, those of us who are following this kind of thing, we have gotten kind of accustomed to these tremendous amounts of credit and liquidity that were put into the financial sector in the crisis era. I believe the number is the federal reserve basically backstops 16 trillion dollars of credit and liquidity that it put out to other banks around the world and then of course it created almost 4 trillion dollars here in the US which it used to buy mortgage backed securities and treasury bonds.
And so these are immense sums of money and so they have had an effect but they have had a perverse and unintended effect, which is they have created incredibly difficult-to-reverse income and wealth inequality and of course we are talking about financial repression here right, is that they basically made the wealthy even wealthier and by boosting assets because that’s where all the liquidity and credit went. And they actually reduced the purchasing power of the bottom 90% households earnings because creating all this money and credit did create some inflation and we can see it in healthcare, higher education, rents and so on so they basically beggared the bottom 90% and enriched the top 10% and now this is creating political blowback.
FRA: Yeah, it has exasperated the whole wealth inequality, wealth income, just in general as the idea has been to benefit those that are closest to the money more so than others so people in the banking sector, the financial sector, have befitted more through this asset inflation because essentially the financial sector has the ability to go to the central bank window and borrow at very low interest rates and then turn around and do a carry trade that perhaps even just buying a simple 10 year bond at 3% and borrowing at the 25 basis points at the central bank, then you get 2.75% for free essentially. So that has been levered up, it hasn’t really benefitted much of the regular economy, the real economy. Would you agree?
Charles: Yes, absolutely and I think a lot of financial pundits of this sort of conventional sort, they follow the thinking of the FED that the FED’s idea was to create a wealth effect. In other words, by boosting stocks which- let’s face it, have basically quadrupled in the last decade and real estate that this wealth effect would create a sense of confidence if you will, in the institutions and in the economy so that people would borrow more money and spend more money therefore boosting the economy. And because they felt wealthier and they felt that the system was working for them but the problem with that is the top 10% in America, top 10% households own 85% of the stocks so all that wealth benefit, wealth effect benefit only flowed to the top say, 6-7 million households out of 120 or 110 million households.
So, it actually narrowed the benefits into the top tier and of course if we look at income, we see that the same thing happened. Most of the gains in income went to the top 1/10th of 1% for the reasons you just described. You know that once you can acquire productive assets at bargain basement prices then you get all the income and so I see having living part time in northern California, but you see the same thing in Seattle, Portland, Denver, Brooklyn New York, Boston. In all these really high real estate markets, we see that those with easy access to credit have been able to buy commercial rental properties, commercial properties rental housing, and the rents in these places have gone up 40-50% in the last decade as a consequence of the rapid inflation of those assets.
Because there is money chasing a limited number of rental units and commercial units and so the federal reserve claim that the wages for the bottom 90% have gone up 23% or something in the last decade but then rents are going up 40-50% so the people who are least able to access the benefits of quantitative leasing, they are seeing their wages buy less and less and is creating what I calling a pre-revolutionary state of conditions where the economy is not working for the bottom 90% and is working really great for the top 10% but the bottom 90% are not only losing ground due to inflation and stagnant wages, they don’t own the assets that are skyrocketing and they don’t have political representation. This is what the yellow vest and the Brexit and the Trump supporters are all about. These are people who felt completely disenfranchised by the status quo; you know, ruling elites and so we got this mix of, and since you asked me to tie them together, we have this volatile mix here where we’re seeing the political institutions fail or fall into dysfunction and then there’s a loss of trust that we talked about last time. And then we have that combined with the perverse and unintended consequences of tremendous financial repression, soaring wealth and income inequality and a sense that the system doesn’t work for the bottom 90% which then exasperates the political sense of disenfranchisement.
FRA: And your blog post on the credit exhaustion. Have central banks, do you think, painted themselves into a corner? Are we now at the limit of central bank utility in terms of how much more credit can we create in the system if it is not moving the economy?
Charles: I think it’s a great question Richard and of course we can start with the fact that most of the new money in the economies, the market economies including China is not created by the central bank, it’s created by financial lenders who then create money when they issue a mortgage and so on. It’s very important for the economy, for the FED and the other central banks to stimulate private borrowing. They can’t or don’t anticipate or they don’t consider it a success if they have to create 100% of the credit, and so how can you create private lending?
So they did their part by lowering interest rates which stimulated real estate borrowing and pushed up housing prices and so on. But at some point, in an attempt to normalize it, at least in the US and the FED has allowed interest rates to creep up as they’ve lowered their balance sheet and so now it’s a little more expensive to borrow but there’s also a point at which now so many households can’t afford to buy the house, regardless of the interest rate because of the FED’s financial oppression has pushed housing out of range and if we look at vehicles. Vehicle prices have continued soaring every year, it’s another thousand or two on top of the existing price and so there’s been no deflation in the expensive items in a household’s budget. In other words, higher education costs are continuing to go much higher, healthcare costs continue spiraling higher and vehicles and so all these things keep going up in price and so at some point, people go “I’m not going to borrow, I decided we aren’t going to buy a new vehicle. We are just going to live with the one we have. It’s going to put too much pressure on our budget or we’ve already borrowed too much”.
So, my point here is no central bank can force private individuals or companies to borrow money. If they don’t want to borrow money, then the fed can’t force them to. And so, I think that is the sense of exhaustion. That everybody that has been qualified to borrow money has already done so and there isn’t that many people left who are qualified who want to borrow more or can afford to borrow more. And then on the reverse side of that the feds can’t really force private lenders to lend money to unqualified borrowers, because that’s the whole subprime mortgage situation that blew up in 2008. Is that most of the borrowers in the subprime mortgage sector were simply not qualified to borrow money through the conventional system and so they would wire loans and basically embezzlement and fraud was how the mortgages were initiated and originated, I should say.
In any event, so now how do you force lenders to lend to unqualified borrowers and how can you force people who don’t want to borrow anymore regardless of interest rates? You can’t, and so that is why I am calling it credit exhaustion and as the credit impulse declines, which we are seeing in China as well as other economies then the central banks are really powerless and as you say, they boxed themselves in because they already lowered interest rates and so they can’t go back to that well and there is not really much they can do to force people to lend or borrow.
FRA: So now where we stand if we have a situation where people have lost faith in the political system, government institutions and if they’ve gone to look at what central banks can do and how they can help but nothing is happening there either. Could there be a movement at this point to QE for the people, the so-called modern monetary theory in terms of helicopter money drops to finance infrastructure projects by having the central banks create money out of thin air, or even just direct from the government treasury departments. Could that come into play at this point, given all the backlash especially for helping, using QE to help the financial sector only so could there now be a movement? You know, to push for QE for the people?
Charles: I think you are absolutely right Richard, and we are seeing that with Alexandria…
FRA: Ocasio-Cortez.
Charles: Thank you, yeah, Cortez, AOC. She has come out of nowhere and grabbed tremendous media exposure for a number of reasons but one of which is the ideas she is promoting and QE for the people is certainly central to it because that is part of the new green deal which was to borrow and spend money on socially useful infrastructure as opposed to private assets and there is a certain sense, makes a lot of sense that we can go back through history and find many examples where governments funded railroads and dams and various basic infrastructure either by giving collateral, like land to the railroads so they could then borrow the money privately or by just funding it by deficit spending.
So, another way of looking at this movement I think, is that as credit exhaustion or credit saturation kicks in and private borrowing declines, then really what QE for the people is doing is its substituting government borrowing for private borrowing. As the economy spirals down into recession because private individual companies are no longer borrowing then QE for the people is substituting that private credit for government debt. So now the government should go and borrow another trillion a year and spend it and so that’s the sort of fix. And the problem with that as a fix of course, is the government, the public debt will skyrocket to the point where interest becomes crushing and Japan is kind of a lesson in both debt saturation and debt exhaustion and also what happens even at very low interest rates, now a big part of Japan’s tax revenues are just devoted to paying interest on public debt at very low, a quarter percent, not even a 1% interest and yet if you borrow tens of trillions of dollars or in their case, hundreds of trillions of yen, the interest piles up to where it’s starting to squeeze other government spending. Even if you don’t get inflation, which becomes much more likely once you borrow and spend and pump trillions of new money into the economy, even if you don’t get inflation, you’re going to reach a point where the government can no longer fund all of it’s expected activities and pay this ballooning interest on this tens of trillions of new debt.
FRA: So, you see potentially either the idea that there’s that problem of the interest servicing of debt, or at some point large inflation in the real economy in terms of the consumer price inflation?
Charles: Right, and I think the key dynamic here Richard is QE for the financial sector. That money almost all of it flowed into the financial assets that’s why real estate’s gone up 50% and stocks are quadrupled and so on is that that money flowed into financiers and banks and corporations which then bought assets because wealthy people don’t really spend that much of their income. If they get quote free money, they’re going to buy assets with it. But MMT and QE for the people, the whole idea and basic universal income is to put new money into regular households’ pockets and the vast majority of those households are going to spend that new money. Whether it’s a job for infrastructure, for a new green deal or it’s a thousand dollars a month from universal basic income. That money is going to flow into the real economy and the MMT and Keynesian proponents are working on an assumption that is questionable and their assumption is: There’s a huge amount of slack in the economy and once we borrow and spend another trillion or two a year, then the economy can easily expand and pick up that slack and there wouldn’t be any inflation.
But that I think is a theory, not necessarily practical because there is a lot of bottlenecks and limits in the real economy. There is not much more farmland you can add to the US that isn’t already marginal and there is not much more fresh water for new development. In fact, in a lot of places fresh waters on a very severe limit already and theses are just resource limits but there’s also limits on certain kinds of labor and skills and so we may get real world inflation on top of big ticket inflation that I mentioned before in healthcare and higher education, childcare and rent. And so at some point the federal government will have to, perhaps be forced to start recognizing real world inflation which they sort of suppressed with a kind of jury-rigged CPI calculation so what happens when inflation starts running hot like it did in the late 70s, 10-12% a year. And then you’re forced to raise interest rates and then that kills off borrowing and so there’s a lot of perverse incentive created by this idea that we can borrow and spend unlimited sums and it’s all OK as long as it is flowing through QE to the people.
FRA: So, what are the implications of all this politically, economically, investment-wise? So, let’s take the politics first; do you see perhaps most politicians that are offering to finance new projects and all kinds of spending type of activities?
Charles: Yeah, I think that’s one way that you can guarantee your popularity right, is because if you’re borrowing two trillion dollars a year and you’re blowing it on a bunch of stuff, that is going to be politically appealing and of course the interest on that two trillion that you borrowed and spent, that’s for later politicians and people to worry about. So, it’s one of those things, spend now and worry about it later.
But I also think we should go back real quickly to your comment about last time about Martin Armstrong’s focus on loss of faith in the institutions. As MMT and QE for the people, as it fails as it doesn’t create a zero inflation, high growth economy. As it creates inflation, it eats away at people’s purchasing power, there will be an acceleration in the lost of faith in the institutions because right now this is the big hope for the political system is if we can do this QE for the people, a new green deal then it’s all going to be fixed and everyone will have more money, there will be no more inflation, and it’ll all be good. But so if that goes, if that unravels and creates inflation, then there will be even more loss of faith in the political system because that is the political system’s big fix: Borrow and spend another trillion or two a year and so if that doesn’t work out we are going to see more loss of faith and I think there’s also going to be a tremendous loss of faith in central banks because they have been writing on the glory of having inflated a third bubble here over the last decade and so far it’s like “See, it all worked, we created a wealth effect and we saved the world” in Ben Bernanke’s phrase. So, as that starts unravelling and failing then we are going to see a loss of faith in central banks and the last thing is how do you deal with inflation when it finally does arise and there are no good solutions right?
FRA: Exactly. I mean, inflation could also be made worse with climate change so that’s also what Martin Armstrong has written about recently is the effect of climate change on particular agriculture, which could drive food prices much higher, making the overall consumer price inflation much worse.
Charles: That’s right, that’s absolutely a factor. Look at the flooding in the mid-west and the US, the recent flooding as apparently a lot of people feel it’s going to have a tremendous effect on crop yields and so there’s that factor and I think, I would sort of summarize the situation in this way Richard. When the pie is expanding, which it did in post-war era from 1946 through, let’s say 2005-6, when the pie’s expanding, everybody can get more and so then it’s actually enjoyable to be a politician because you’re basically divvying up a pie that’s getting bigger and bigger so you can always satisfy some constituency with a larger slice of the pie and it’s not a zero sum game because the pie’s expanding so everybody can get a little more and there’s of course trading but it’s all good. But when the pie is shrinking, and I think that’s what’s happening now.
The actual real world collateral and real world wealth is actually contracting, then politics becomes no fun at all because it’s become a zero sum game where to give more to one constituency or some special interest you are going to take it away from somebody else and that is why we are seeing this frenzied enthusiasm for MMT and the new green deal is everyone’s looking around going “how can we make the pie get bigger” because if the pie is shrinking then somebody’s going to lose out and that is how you get revolutions.
FRA: Exactly, and the idea of having loss of faith in government institutions at some point will very likely lead to a currency crisis in terms of having the purchasing power of the currency lower to a dramatic extent, do you agree?
Charles: Absolutely, let’s remember inflation starts running at 10 or 12% a year, people can stand that for a year but what happens over 5 years that’s a loss of over 50% and if your wages aren’t rising by the same amount, you’re losing ground tremendously. It really is robbing people of their income and so that’s I think a very serious consequence of inflation that there’s no simple answer to. And if you raise interest rates like Paul Volcker did in the early 1980s, you basically kill off your economy. And when interests go to 10 or 12 or 15%, the US economy was able to survive that blow because we had much less debt and the economy was more resilient. But the economy is much more precarious and fragile and it’s not going to survive 12-15% interest rates and so once inflation rate kicks in it’s the end of FIAT currencies and so hence everyone’s interest in precious metals and cryptocurrencies.
FRA: And how does your new book fit into this, the suggestions made in your book “Pathfinding Our Destiny: Preventing the Final Fall of Our Democratic Republic”, what are some of the suggestions you have from that book?
Charles: Well thank you for letting me summarize that; the basic idea of “Pathfinding Our Destiny” is: Only resilient, flexible systems that can evolve quickly will survive this revolutionary era that we’re entering and so if you have a static, rigid, inflexible system that is going to cling to the status quo at all costs. That’s the system that breaks and breaks down. And so, the system that is decentralized and more of a network of nodes of semi-independent nodes, that kind of system you can say is a small scale capitalism where capital and control is decentralized so everybody can shift and adjust and evolve as needed. That system is going to be much more survivable than one that is very centralized, very hierarchical, where all the control is at the top. And that’s the system that predominates around the world, both in China and Russia, the US and the EU. Basically 400 bureaucrats at the apex run these entire economies and so that’s the penultimate example of a rigid, inflexible system and so that is what the point of the book is. We need to radically decentralize political control and capital and push down the decision making and the capital so that the people can adjust enterprises and communities can adjust much more freely and quickly as conditions change.
FRA: And will this be possible, to implement some of these suggestions. Do you see this happening or what will it take for people to come to that type of realization?
Charles: I think Richard there is one positive thing, which is kind of drawing upon books, Buckminster Fuller’s insight is you can’t really reform a status quo, you basically obsolete it. So I think the technologies like cryptocurrencies and some of these other web/internet-based technologies, they are basically running an endgame around the status quo and so I think we are going to see a lot more peer-to-peer activity which is the kind of networked nodes that I was mentioning and so as the status quo breaks down, people are going to come up with systems that are decentralized by default because that’s the kind of way you obsolete a dysfunctional centralized system is you decentralize and you obsolete the system. So for instance in banking instead of going to these five money center banks, we may see more and more peer-to-peer limit and instead of relying on a government currency we might be seeing a proliferation of cryptocurrencies and possibly gold-backed cryptocurrencies and there is a lot of ferment out there, in ideas that would obsolete government issued FIAT currencies. And say in healthcare, there could be the rise of cash only small-scale clinics that just completely are outside of Medicare and the insurance sector completely and so that would obsolete all those dysfunctional high-cost systems, so I think we can look forward to a lot of information that would obsolete the dysfunctional systems we have.
FRA: Well that’s great insight and very positive view that we can end the discussion on as we have run out of time today but yes, the idea of a movement towards a more flexible, decentralized sustainable democratic opportunity for all nation.
Charles: That’s right.
FRA: Thank you very much Charles, how can our listeners learn more about your work?
Charles: Please visit me at “OfTwoMinds.com” and there’s free samples of my most recent books for you to download and read and lots of other stuff that I hope you’ll find interesting.
FRA: Thank you very much Charles!
Charles: Thank you Richard!
 03/07/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Beginning of Central Bank Capitulation
03/07/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Beginning of Central Bank Capitulation

Transcript: Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Beginning of Central Bank Capitulation
FRA: Hi, welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Yra Harris and Peter Boockvar. Yra’s a hedge fund manager, global trader in foreign currencies, bonds, commodities and equities for over 40 year. He was also a CME director from 1997 to 2003. And Peter is Chief Investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group. He has a newsletter product called boockreport.com, which has great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentlemen!
Peter: Thanks Richard!
Yra: Thanks Richard!
FRA: Great! I thought today we’d begin with a discussion on what’s happening in the markets, and it’s the 7th of March, we just had some news from Europe on the ECB, what are your thoughts on the announcements and ECB policy in general? We can start with Peter!
Peter: So, the ECB is basically turning into, and we saw it officially today into the Bank of Japan, and that their obsession with generation higher inflation caused them to go to all extremes of the earth to QE and have negative interest rates to try to generate that inflation, not foreseeing that what do they do if they go into an economic slowdown. Well now they’re in an economic slowdown to the point where they’ve cut their GDP estimates from 2019 to about 1 percent and they still have negative interest rates, they still have a balance sheet that’s 40 percent of the European region economy. So unfortunately, because they actually believe in the ethicacy of negative interest rates, they said they’re going to continue with negative interest rates for longer than what they said beforehand whereas before they said it ended sometime this summer. This would continue through the end of the year. Unfortunately, the European banking system is suffocating from negative interest rates and basically no yield curve and they’re basically bleeding from that and instead of giving them some sort of relief, Draghi stuck them with more blood and that’s why the European Bank stock index fell more than 3 percent today. So we’ve reached a point, today can actually be a very important inflection, where the market is not rallying on further central bank easing. It’s actually now scared of further central bank easing and if that is the case we’re in the new investing world.
FRA: Your thoughts Yra?
Yra: I can’t agree more with what Peter said and not only did the equities not rally today, gold really struggled because the dollar, as we’re talking before and I think Peter (inaudible 3:49 – 3:51) is that the strength of the dollar today kept the gold bulls in check but really what Peter talks about and what we did see is this the beginning of the capitulation of central banks to finally admitting that they really don’t know what’s going on and they’ve made such massive bets about it, and as Peter says, we’re all basically, especially the ECB, is now mimicking the Bank of Japan because it doesn’t know its way out of here. It has no concept of how it gets out of here.
What was interesting today, and I’m planning on blogging about it tonight, is that Draghi, who wasted everybody’s time for 45 minutes because you really had nothing to say and people who were surprise by what was said about the TLTRO and they haven’t been paying attention because I think this was very well telegraphed. There’s no way that they were going to be raising rates and they’re really trapped here and again they play with the numbers because now you know they’ve lowered the GDP forecast down from 1.7% to 1.1% for the Europeans Eurozone and that gives the ECB cover for what’s taking place. What Draghi did, there was a question about the euro bond and we’ve talked about this I know Peter and I’ve talked about this and with you Richard many times over the last four years, you know the euro bond and was that going to come to fruition and Draghi actually handled it by saying look it you know make me he’d love to see it but he admitted it’s a political decision. But I think that’s nonsense because it’s not a political decision; when Mario Draghi himself in July of 2012 said ‘oh we will do whatever it will take’ therefore it can’t be a political decision and the ECB sitting on this massive balance sheet, which is built on the capital key based on the GDP ratios of everybody within the Eurozone. I’m willing to wager that I don’t know when it’s going to be, it won’t be when Mario Draghi’s there, but the wish of George Soros and others is to create a euro bond and they’re going to do it synthetically by just folding the entire ECB balance sheet into a euro bond. It’s almost going to be like what Alexander Hamilton did in 1790 when he took on the debt of all the individual states but it will be interesting because it will have to take a major capitulation by the Germans. If the Germans don’t go along with it it’ll never happen and that’s what Draghi alludes to by saying it’s a political decision. If they get the Germans to do it but if the Germans go kicking and screaming the turmoil that you will see in the global financial markets will be unbelievable but this is the path we’re on but more important I think Peters point about the especially the U.S. stock market and European stock markets not being able to rally today is a sign that the market is starting to get tired of this (inaudible 7:26– 7:30). I said to Peter is Elmer Gantry and it is Elmer Gantry Mario Draghi is when they make the movie of this (inaudible 7:39 – 7:41) so that the role is really reprised to function effectively but I agree with everything that Peter had to say.
FRA: And Peter, what are the implications of this beginning of central bank capitulation? Do you see a new investment environment, as you mentioned, and what does that mean?
Peter: Well, if you believe that the valuations of assets were inflated by what they’ve done well then you should be worried. Now granted this is right now just on the equity side because fixed income is certainly rallying on what Draghi announced, particularly the European bond market where the German 10-year yield ended the day at just under 7 basis points in the 10-year yield and the U.S. is down to 2.64 so bonds are certainly a beneficiary of this, at least for now, but (inaudible 8:37) the stock market that has had a nice rally this year on the Fed backing off and hopes for a China trade deal. Well, if you take away that so-called central bank put and when I say take it away the put is still there but it may not pay out. In other words, if the markets change their viewpoint of the effectiveness of central banks to save the day then that put as I said is not going to pay out and you’ll go right through the strike price. So, I think that’s what people should understand you know there’s ten years of this, everyone’s trained to bond the dips and everything’s going to work out and all we need is a dovish comment and everything’s going to be fine and I want to make a point that this is no longer accommodation, at least in Europe, and Draghi talked about that day. This is, what they announced today, is furthering the accommodation not just keeping things steady-state and I argue that if you are going to damage the profitability of your baking sector, which is the transmission mechanism monetary policy, well then that’s not accommodative having negative interest rates for longer. It’s actually contractionary because the banks are the lifeblood in an economy and if you damage their profitability you’re going to slow growth. So again, monetary policy is not accommodative anymore it’s constructive and unfortunately they don’t yet see that in fact Draghi specifically was talking about the impact of the banks and he still was confident that negative interest rates, which I believe is I’ve said this before the dumbest idea in the history of economics, he thinks that it was an effective tool and remains so.
FRA: And, Yra your thoughts on changing investment environment? How will this affect the steepener type trades that you have been mentioning on U.S. yield curve?
Yra: Thank you Richard for bringing that up. The 530 has made a multi-year high, believe it or not, it got up to about 59.2 I think on the 530. It’s interesting that the 210 sits in here though but I think some of the bid, not some but a lot of the bid on the U.S. long end came because of this, Peter rightly points out, there was a massive rally in the European bond markets today because you know TLTRO does alleviate some of the pressure and especially with banks in Europe who are laden with their sovereign debt. Look at Italy, Italy had a massive rally, usually Peter brings this up so I’ll fill it in for him that the Italian 10-year today is actually 2.46, which is 17 basis points lower than the U.S. 10-year so we’ve had a massive rally. Well, the Italian 10-year yields actually dropped 13 basis points today off of this; it’s an amazing move.
So, we’re starting to see this play out and it is so interesting and I know we’ll get into it more because this is already one of the themes of your work Richard, is that this is all taking place while there’s a huge discussion of course on Modern Monetary Theory, which I know we’ll get to in a little bit, and the fact that these curves can’t steepen (inaudible 12:26) is just mind-boggling. But it is because the central banks are so unified I mean if you listen to Draghi’s words today and you close your eyes you would think you were listening to Jerome Powell because we’re data dependent, data dependent, we’re data dependent! So meanwhile they’re building to manipulate the data to fit whatever the policy that they really want to craft is the key to it and it will take a while. I still say that these curves are going to steepen, we saw a little inversion on the shorter end of it but I think that is really one of the elements that is frightening the Fed here and now they’re all getting in line because as much as what Draghi did today in Europe, to me he absolutely trapped the Fed here because with the Europeans now pivoting back towards not tightening, the Fed cannot possibly tighten and we’ll certainly hear. I’m waiting, while we’re probably recording this, it wouldn’t surprise me to see Donald Trump come out and say you know we’ll wait for (inaudible 13:39 – 13:40) and it’ll be complaining if the dollar is too strong the Fed is too tight yada yada yada and but Draghi has trapped out. The Fed can’t move and of course we had Lael Brainard whose as political as Trump is as far as I’m concerned directly monetary policy talk about that the slowing global growth is a reason for the Fed to hold its fire. So, we have a lot of things in play here but we should certainly hear from the president maybe we’ll wait until after tomorrow’s unemployment number but it is very interesting.
FRA: And if we look at what’s happening in China with a slowdown there and a massive debt problem, could there be a Chinese currency yuan devaluation to address those challenges and what would be the effect on Europe? Could that exacerbate the situation in Europe? Peter?
Peter: I actually I don’t think that the Chinese want to do that. I think well first of all the pressure from the U.S. would be extraordinary and I don’t think they want to invite that and I think number two well maybe a weaker currency is inevitable in China with all their imbalances on the trade side, the current account is going negative, the amount of debt that they have, balanced payments shifting so the weaker yuan may happen anyway but I don’t think there’s going to be an intentional devaluation. It would be more market driven because I think the Chinese know over time they’re going to be shifting their economy away from fixed asset investment as a main driver and more to the services side and consumer spending. Well, they need a stronger currency for that or least a stable one. So that’s how I would put it.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I think Peter is absolutely right. If it happens it’ll be because of things around it because I don’t think the Chinese really they don’t want to run a follow of I’m not going to say Trump but Lighthizer and Lighthizer’s one of his favorite tools is currency valuations and I think the Chinese understand that they’re not looking to tangle with Robert Lighthizer and I don’t think it’s in their interests. You know if you’re trying to pivot your own economy into more domestic consumption you don’t want a weaker currency. A weaker currency is not going to (inaudible 16:16 – 16:17) so I agree with Peter. I think that’s not what’s going to be a catalyst and Europe has just enormous problems, political and economical. Well the political I think is really is affecting the economic and they don’t have an answer to it and again going back to the Draghi press conference today, he talked about you know the necessity of a banking union in the capital markets union, which of course is the creation of a euro bond. They did this all backwards and you’re paying a price for (inaudible 16:51 – 16:53) and it will be interesting the way this plays out. But their situation with China is of course you know also spills out from Germany because the Germans are major trade partner with China they do huge business there, there’s the high-end engineer products that Germany does produce especially when it comes to machine tools and automobiles and always have done very well so there’s so much (inaudible 17:30) but I don’t think that the Chinese are looking to depreciate the currency. They don’t want to wrath of the world right now. In fact if anything they’ll avoid it because they’d rather divide and conquer the U.S. and today was interesting because of course we had the Italians come up, which the Italians are interesting to watch now because they came out in support of the Belt and Road Initiative, which angered everybody in Brussels and Washington and other places and it’s interesting to see how the Italians are so in depth now and sticking their fingers in everybody’s eyes in order just to raise the heat on a lot of different issues but I don’t think there’s any need for the Chinese to play with their currency at all.
FRA: Okay, let’s move on to a discussion of Modern Monetary Theory MMT. What is it and could it be applied to infrastructure of spending? Does it make sense to do that, what are the issues and concerns around MMT does it make any sense? Peter?
Peter: It’s more crackpot economics in Keynesian economics to the extreme that money grows on trees and we can use that money that grows on trees and spend it any which way. The problem is it assumed that we have like a closed economy and that foreigners who hold a lot of dollars they’re not going to be bothered by all the money printing. It assumes that we have all these excess resources that can easily be utilized to carry out whatever spending initiatives we have. So yeah let’s print money and go fix roads and bridges well where are the workers for that? Well they’ll have to come off the lots of housing construction. Well then whose going to build the houses? I think and also its potentially hugely inflationary and that you know there’s a fixed level of supply for things and you just spend money that falls from the sky well then that demand will overwhelm supply and you’re going to get much higher inflation. So it’s economic nonsense but you know we live in a world with a lot of economic nonsense.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: Well I mean there’s so many ways to go at this. Peter you know who was after that way and I agree with that and yet you know I’ve spent a lot of hours trying to look at this and trying to understand this because what am I missing here because I said well it’s getting so much play and actually the proponents of it have gotten exactly what they want because the fact that we’re sitting here discussing it which pales to the fact that Krugman and Rogoff and Summers and now they’re thinking of that there is some giants who are having who are being forced to respond to it so they’re getting a lot of play which is what you know probably part of their issue was. It was interesting today too and this didn’t surprise me to see Paul McCulley who a PIMCO Fame, in fact I’d argue was really the great brains behind PIMCO all those years, Bill Gross would probably take umbrage at that, but I had a lot of respect for Paul McCulley but Paul McCulley came on said well you know what don’t just brush this off so rattle it so quickly there may be something here to it which didn’t surprise me because one of McCulley’s (inaudible 21:23 – 21:24) going back a couple decades is the Keynes concept of the paradox of thrift and was one of the big issues from Paul McCulley.
And the MMT discussion actually falls within that paradox of thrift and how to counteract it, which you know Maynard Keynes was very worried about it because when you anticipate that when things have feedback loop that turns recessions into depressions as people start to save more and demand diminishes dramatically that as you save more there’s less investment and there’s less activity in because nobody’s investing because there’s no demand. So, I could see how McCulley would go that way I just cannot wrap my head. The more I think about it the more ridiculous it becomes and as Peter rightly said the biggest flaw in it is that it depends upon its models built on a closed economy. Well, the United States the dollar is the world’s reserve currency. With that it comes with a fiduciary responsibility and the MMT argument is the most irresponsible form of economic action that I can imagine and it’s you know what but it doesn’t surprise me because it mimics what the Swiss National Bank has done. You know that was going to be the problem is that you cannot create a perpetual money machine. If that’s the case then you know what I may as well quit working, take on as much debt as I can and then wait for them to print money because what’s the difference? So you’re basically telling me that wealth can be created merely in a printing press. Well, if the wealth can be created as a printing press then what are we all working so hard for? And you know what, nothing then matters so I just I can’t get there and I keep trying to struggle as to where these people come from and I know that as Eric Peters pointed out in Ben Hunt that one of the major flaws in this says that it depends upon a engaged and enlightened electorate. I mean that’s what Warren (inaudible 23:54-23:55) talked about and if you think that’s what we have well we’re really in trouble. So I am really I’m nervous about it because the biggest flaw to me of course is that it breaks down the firewall between monetary and fiscal policy and puts it in the hands of one political entity and that should make all of us nervous so I am not a proponent.
FRA: And along with this discussion is usually mention of debt and deficits. Do they matter or should we overlook it or downplay it? When will this become apparent in interest rates in a bigger more apparent way an accelerated way in terms of rising interest rates and U.S. dollar weakening? Peter?
Peter: I mean we’ve been trying to figure that out for 30 years and it was the 1980s when people we’re talking about the exploding budget deficit and rising debts, so it’ll matter when it does and it doesn’t matter until it does and trying to figure out when it does is is really difficult. I mean it mattered in Europe in 2011, 2012 and we saw a spike in yields, an increase in the periphery. It certainly mattered last year when Italy when you saw basically a crash in the Italian bond market. When it’s going to matter for the U.S.? I think it begins to matter not necessarily initially from a market perspective but when interest expense starts to take up a greater portion of the budget and starts to crowd out other things. I think that’s when it will get a lot of attention but until then I’m not really that sure I mean I do have to say well you know Treasuries are rallying today for example in the ten year is down to the 2.64. The 10-year yield is 2.40 at the end of 2017. So here we have a global economy that’s clearly slowing. We have a stock market that hasn’t done anything in basically a year and yields are actually still higher and you know and then that’s with German yields back down again, that’s where the Japanese ten-year below zero again and U.S. yields are still higher so I’m not sure yet what that means I don’t know if that means that people are beginning to care and that the Fed is no longer buying and foreigners have dramatically reduced their purchases of U.S. Treasuries and the Chinese and the Japanese aren’t buying any and we’re beginning to push back against these rising debts and deficits that remains to be seen. But it is something that we should pay attention to because you know nothing matters nothing negative matters when you’re in a 35-year bull market which is what we had in bonds but maybe if things have shifted and it’s no longer a bull market maybe things like debts and deficits actually do matter but timing wise that’s really difficult.
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I agree with Peter it’s well said and I just look around the world and yes I know people are chasing yields and I shouldn’t I talk to people and I go why would you buy a 10-year note? I said why would you have somebody buy a 10-year note? If I’m wrong and I’ll speak for Peter if he’s wrong about what is going to take place here, what is it going to cost you if I moved everything into a 2-year Treasury from the long end which actually Rogoff talks about to, what’s it costing me? 15, 16, 17 basis points to take on that shorter duration with all the uncertainty and with the growing debt levels? MMT’s music to Donald Trump’s ears because if none of this matters well spend freely and again you know I’m always bothered by the fact that we’re running a trillion dollar deficit in a time you know as the White House would say a booming healthy economy. But there’s something majorly wrong here and then as I maintain the MMT crowd, whose an anti-trump crowd, is actually forming the runway for him to do whatever he wants so I don’t even understand the politics of it and I don’t think they do either, they haven’t thought it through. So there’s so many things afoot here but if I was a foreigner sitting out there and I’m sitting on lots of dollar assets, I would be moving the short end as I could be if not moving totally out of dollars because this discussion the fact that this discussion has reached the level that it has, when I say level I’m talking about the fact that you have some of the top economists the giant’s in the Neo-Keynesian role of economics, people who have won Nobel prizes entertaining the discussion I would be starting to move out of dollar assets just as a safety mechanism. They sit here and I’m not sure whether it’s just the algorithm. I’m not sure what this is but for doing this for as long as I have I scratch my head and I go people are acting very very irresponsibly by not moving and getting ahead of this and waiting for the events to unfold and then it’s going to be a sorry world.
FRA: Fully agree. Recently an Australian economist Satyajit Das wrote about the risk of collateralized loan obligations. These are securities consisting of a pool of loans organized by maturity and risk typically. These CLO’s a lot of them have been purchased by Japanese banks. Do you see this as a risk to the financial markets and the Japanese financial system? Peter?
Peter: I don’t see it as a risk to the system. I see it as an area where there’s been access and in response to lower interest rates and the leveraged loan market is now bigger than the high-yield market and when you have a search for yield you have investors that don’t make the best decision and if this financing spigot gets turned off, because the cycle turns and companies with too much debt and not enough cash flow get hurt, well then there’s going to be a credit crunch and there’s going to be a credit crunch across the spectrum. So that’s the risk and a lot of the credit quality is weak, the covenants are non-existent and this is an important area to focus on and like I said this was an area of access this time around. So you have total business debt, whether its corporate or partnership or private or whatever, as a percentage GDP is the highest on record not including the recession in Q1 of ‘09 and yeah that’s going to matter at some point and you know as he (inaudible 31:28) pointed out, households balance sheets have improved in the cycle that’s where the access was though last time and the excess outside of sovereign balance sheet is certainly in the corporate balance sheet. And that’s why I’m expecting a focus this year on deleveraging and that companies are going to be focused on improving balance sheets and that every conference call you will be hearing the CEOs being asked ‘what are you doing to improve the balance sheet’ so you’re going to hear a lot more about that. Now some companies will be able to get away with that and they’ll be able to cash flow their way to a safer spot but there are going to be plenty of businesses if the slowdown continues that are just going to choke on too much debt.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra?
Yra: Exactly where the world sits right now and I find it more troubling that here in the U.S. rather than building up those counter cyclical buffers that even the Fed voted you know to provide some relief with. I just don’t understand it because you have government quarrels in his role as chair of the Financial Stability Board or actually I don’t know if he’s the chair but he has certainly an important position there they’re talking about this and yet they’re rolling back, their lightening up on some of those rags and that’s the wrong ones. The banks should be building these counter cyclical especially now that your profits are up even though of course some of these policies are so stupid from a central bank perspective (inaudible 33:14-33:16) domestic bank earnings but I would not be rolling back these counter cyclical bluffers I’d actually be mandating that the banks actually roll up their capital base as long as they’re going to be walking down this road. I think it’s not a healthy sign and you know it’s not like the banks are in such great shape. I was showing some people I said you know if we went back 12 years (inaudible 33:39-33:42) is 10 percent the value that it was 12 years ago because they did the reverse split of one to ten. So, the stock trades is sixty-two dollars well on a split adjusted basis it was six hundred and twenty dollars so the banks have really not you know some of course you know that’s a broad brush but a lot of the financial institutions they’d never regained the stress that they saw prior to the onset of the financial crisis. So and these outstanding loans as people are chasing yields and leveraging themselves up in order to find greater returns are very problematic especially with the global economy slowing.
FRA: And finally, what are your thoughts in terms of the other risks to the financial markets and the economy do you see that we haven’t covered as yet? Peter?
Peter: I think one of them is maybe there is a day when the ECB, because it won’t be Draghi because he’s gone in 6 months, that the central bankers wake up and say you know what negative interest rates was a really bad idea, we’re killing our banking system and we need to get out of it. You know problem is that that would tank and pop the balloon of the biggest bubble in the history of the world, that being sovereign bonds and negative yielding securities, which total depending on who you look at eight to eleven trillion dollars and a lot of these banks in Europe hold a lot of these bonds. So, from a systemic and earthquake-type risk it’s that in my opinion.
FRA: And finally Yra your thoughts on that? Other risks that you see?
Yra: Well you know it comes back to the banks and it’s interesting that now the BIS is starting to relook at it again and the fact that these European banks, the domestic banks, are stuck to the (inaudible 35:57) with their own sovereign debt because they carry the zero risk waiting. Are you going to tell me that (inaudible 36:05) 10-year are zero risk weighted? I mean, in what world could that possibly be accepted in the world of the Jabberwocky of Draghi going down the rabbit hole with all the other central bankers. It’s insanity and that’s a serious issue because if you were to change that, which it needs to be changed, the hit to the bank capital would be dramatic but this needs to be dealt with because there is no way in this world that all sovereign debt should be zero risk weighted as an asset just no way and especially with this conversation of MMP. That is ridiculous because you are now telling me that you and if the conversation continues to grow the impact is just going to be phenomenal and you have to deal with this now so I’m right in line following Peter and this zero risk waiting is a very very very dangerous systemic risk and it has to be dealt with by the regulators. Unfortunately the regulator’s are the same one who are benefiting from the fact that you know sovereign bonds are zero risk weighted because it makes them a desirable asset from a lot of different participants. So, there is a very ugly relationship that goes on there and it is systemically very destabilizing.
FRA: Wow great insight gentlemen! How can our listeners learn more about your work? Peter?
Peter: They can go to bleakley.com and reach out to me if they need any help with wealth management and managing money where they can read my daily work at boockreport.com.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: Just notesfromunderground or yraharris.com and of course these podcasts which I think you know provide a lot of good inside and that’s the feedback I get from people around the world, how much they enjoy them because it brings a level of discussion that needs to be had out there and that people need to understand and get a handle on. So, the markets show great complacency and I think Peter and I would absolutely find camaraderie in the great complacency in the world and yet there are so many things in the boil that right now I’m very nervous and I think todays stock market action should send off some concerns of that but again notesfromunderground and keep reading Peter’s stuff because he’s on top of this stuff as well as anybody else’s.
FRA: Great! Thank you very much gentlemen! Thank you!
 03/01/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On Debt & Demographics Leading To Government Crisis and Financial Repression
03/01/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On Debt & Demographics Leading To Government Crisis and Financial Repression

FRA: Hi, welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. today we have Charles Hugh Smith: author, leading global finance blogger and America’s philosopher, we call him. He is the author of several books on our economy and society including “Erratically Beneficial World”, “Automation, Technology and Creating Jobs for All”, “Resistance, Revolution, Liberation”, “A Model for Positive Change” and “The Nearly Free University and the Emerging Economy”. His blog OfTwoMinds.com has logged millions of page views and is a very high at number 7 on CNBC’s Top Alternative Finance Sites. His recent book is called “Pathfinding Our Destiny: Preventing the Final Fall of Our Democratic Republic”. Welcome Charles!
Charles: Thank you Richard! I’m always impressed by your lead-in and I don’t know if I really match those high expectations, but I think we got a great topic today and will try to add some value.
FRA: Always meet and exceed expectations here, your work is phenomenal. So today, I thought we would do a discussion on bringing together a number of pieces that you have written about, on different types of trends that are happening in the economy, in the financial markets, in our society as a whole and how it all gets dotted together what are the linkages between them and where this is all going. So, we have a number of topics to discuss in this regard but just from the base, from the beginning we see demographics challenges and debt exhaustion as two of the key trends happening and can you elaborate on that based on your recent writings?
Charles: Yes, and just as kind of our context that we are talking about here is demographics are obviously sort of like long wave or long cycles. In other words, the workforce can only go up or down by so much, given that the people who are entering the workforce were born 20 years ago. So, it’s not something like debt or GDP or something. It’s not a statistic that’s a financial statistic that can be manipulated or massaged. It’s like demographics define the society and the economy in a fundamental way. And so, what would people like Chris Hamilton, who is currently writing some great work on demographics and the economy and people like Martin Armstrong and Peter Turchin, people with a long historical view. They all point to basically one issue, which is: promises that are made by the government to the people in boom times.
They cannot be met you know, once the situation starts stagnating. In other words, boom times go to low growth or slow growth or no growth right, because the workforce that has shrunk or has reduced jobs or the reduce in the work force in terms of age. That workforce’s too small to support all the promises that were made to the pensioners and to the government’s other programs and so this shortfall in wages and profits that can be taxed, that forces the government into making some sort of adjustment or attempt to fill in the gap between what’s actually affordable and what was promised and of course there is great political pressure to fulfill what was promised.
So throughout history governments has always tried to borrow money from the future in order to meet their obligations today and that can work in a very short timeframe, like if you need to borrow money from next year and your tax revenue is going up next year and borrow a little bit from the future would be OK but if your tax revenues and your overall economic picture is not growing as fast as your debt than eventually what happens is where we are now, that the debt is growing far faster than the ability to service that debt. And so, I call this ‘debt exhaustion’, some people call it ‘debt saturation’ and so what it means is then the government and the people start demanding even more adjustments and as a result it becomes visible that we can’t meet the promises that have been made. So, then the people start demanding that the government borrow more money and distribute it as universal basic income or some other kinds of programs and the government starts looking at some of it’s trading partners and going “well we need to get some more money out of trade” so then we have tariffs and trade wars. And I think what the linkage to me every so-called solution to the problem is that we no longer have the resources necessary to fulfill the promises that were made in boom times. Every one of those so-called solutions creates even more of a problem and it usually ends up being expressed in debt and social or global discord.
FRA: Yes, and that’s a theme there where this continuous, feedback loop with government getting into more and more debt trying to solve these challenges that happen. Even Illinois the other day has it going into more debt with all kinds of crises, pensions crises, what is their solution? Well let’s create some more debt. And you know, try to buy some more time. So, it’s a continuous cycle and more and more we get to this debt exhaustion phenomenon as you describe it. And then that’s also all-together with demographic challenges leading to essentially a crisis in government and that’s what Martin Armstrong has been talking about a lot recently as we go into 2020 in particular where he sees a crisis in government with the government being a problem, more of a growing awareness that government is the problem. Alongside that would be a loss of confidence in government and government institutions, your thoughts?
Charles: Right, excellent, that’s certainly a good description of what we are seeing already, and I would just want to add that one of the so-called solutions that the central state has attempted recently, which is manifested in the central bank policies as opposed to the treasury or fiscal spending. The central banks of the major economies have attempted to create new growth or spark growth in a stagnate economy by financial oppression by forcing capital into risk assets and generating or inflating these asset bubbles which generate a lot of phony wealth. The house is not providing any more utility value than it was before, but it was once worth $150,000 but now it’s worth $900,000. Some of that is supply and demand and a lot of it is phony wealth that was created by financial oppression and so those people who own the assets that have been heavily inflated of course have benefitted greatly and the people who don’t own those assets have not benefitted from those policies right, and so we know that it’s a fact that roughly the top 10% of US households own 90% of all financial and capital assets. And so that concentration goes up to where you know, 5% of the households own something like 80% of the wealth in the US and I think that’s paralleled in a lot of nations, especially in China. You know that the wealth is generally held by a relatively small percentage of the population. So that wealth inequality which has been driven by central bank policy then creates even more social discord because the have-nots look at these policies that are so blatantly unfair that they favor speculating capital over other kinds of capital investments and over labor and so then they demand redress. So these are the demands for free health care, free higher education, debt forgiveness, universal basic income and then the question becomes: how is the government going to pay for these trillions of dollars and so called QE for the people and you know those demands we understand where they come from right, and in other words this financial oppression does favor a specific form of speculative capital over all other forms of capital and labor so it is unfair and so people are responding to that unfairness but how is the government going to fund that out of a dwindling tax base?
FRA: Yeah and another example of that is how those who are close to the money could be able to borrow from central banks at very low rates, 25 basis points for example. And then turning around and buying bonds paying say, 3% so you’re getting 275 basis points essentially for free. Now you and I can’t do that but those that are close to the money the banks in particular commercial banks are able to do that and then there’s a leveraging process that goes along with that so that has exacerbated the wealth inequality and income inequality.
Charles: Yeah, absolutely and there is another mechanism here that since we’re talking about debt and as peoples’ earned income has stagnated as a generality at least for the bottom 90%. Then they’re borrowing more right, and we see people borrowing huge amounts of money for higher education, for college and for vehicles that are now very expensive, 35 or 50 thousand is not an unusual price anymore, as well as credit card debt and so this- all this debt, whether public, private or corporate is actually sapping the ability of those entities to save and invest in the future right, because as more and more of your income goes to servicing debt you have less and less to invest and so depending on debt for this cheap, easy shot of growth in the present is actually strangling income and investment in the future. And so, where does real wealth arise? It arises from increasing productivity that requires massive investment and skills and equipment and other forms of capital so if you’re basically over-borrowing in the present to fund today’s promises you’re basically strangling your economy’s future hopes of generating higher productivity because the money to invest simply won’t be there. It’s all spent on servicing existing debt.
FRA: And so instead of taking that avenue and the solutions that you detailed in your current book, “Pathfinding Our Destiny: Preventing the Final Fall of Our Democratic Republic”, we seem to be on a different path and that is towards populism, polarization, extreme political views in both directions, to the far right, to the far left. Extreme type of suggestions like universal basic income and MMT, all requiring more spending and more debt as you mentioned. And in particular we see now movements to the far left, as far as socialism is concerned with the millennial Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and just recently Bernie Sanders announcing that he will be running again for president. Your thoughts?
Charles: Yeah, and again I think the core dynamic I see is the policies of central banks have increased wealth and income inequality, that’s a reality right. And so, what’s our response to that reality and of course for people who feel that the system no longer works for them, that they have been left behind then they want some sort of redress. And so, when we look at the popularity of Bernie Sanders and AOC and their degree in new deal, these are all attempts to redress this rising wealth and income inequality right. And that is understandable impulse right, we understand that. And it’s not a bad impulse in and of itself, it’s a matter of how do we reach that goal of levelling the playing field of redistributing opportunity and capital more fairly than it is now.
So what I think we are really facing is, how do we start facing living within our means, and that means demanding sacrifices of everybody in the system and why there is a lot of resentment in it politically now is people understand intuitively that a certain segment of the population that has been favorited by central banks and financial oppression, they haven’t sacrificed anything. They have actually benefitted enormously from these policies of asset bubbles so on and huge debt, huge accumulations of debt and then it’s everybody, the bottom 95% who have had to make the sacrifices of higher inflation, higher debts, stagnating wages and so on. So I think we need a reset of the system where the solutions are not to borrow more through central banks and central governments but more like decentralized, more flexible, more adaptable, more localized solutions that are more like focused on generating opportunities for everybody that is participating in the economy and trying to find ways to lower costs as opposed to borrowing more money to pay highly inflated costs for things like higher education and health care and so I think the solution set is to use innovation and innovative social policies to try to create a more adaptive, flexible localized decentralized economy. And I think that a lot of these problems will start melting away because it’s a lot harder to manipulate and impose some kind of centralized privilege on a very decentralized system and so these people of the AOCs of the world of course seeing the central government and the central bank as the source of the solution where those of us from a little different point of view see them as the source of the problem that will never be solved by borrowing tens of trillions of dollars into the future because that will eventually destroy the currency and that impoverishes everybody. Rich, poor and the middle alike.
FRA: Exactly, whether it be increasing the size, complexity and cost of government from the left or from the right. Is basically leading to similar end results in terms of loss of, decline in standard of living, loss of purchasing power and ultimately capital wealth drain and brain drain at the same time and this has happened many times in history. So, as you mentioned the answer is more as you have outlined in your new book, more of a limited centralized form of government, more efficient, increased efficiency but at the same time lowered cost of that.
Charles: Right, that’s where innovation is almost intrinsically deflationary right, in other words what was once extremely expensive becomes a lot cheaper once it’s commoditized and innovations arise in both product lines and service lines. I want to mention real quickly there is a lot of talk today of trade and tariffs; trade wars. I just want to fit that into the puzzle we are assembling here is that again as the economy stagnates, so does the government’s revenues right, and so the government is then seeking some redress, like some way to jumpstart the economy you know, or get more growth and then trade comes up. Because if it seems that some other nations are taking advantage of your nation then you want to eliminate that imbalance if you will, and bring back some of the benefits back to your own country so this is the basis of a lot of ideas about reshoring the industrial base back to America; reshoring manufacturing and so on and this is understandable and from the Chinese point of view they have the same concern. They are afraid that if they lose trade, then their economy will stagnate, and they will have all of the same problems that the older western powers are facing because the demographics are not favorable in China either in terms of the one child policy, has created a much smaller workforce than the pensioners who are expecting the government to fund their retirement in China. So, these are global issues and that may be partly why we’ve got global discord.
FRA: Yeah, and I want to mention a book that also recently came out called “The Prosperity Paradox: How Innovation Can Lift Nations Out of Poverty” by Clayton Christensen. It’s a fascinating book, I’m looking forward to getting a copy in the next few weeks here. But essentially what he suggests is a better way of approaching innovation; using innovation to help build a framework of economic growth that is based on entrepreneurship, market-creating type of innovation. So, this is his solution, very inline with what you’re saying in terms of more decentralist, decentralized form of government and being able to apply innovation. I might add also that there’s a new framework today in the economy called Agile, is also a way to help foster this innovation that is more efficient, lower costing overall for governments, so the application of agile technology to innovation in this approach that both you and Clayton are mentioning seems to be the right way to go.
Charles: Right, right, and I guess I would sort of summarize that particular aspect of what we’re talking about, is there’s you hear a lot of talk now about how capitalism has failed right, and you hear other defenses of capitalism and of course the root problem is we’re using one word to describe two different economic systems right, and so called ‘bad capitalism’ is what’s- there’s a lot of that dominates the US economy where I would call the cartel state economy. In other words, cartels which then raise their prices while reducing the quality and quantity of their services.
So, once you get a quasi-economy situation that’s enforced by the state, you get bad capitalism. You get pharmaceuticals that there’s no competition for, that can charge $100,000 a dose and so on. And that’s bad capitalism. And of course in other situations bad capitalism includes crony capitalism where corruption is rife and where the sweetheart deals and soul bids for contracts and so on and so on and this is bad capitalism; it’s not really the entrepreneurial capitalism that you are describing where entrepreneurial capitalism is based on a level playing field where everybody follows the same rules and there’s open access to capital and labor and there is competition because competition is what keeps people honest and it drives innovation and if you could just keep raising prices while producing really poor quality then you got no motivation to improve your quality. So, we’ve allowed a lot of bad capitalist situations to arise where competition’s been stifled or snuffed and there’s a lot of mechanisms for doing this. You raise regulatory barriers so nobody else can afford to compete with you and these kinds of things and there’s a lot of games that involve the central state so in other words I don’t think you can get the worst forms of capitalism that kleptocracy without a central government to enforce them. So when we talk about innovation and decentralization and agility what we really want to see is a very limited form of central government because if you allow the central government to get that much power than they can enforce monopolies for their cronies and this is what we see in industry after industry and so to have a level playing field you have to decentralize power and capital as well as opportunity.
So that’s kind of the foundation to create an agile entrepreneurial society so you have to have a level playing field like enough regulation to make sure you don’t get overwhelmed, a monopoly that ends up being enforced by the central state and you want opportunity and opportunity to gain capital that’s broadly distributed and so a centralized model just really reinforces bad capitalism and it decentralized model reinforces good capitalism.
FRA: And your final thoughts on how we can get there is the question: Do you see us happening through a crash and burn type of scenario or is there a better way, a sort of easier way to get there from point A to point B?
Charles: Well I wish there was, but actually Richard, that’s a great question because we referred to Martin Armstrong and I often refer to historian Peter Turchin and when we look back in history, history doesn’t have many examples of an easy peaceful transition from one social-economic order to the next one and so history suggests that we are going to have to go through a period of turmoil and discord that will see a reset of the system where the system breaks down. And I think what we were talking about today is a system where debt will reach levels that are unsustainable and attempts to service that debt and expand that debt will destroy the currencies that people depend on that will be the crisis which enables a reset of the entire system but it’s gonna be painful for sure.
FRA: And on that note, we’ll end our discussion for today but that’s great insight Charles. How can our listeners learn more about your work?
Charles: Please visit me at OfTwoMinds.com, you can download free chapters of my last couple books and look at my archives and I hope you find some value.
FRA: Great, thank you very much Charles!
Charles: Ok, thank you Richard!
 01/31/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris and Bill Laggner on Global Financial and Economic Risks
01/31/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Yra Harris and Bill Laggner on Global Financial and Economic Risks

By: Tenzin Lekphell
FRA: Welcome to FRA”s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Bill Laggner and Yra Harris. Bill is principal and co-founder of Bering Asset Management. He and his managing partner, Kevin Duffey, managed the Bering fund using an approach based on identifying boom bust cycles, value in the marketplace, bubbles, and distortions created by both fiscal and monetary authorities. Yra is an independent trader, a successful hedge fund manager, a global macro consultant trading foreign currencies, bonds, commodities, and equities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997 to 2003. Welcome gentlemen!
Bill: Hi Richard!
Yra: Hey Richard! Great to be here.
FRA: Great! I thought we’d do a focus today on what we see happening for the coming year, 2019, and the economy and the financial markets. What distortions and imbalances can be identified for potential investments and/or trading opportunities? Maybe we begin in China with the China slow down. Did you see a potential unfolding of a severe credit crisis in China and and could this be a catalyst for other effects globally such as in Europe for the European bond market? Bill do you wanna begin?
Bill: Sure I sound like a broken record on China. I’ve been talking publicly for over 6 years now. The Chinese miracle, the Chinese situation is I think late innings we’re seeing more signs of that now. The Hong Kong property market falling out, the amount of capital that has fled the country over the last 4 to 5 years. I think that China’s trying to deal with multitude problems and a lot of that stems from central planning. The illusion works great when asset prices are going up and people have this perceived better standard of living but the reality is that it’s all built on debt.
If it’s not built on debt, it’s built on a series of other government policies that, lets face it, all of us have seen in history only buy so much time. There are costs to these interventions and I think we’re in the early stages of seeing what those costs are.I think the economy slowing down, I think they’ll break the peg to the dollar and I think the global slowdown is China, let’s face, is a major player in manufacturing world. So the continuing slowdown in Europe, the stagnating economy here in the US, I think wreaks havoc on the Chinese and I can see that there is even more in last 18 months of so, more disagreement within the Chinese party and I think that’s yet another reflection of an economy going in reverse. There turning on one another. They’re very similar to what’s happening in US and even in Europe. The political classes are turning on one another and those are all indications of late stage behaviour of the cycle.
FRA: Just a quick follow up question on that for China you mention that you see the potential for the break of the peg, would that be a devaluation on the currency and if that were to happen, could that affect the European bond market and the euro?
Bill: Yeah I think they have to break the peg. Years ago they did a devaluation for a short period of time which was 40/50%. Will it be as severe this time around? Maybe not but I do think they need to weaken the currency and in their mind, they’ll try to buy them more time and they can continue to try and export products and keep the illusion going.
But the problem with China is, and of course they’re also trying to attract foreign investments, but what are the rules in China?
The rules seem to change weekly so I don’t’ see long term capital making its way into China.
I think they end up having a devaluation of the currency, they may do it in stages, most smart macro people I know think they do it in stages and they’d probably agree with that.
They’ve got massive debt issue and so when countries have massive debt issues they resort to devaluing the currency and they do it in ways we’re witnessing today.
FRA: And Yra your thoughts on that?
Yra: ( inaudible 5:17-5:20) sitting here dazed and confused in some ways because I go back to the comments that come out of the White House Administration, from the Chinese which is well if we can work through this trade situation; we can take your trade deficit and basically balance of payment problems and we can take it away because we can buy so much stuff.
When I heard that, it was an interesting comment that of course S&P rallied dramatically off of it. Couple other things didn’t happen; at that time, the Yuan didn’t rally and when I read people analysis they said well that’s because in order to do that, they have to weaken the currency and number 2, the most extensible reaction should have been the Mexican peso should have soared. If China were to actually embark on a massive consumption program which that statement to me (inaudible 6:31) and that’s what Michael Pettis, who I have a lot of respect for, he’s been arguing for 10 years or as long as I’ve been reading his work which is (inaudible 6:39) professor he knows China really well. Because if you embark on a massive consumption program, that Yuan has to go higher because otherwise you would crushing your middle class or trying to aide because a weaker currency would mean you’re paying more for imports and that would be exactly what you’re trying not to do.
I’m perplexed wherever we’re at here, with all that discussion that takes place and again because of global supply lines, if China were to massively import massive consumer goods,
Mexico would benefit more than any other that’s because the peso on a relative basis is probably of the mainstream emerging (inaudible 7:30) is weakest of anything in the world.
We can probably argue the Rubble but Mexico and Russia serve different purposes in the global arena. So I understand people talking about depreciating the Yuan but since that announcement came out, the Yuan has dropped about 6.87 down to today about 6.72 so i’m not sure and then I’m gonna add in what happened on Monday; the Chinese actually invited S&P to come in and start rating some of its bonds.
When I saw the headlines which didn’t get much play than anything else but I thought it was interesting because it tells me the Chinese don’t proceed willy nilly.
I happen to agree with Mike. I don’t trust a thing that comes out of China statistically and I’ve vlogged about that for 10 years and thought about it for 20 years because my sense of that whenever I would speak on panels, it’s really a simple rule. If you don’t allow google to operate freely, I can’t trust any information that you’re willing to either put out because you don’t let a free flow of information in.
If you’re controlling what comes in, by definition, you’ve already controlled what comes out.
I don’t give China much credence to that but that doesn’t mean China doesn’t have a concept here. They always have a concept.
How they get there is what we’ll discuss and argue about but think one of the main thrust of China is could they know how important this is? They like to establish a true competitor to the US dollar as a reserve currency. I believe that because they don’t trust the US and there’s a lot to not trust about the US. One of the things we’ll get into I’m sure and going forward this year and what staggers me and makes me less bullish on the United States in that regard is we’re operating at full employment and yet have a trillion dollar a year deficit. That is a problem to me.
Last time we had a full employment economy in 97, 98, 99, we were running budget surpluses. We’re in a whole different atmosphere here and then you follow the arguments that are actually building and I love that they’re making it out to the mainstream thought on the MMP, the Modern Monetary Theorists and how you don’t have to worry about deficits just print out more money.
In that regard, I think the Chinese hold a lot of dollar assets as to others. Any type of reaction from a monetary authority to just print more money should make everybody nervous about holding that asset and because the dollar is the reserved currency of the world, we’re all forced to hold that asset. So I’m not sure about the long answer, I’m not sure about the depreciating of the yuan so I’m gonna hold my powder on that and I need to see other things here and me I’m more concerned right now; yes the Chinese have a massive amount of debt but relative to other things, they’re debt is not great to the US and the US is hemorrhaging debt at a time when they ought not to be. If you’re really a Keynesian, you should accept that premise because Richard, we have a lot of Austrian discussion on these podcasts and I’ve been very proud to do many of them and the Keynesian views, is hey, Economic times are good; you’re supposed to run surpluses at least not massive deficits.
The deficits come from demand stimulus and we certainly don’t need that so I’ll stop there.
Bill: Can I just add one more thing to what Yra said? I read Michael Pettis’s work too and I like a lot of his work. I think the most difficult thing you hit on it is we really don’t know the extent of the debt situation in China and because Google and other groups are not really allowed to get data whether it’s on Chinese banks etc.
I just think there’s such a black hole that is very difficult to analyze this properly. We realize that it’s a lot of debt, we realize the global economy is slowing, yes they wanna get into consumption based economy but what are they trying to build their “economy” on? If it’s layers and layers of agency debt or debt in various industries etc.
The banking system, many people think they need to recapitalize the banking system. I’m in agreement there.
The world is in debt and they’re all playing the same game so it’s gonna be fascinating watch it all unfold.
FRA: And on Europe specifically, Bill what are your thoughts in terms of the evolving central bank policy, trends there, and potential for the financial crisis phase two, if you will, to start out of Europe?
Bill: So I remember going back to the Greek situation which was 2011. I was convinced that Greece would leave and you would start to see the breakup of the European union of course the decisions that they make to essentially keep Greece within the EU and start this process of bail out and more taxes and more (inaudible) on the future livelihood there. Deutsche Bank Company, that we’ve been sure for quite a while now, Deutsche Bank is telling you there are problems, I think, 2 years ago there was a French junk bond issuer that was refinancing debt for 3 years that are negative interest rates all thanks to the ECB, you know, I think they are what 50% of GDP now the size of their balance sheet.
So you know Draghi was listening to himself speak the other day. I just think that they’re going continue to intervene. I don’t see them, you know, tightening policy there and it’ll just be whatever the interventions look like in the future they’re all going to equate to the same things which is loose monetary policy and trying to keep nominal asset prices from declining too much.
FRA: And Yra you’re thoughts on Europe and the potential for financial crisis to begin from there?
Yra: Well Bill, we find great commonality in Europe because the most nefarious man in the world is Mario Draghi. People really don’t understand what he’s done here but building that massive balance sheet has trapped everybody in Europe. I mean i’m in a 100% agreement with you. Europe is a mess and they’re walking down this road of perfidy and it is perfidy because Mario really has no plan. The most honest thing he ever said was you should do whatever it takes to (inaudible) to preserve the euro and in that regard he has really saddled them in a terrible, terrible situation.Of course Merkle was his guardian angel. There is nowhere for them to go.Nowhere! What was last week’s blog about Richard? Mario Draghi’s circus, which this circus was in town. Nothing he said had a bit of honesty to it. He tried to control the narrative and now the narrative is his two words; persistence of conditions that they can control and makes the assessment difficult.Of course it’s difficult. They’ve destroyed the German favours because i’m on the financial repression authority so if you want to see the master of financial repression, take a look at Europe at what they’ve done to German favours because if you’re running inflation in a country, of 1.6/1.7, you got a GDP of over 2% and you have negative interest rate on a 2 year note of 60 basis points, you got a serious problem. While they’re sweeping it all under the rug, the problem is just building, and building, and building. I think that’s the real (inaudible) block to where we’re going here.China is interesting and Trump really his disdain for Merkel and Macron, and here’s a man who doesn’t take those (inaudible) lightly so I would watch his response. The German auto sector is definitely afraid with a 25% tariff and while we’re concentrating on China, we don’t hear much about Europe.I’m very cautious here and the European central bank again has put the world into a very difficult situation and it’s all based on debt and somebody calls it the doom loop because you have the European commercial banks buying sovereign debt. Why? Because its zero risk waiting so i can buy all the Italian bonds i want no matter what you think about them and I get to carry about them in my books with no reserves. Yeah it’s a pretty good game.
Bill: Can I just add one more thing about Europe? I got great points about Germany by the way.I look at what happened in Greece, and you know people forget about Greece. You look at what happened in that country since lot of corruption in the country and of course you know how the euro was created what they did to the Greek economy. Thank you Goldman Sachs. The fact that these new taxes and other regulations were then brought into the Greek economy. It’s throwing in another wet blanket on the fire and I see the same things happening. Look what’s happening in France for example, or look at all the different taxes and so on, they got people protesting and essentially these systems that they’ve created are unwinding in slow motion. It just doesn’t work anymore.
Yra: That’s absolutely right and you know it. (inaudible) they slapped him pretty good.
Give me (inaudible) because I’d rather listen to him. I think he talks more of the truth. Again, it’s not their narratives but it’s the narrative of what’s really going on and they applaud Spain is still 14.5% unemployment. So they’ve got massive problems and a lot of them start with the monetary policy because Mario Draghi did follow Ben Bernanke down the rabbit hole.
You know, one pill makes you smaller, and one pill makes you tall. He took the one that made him tall and he just can’t get out of from that rabbit hole. You will not sit back through it.
FRA: Bill for 2019, what do you see as the biggest risk factors? Market risk, credit risk, geopolitical risk, where do you see those?
Bill: That’s a great question. It’s pretty clear the economy is slowing globally. Many of the (inaudible) figures show that. I think the fed is done raising interest rates. I don’t think the Feds can continue to tighten interest rates. I do agree with Yra that the US and the rest of the world will run these deficits, will have more interventions, fiscal and monetary interventions, probably later this year, and of course credit spreads widen, we already see the beginning of credit spreads widening, the leveraged loan market pretty much shut down the end of last year and commodity prices look rather weak so you could see an interesting contraction unfold this year.
Their not gonna sit idle. Their gonna try to fight it is my guess and so I could see the stock crisis could go down at least 20 % or 30% from here.
I think earnings are gonna be a major disappointment and credit spreads will continue to widen.
So again they are not gonna sit idle, they will immediately intervene, they will basically threaten to go to negative interest rates.
I’ve been saying this for several years, the central banks want to tighten interest rates because they can. The economy is too weak. The economy is weak for all the reason we were discussing earlier; intervention, debt, the size of government, vis-a-vis the real economy, regulation, so I think they’re gonna intervene, I think they will threaten to go to negative interest rates and I wouldn’t be surprised if the deficits go north of a trillion dollars a year here in the US. I could see where the deficits go to $1.5 trillion very easily.
FRA: And Yra your thoughts on the biggest risk factors?
Yra: To me there’s so many of them. I come back to it and Bill was nice enough to give me the push of the edge which is the debt levels and I agree with him. I think that there’s no way that earnings could sustain themselves here with higher interest rate costs and on top of that,
if you get higher wages, it has to eat into profitability so these people who put forth the growth and profit numbers, which you’re not coming off of low profits historically, you’re at basically historically all time high of sustained level profitability which can’t sustain itself if labour is to get a bigger piece of the pie and interest rates take a bigger hit. I just don’t see. Now does that result in geopolitical problems? Not sure. We’re seeing some of it but on a global basis where i see the greatest threat is of course from the prime minister of Turkey, Erdogan who continues to get favourable play and I certainly don’t understand how because he always takes the other side of the United States. The don of Venezuela, Putin, Erdogan, the Chinese, the lineup almost looks like the scene of blazing saddles where all the bad guys are lined up waiting to get signed up. They cant get out from themselves. I make the mid east with Erdogan and whatever he’s really trying to do there, potentially a major, major global risk. There’s so many. I can’t even innumerate which one would be the most because I been to economics. This debt issue is really bothersome to me so i’m gonna go (inaudible) with that.
FRA: Given all this backdrop Bill, where do you see trading opportunities, investment opportunities, in particular, what are your thoughts on the gold euro and gold yen cross rates as well as yield curve steepening or flattening?
Bill: I don’t see again because I believe we don’t have bond markets anymore. I think central banks have distorted the, Jim Grant likes to say there are no more traffic signals right? They’re all flashing the same colours so central banks intervene, they distort the prices, create these false signals that enter the market place. I’ve been bullish on gold since 2002. I (inaudible) they were gonna print a lot of money and they have and they’ll continue to print money.
So gold looks like it’s finally breaking out of a, I’m not a hard core technical analyst but it looks like it’s breaking out of a falling wedge since 2011 which we were up around 1750. So i’m bullish on gold and i’m bullish on gold not just against dollars but against yen and euro.
Whether or not the yield curve stays inverted, it’s hard to say. I think what we’re really betting on is how quickly will the central bank here in the US will cut interest rates.
Yra brings up a good point. You got wages rising so maybe they don’t have the room that they had at this juncture that they had in 08,09, or 2010. Bullish on gold and the other thing that is interesting is watching the FAANG stocks decline. A lot of the movement coming out of 2015 the NASDAQ was just a handful of companies and it looks like the FAANG bubble has burst and so I think that’s gonna be real problem for the broad market as well.
FRA: And you say interest rates falling as you’ve mentioned earlier.
Bill: I think the central bank they talk a good game, you know, Powell has already flip flopped 3 or 4 times from Christmas eve when things were melting down. My guess is that they will try to lower interest rates and/or the government will run a greater deficit if the economy slows drastically in the 2nd half of the year. I’ll add the following. I do, without getting too much off topic, think that the technology wave of decentralization is a something that is very positive catalyst for the global economy but its a tiny tiny piece of the economy today but I do see how that could be a very positive outcome for the global economy. That doesn’t mean we’re gonna dodge the debt bubble or dodge the recession. I just think in the longer term, it’s something to keep an eye on.
FRA: By that do you mean block chains, robotics process automation?
Bill: Yeah I mean internet things, block chains, i sent a lot of time in the space last 5 years. When I look at all of the inefficiencies like just in supply chain for example, you’re talking about a couple of trillions of dollars (inaudible) in inefficiencies and so the movement of money, you know, why is the foreign exchange market 25 times the size of the global economy? The disintermediation of finance is something that I think will change the world but that’s a longer intermediate longer term phenomenon.
FRA: And Yra your thoughts on trading opportunities, investments, and in particular for the gold euro, gold yen, cross rates and the yield curve?
Yra: Well Bill and I never talked but those have been my favourite trades and in fact my biggest trade I took it off this morning with long gold and short the Swiss which has been good because the Swiss was a little unnerving but, you know Richard, I always give the alchemist, it used to be a year, now it’s a decade, now it’s probably a millennium and I’m going back to zero. The Swiss national bank is of course the alchemist of Europe because they get to print Swiss Francs that don’t seem to go down in value anyway and buy global equities. What better is that?! That’s the dream of the MMP (inaudible). Let me go print a billion Swiss francs and go buy a billion dollars worth of Apple stocks. Thank you very much! And that’s what they do and then they’re trying to figure out how they can get out of this hole. The rest of the world will start to mimic them but I believe in all of the gold currencies. The gold dollar has not been great but US rates have been going up and two things and I have this discussion constantly because my phone rings off the hook all the time talking about gold, don’t buy into the inflation nonsense. By that time, gold is too late. Gold is a protection against central banks absolutely realizing that they’ve gone down a path that they have no way out of and that the effects of what they’ve done. That’s what you wanna go for. The inflation will be the ultimate ugly effect but it feels it must have been a bad investment. Oh really? How has the dollar done? Would you rather own gold for the last 50 years or to be in dollars if you’re a foreigner? I would say you’ve been much better off in gold. So the gold has done what it’s supposed to, be a store value. Now my attitude is that, and I’ve done a lot of work on yield curves for 35 years, 40 years already, this is gonna get interesting this year and i’m looking for steepeners because my attitude is with this debt overhang, and yes debt does matter regardless of what Larry Summers, and Jason Furman Monday recent articles in foreign affairs, it does matter and then they have a cost and I say that any money manager who would put their clients in anything longer than a 5 year duration of US debt ought to have reexamined because there not operating as a fiduciary because there’s just too much uncertainty with the US debt situation. I’m not even getting into the entitlement argument. Again, we’re running a trillion dollar deficit at full employment. That’s heresy if you’re a Keynesian. Heresy. So I see those as worthwhile investment. I’m looking at Germany though as we come back to Germany because my question to any German is where do you go to invest? What are you doing with your money? Are you buying 2 year German debt? Is that doing it for you? I don’t think so. The shots yield at negative 60 basis points. You’re better off putting it into your mattresses of course because it will do you better. So real estate in Germany has already reached almost a bubble proportion which is highly unusual for Germans because they don’t leverage themselves. So i’m gonna watch the Dax closely. To me the German assets (inaudible) to them of course is that Trump gets aggressive and really starts pushing for tariffs on the German auto sector. I’m not invested there yet but I’m watching because my attitude is where do I go if i’m a German? I also like Mexico because as I say If the Chinese are serious in what they’ve presented on the issue, they’re really gonna ramp up their imports, Mexico has to be a beneficiary of that so I’m gonna watch closely and again on a relative basis, the pesos cheap and they also pays you an eighth and a quarter at overnight interest rates. I’m not involved yet. I’m waiting for the 200 week moving average and I like Bill, I’m not that good of a technician. I used it to establish my losses and potentially if I see momentum but its not the first place I go to do my work and that covers me in the short term here but again, I look at it with a trader’s eye more than I do with a long term investors eye.
FRA: Wow great insight as always gentlemen!
 01/24/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On Pathfinding Our Destiny Amidst Social & Political Disunity
01/24/2019 - The Roundtable Insight: Charles Hugh Smith On Pathfinding Our Destiny Amidst Social & Political Disunity

Download the Podcast Here in MP3
 12/17/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Ronald-Peter Stoeferle & Yra Harris On Gold And Geopolitical Risks
12/17/2018 - The Roundtable Insight: Ronald-Peter Stoeferle & Yra Harris On Gold And Geopolitical Risks

 11/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith On How & Why Financial Repression Continues
11/28/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith On How & Why Financial Repression Continues

podcast to be posted shortly ..
 11/19/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – David Rosenberg, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Economy, Markets & Investing Going Into 2019
11/19/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – David Rosenberg, Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Economy, Markets & Investing Going Into 2019

FRA Roundtable Interview: Nov 20th
By: Tenzin Lekphell
FRA: Hi! Welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight! … Today we have David Rosenberg, Yra Harris, and Peter Boockvar. David is Chief Economist and strategist at Gluskin Sheff. He has a focus on providing a top down perspective to the firm’s investment process and asset mix committee. Prior to joining Gluskin Sheff, David was Chief North American Economist at Merrill Lynch in New York for 7 years during which he was consistently ranked Institutional Investor All Star Analyst Rankings. Prior there too, he was Chief Economist and strategist for a Merrill Lynch Canada based out of Toronto. David is also the author of Breakfast with Dave and Espresso with Dave (publications of his economic and financial market insights). Yra is a hedge fund manager and global trader in foreign currencies, bonds, commodities, and equities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997 to 2003. And Peter is Chief Investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and Advisory. He has a newsletter product called BoockReport.com which has great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators.
Welcome gentlemen!
Peter: Thanks Rich!
David: Great to be here!
Yra: Thanks Richard! It’s a great pleasure to be here.
FRA: Great, awesome! I thought we’d begin and look at the Central Bank policy. David you recently feel that the Bank of Canada should pause on its interest rate hikes but the Fed reserve does not have to. Can you elaborate?
David: Well firstly, I think that the US economy for the time being is already, not just at full employment but at 3.7% unemployment, is already through full employment and the FED is below it’s own an estimate of neutral so I always felt comfortable with the view that in the United States and the fully employed stable price environment, you don’t have a 2% Fed funds rate, you have a 3% Fed funds rate. We’ll see if the Fed ends up getting there this cycle. There’s more skepticism on their view than there was just a few weeks ago. Look, the Bank of Canada, the level of capacity in the economy is far different. Canada is not nearly as late in the cycle as the US is point number 1. The Bank of Canada never stimulated the economy in Canada by expanding its balance sheet and never had a present balance sheet to provide stimulus. That’s point number 2. And we don’t have fiscal stimulus in Canada so that may change with next year’s budget but that’s a long ways off but the reality is that if you look at capacity levels, unemployment, fiscal stimulus, there’s far more reason for the Fed to be more hawkish than the Bank of Canada. And so that’s been my premise here that the Bank does not have to follow in the same footsteps as the US’s on those basis.
FRA: Yra do you feel likewise?
Yra: (inaudible 3:11-3:13) I think Canada is really well taken. It’s been one of those things that when you have to look at if the Canadian economy could really muster some continued growth. I mean it has to move back but they won’t have to overcome a balance sheet situation because I think they, well first off they weren’t in the same situation because of the banking laws and regulations in Canada and the dominance of the (inaudible 3:40-3:41) and the way they do their business so they didn’t have that situation but outside of that, yes I agree.
(inaudible 3:46- 3:48) a good point and I scratch my head for quite a while why the Canadian dollar hadn’t been stronger through this period? Yes I know that it’s tied heavily of course to the energy markets, some would say commodity markets. Canadian oil has blown a price of discount for quite a long time first of all because of the nature of a lot of it (inaudible 4:17-4:18). But I agree. I agree with that very much.
David: (inaudible 4:22-4:23) that Yra just said, the Canadian benchmark gold prices are down to $14. Now we know that every benchmark comes down but (inaudible 4:32) to say that if WTI got down to $14, we’d be talking about recessed in the US and the Fed easing policy. Well that’s where the Canadian benchmark is right now is $14. On top of that, household credit demand numbers in Canada have really slowed down remarkable. I mean maybe I’m old school but normally when you have decelerating credit demands, interest rates aren’t going up, they tend to go down. So, I think the Bank of Canada is offside if they continue to raise interest rates in this environment.
FRA: And your thoughts Peter?
Peter: Well I was gonna add to what David just said about that last point about Bank of Canada having to manage high debt levels of moderating housing market in certain markets and you know creating some sort of, I don’t want to say deleveraging because it’s not really deleveraging, it’s more of a slow credit growth type situation.
FRA: And let’s move to a discussion on trade challenges, given local and global trade challenges, what are the trends that you see on economic activity resulting? David your thoughts?
David: Well look, if your an investor right now, not just an investor but a business, you’re fighting a war here, I guess Jamie Dimon called it a squirmish, he was being polite but its truely multifaceted. For one thing, we’re all waiting with (inaudible 5:54) whether or not there’ll be some sort of agreement at the G20 summit at the end of the month and that’s an on again off again situation. But I was telling everybody that even if we managed to cobble together some sort of agreement with China, which I think is going to be very difficult when you think about what Xi Jinping actually put down in the constitution on what they can actually do to the appease the U.S. How this ends up, I just say that I don’t think there’s going to be some some big deal that causes a lot of euphoria and then we’re going to be left on January 21st where the tariffs on China are going to escalate dramatically from where they are right now. Remember that’s January 1st. That’s what’s hanging in the balance.
But let’s even assume that we have a trade agreement with China that reduces the pensions. Then the next phase is the trade war with the EU. The next phase is trade war with Japan and now all of a sudden, we got the House of Representatives, which are now controlled by the Democrats, who don’t seem as a group to thrilled about the USMCA and there’s no more for negotiating a new North American trade deal because Donald Trump signed that with the with the outgoing Mexican government and will not be able to cobble the same deal with the new Mexican government. So we can a situation where we’re back even if you assume that things with China go great, we’re back to uncertainty over NAFTA because if Trump doesn’t get this deal through with Congress, and I think that actually doesn’t get discussed but that’s gonna make the front pages for the next couple of months.Then we’re back to first principles with the President when he said, during the campaign and after, that his preference is to walk away from NAFTA. So that’s actually the dark (inaudible 7:46-7:47) that people aren’t talking about right now is that this North American deal is not a done deal at all.
FRA: Yra your thoughts? Do you agree?
Yra: You know there’s so many moving parts here that I can’t even disagree with. There are great many moving parts. But the overhang to this entire market of course is the fact of the global supply chain and we don’t know what the effect is going to be, about how much disruption is going to take place through all of this.There are so many unknowns and when they get to the G20, as long as we’re going down that road, (inaudible 8:22-8:24) come away with some type of positive outcome especially the Trump Administration is so attuned to the equity market that they’ve tied themselves to the mass of a positive equity market as being the velometer of their success. So they’re gonna have to figure out something (inaudible 8:47-8:48) equities market under (inaudible 8:50) you wait for (inaudible 8:53-854) Mnuchin to show up with some kind of statement, oh we’re doing this, we’re doing that.That’s kinda getting old. Unlike the last G20 meetings, I probably wouldn’t say last, 5,6,7,8 G20 meetings where they really accomplished nothing except maybe climate change and I’m not minimizing that as nothing. We can disagree about the science but the outcomes maybe we can’t get away from.They need something here and China, you know Peter and I were going back and forth this morning because Peter wrote a really good piece this morning and Pence’s speech, you know these people all have short memory. Pence says, we don’t load our friends up with debt. Oh really?! I studied American economic history for quite a while let alone American history and we do load our friends up on debt and in fact, we use to collect it like the Brits did with (inaudible 9:53) diplomacy. So the better go back and redo their analysis. Of course we did! Whether one is (inaudible 10:00) and the other is (inaudible 10:01) financed (inaudible 10:03).
So they have a long road to hold and they have to be careful because the Chinese have a different memories about the colonial nature of the western world and that come to play in this. So I’m not disagreeing with David. I agree with him and I think (inaudible 10:25 -10:26) harder to get to.
FRA: Just a quick question on that, Yra do you see challenges as being negative upon the US agricultural commodities market?
Yra: Well I think that they’ve explained that already and you and I,Richard, we talked about that long time ago. They couldn’t have time that worse for the agricultural sector because (inaudible 10:51-10:52) right when the Brazilian crop was being harvested, the Brazilian, Argentinian, South American crops were being harvested, and they’re offering discounts because there was so much product, so much Supply.
So the Chinese could afford to play this game and all it’s done is just like it did in the seventies with the Russian wheat deal, you start losing markets. More than the low prices in the short run, the farmers are really upset that markets are trying to build a route in diminished because of this tariff.
Yes, I always laugh when you put on tariffs and through the backdoor, you start offering subsidies to the businesses. You have to scratch you head. It’s a stupid policy, it was mis-timed, they came out with guns blazing because they wanted to make a point and the rural sectors of the United States economy held strong in supporting Trump. But you couldn’t have timed that worse. I would have waited until now but they were in a hurry because of the election cycle and the election cycles are more important than anything else. It’s a terrible, terrible policy in that regard.
FRA: And Peter your thoughts?
Peter: So I breakdown of the goals of the administration in 3 lanes.
1) One is economic ignorance and that’s their desire to lower trade deficits which is nonsense
2) Then its the technology threat by Chinese companies stealing. Well there are ways of dealing with that and right now the U.S government has essentially cut off a Chinese company that was accused of threatening technology for Micron. Not only is that company being cut off from doing business with American companies but they’re also getting tossed into some international courts. That’s the way of handle the theft of technology.
3) And then you have forced into joint ventures where you have to transfer technology. Well no one is forcing an American company to do a joint venture in China and if they do, then hand over their technology. US companies don’t have to agree to that. They voluntarily do it. I’m not saying that’s the right thing for China to be doing, to force the transfer of technology, but no one is forcing US companies to do business in China. They honestly want to do it for growth but its not being forced. So my point is that throwing tariffs to address these 3 things is like throwing a football at a catcher at a baseball game. It just doesn’t apply. The problem now is that your literally freezing global economic activity, (inaudible 13:49 the CEO and CFO of multinational business, you’ve clouded up all visibility, we’re seeing trade numbers from China, to Japan, to Germany, to the US all slowing across the board. So what’s happening is that the administration is taking for granted what was a decent economic start to the year and throwing it in the winds and hoping that t can somehow withstand these tariffs. The problem is, and I talk to and listen to alot of conference calls, 10% tariffs is not good and not fun but companies can handle it. You go to 25% and all bets are off! In terms of what Yra mentioned earlier about supply chains, well many companies that do business in China aren’t going to just pick up and go to Bangladesh, or Vietnam. They’re well entrenched there. They’re happy doing business in China (inaudible 14:41) products and their just going to have to eat this or their customers will eat this because when you throw tariffs to somebody else, it’s your own people that ends up paying for it.
FRA: Great insight! I guess the big question now is, given these trade challenges and transit economic activity, will there be a massive infrastructure fiscal stimulus? And if we can look at that question from the perspective of will there be a massive infrastructure fiscal stimulus in Canada, in the US, and in China where there has been a lot for the new silk route initiatives and also in Europe? As you mentioned Yra, the key to European infrastructure program will be the issuance of a Eurobond, which will begin the process of unifying the European financial markets. Maybe we begin with Yra your thoughts on that, for the massive infrastructure stimulus, will that happen? Yes or no in those jurisdictions?
Yra: When I listen to President Macron, he would like to get there yesterday and then when the Dutch Finance Minister came out today and said he was opposed to what Macron and Merkel had reached on the budget agreement, but that’s really not the issue.
(inaudible 16:02-16:03) George Soros and many others (inaudible 16:05-16:09) I can probably go back to (inaudible 16:11), and if you gonna do this, you needed a real Eurobond not individual sovereign bonds. (inaudible 16:19-16:25) including the French. The French never wanted to relinquish their sovereignty by surrendering their budget. (inaudible 16:33-16:36) but to give up your fiscal policy, that was a step beyond.
Now they realize that Soros and the others were right. You have to create a Eurobond. Now a good way, economically, (inaudible 16:51-16:52) Rahm Emanuel, the Mayor of Chicago, Chief of Staff to Obama would say, never let a crisis go wasted.
Well the Italians, I think are much more flexible in those demands, if they knew they were getting a massive infrastructure spending financed by the capital level (inaudible 17:20-17:21) in Europe and
you could do that! You could do this. You could do this at the G20 and say, hey, we need the infrastructure spending. Let’s do 500, it’s just a number, but what difference does a number mean anyways? They’ve already bought 3.5 trillion of debt that Dragi (inaudible 17:41-17:45).
But if you went a very long way to (inaudible 17:48-17:50) whatever it takes to sustain the Euro. Why go half way?
I think the infrastructure for Europe is easy and you get that Eurobond and to make it all a bigger joke, you have the ECB buy the debt anyways. So go to the German court or European Court of Justice but it would be a needed step that they need to undertake. Is it the best step? No. But they’ve already gone this deep so why stop now?
Which is really the (inaudible 18:31) and it will buy off (inaudible 18:32-18:40) you’ll get the optics of the Italians saying, ok, we’ll back off and everybody becomes a winner and you’ll do it with German money. What better way is that?!
FRA: David your thoughts on potential for massive infrastructure spending in Canada, US, China, and Europe?
David: Well, I’ll just give my thoughts quickly on Europe. The bottom line is that the only country that has the fiscal capacity to fund something like that will be Germany and their infrastructure is top-notch. It’s one of the best in the world so I really don’t know how that’s going to be facilitated.
I look to the US and infrastructure for election is just a classic motherhood. 14 letter word for motherhood, infrastructure, we hear it all the time. It gets people excited all the time. I remember we had an infrastructure package with Obama in 2010 and I don’t remember (inaudible 19:46-19:47), people will talk about how the money never really got spent although I continue to hear things were (inaudible 19:52) already. You can use Canada as a poster child. I mean there’s no plan to boost infrastructure in Canada. There’s other issues here that have to be addressed but the Trudeau government, who got elected at 2015, the first thing they did was embark on motherhood and infrastructure was part of their key campaign plank.
Canada has already started to see that money flow into the economy and at the same time, the Canadian economy is slowing down after never really doing a heck of a lot. I don’t see a infrastructure was a big antidote at what happened at the energy sector and now residential investment is gonna be going into a bear market because of its over capacity.
So I know that infrastructure makes for a nice headline, you know if you’re long on bonds in the United States, you really want to hear about how the federal government will fund infrastructure for the local governments. I’m not convinced that’s gonna happen but if it does happen, you have to remember that the (inaudible 20:52) period for infrastructure is in years.
This is no magic bullet. I’m not gonna say that we can’t use infrastructure to upgrade roads and highways. I’ve been hearing infrastructure for 30 years. We always need infrastructure but as a tool to boost the economy, it’s not very effective. As a tool, to say, upgrade the capital stock on a long term basis, I’m all for that. I’m not so sure given the level of acrimony between the House Democrats and the Administration, I’m not very hopeful we’re gonna get something done on that.
Even if they do, it’s not changing my overall investment philosophy which is extremely defensive at the moment.
FRA: And Peter your thoughts?
Peter: Public infrastructure spending it’s tough to get more inefficient than that and all you have to do is look at, I live in New Jersey, look at New York airports, the New Jersey transit system, the New York City subways, that’s not for lack of money, that’s for a complete waste of existing money and existing resources. So to think that okay we’re going to build some bridges and roads, well that’s being done all the time at the state level. So to see that we’re going to throw some more money at it and to think that’s gonna be efficient use of spend is complete nonsense.
Then it gets to the point where, okay let’s just say we passed something, we allocate money to these different jurisdiction, who’s gonna actually work on these roads? Where’s the skilled labour that’s gonna be tightening bolts on a bridge? I’m not sure if there are plentiful right now so I don’t even know if something was passed that anything would actually get done.
This laundry list of wasteful spending projects that has ended up costing billions and billions more than what was forecasted and for what?
So I would argue that the multiplier is less than 1 and yes overtime, you want a train system that works and you want a bridge that doesn’t collapse, I get that. But the multiplier is typically less than 1 when your dealing with public infrastructure spending.
FRA: Peter moving on to your forecast, what are your thoughts for the U.S Dollar and US interest rates for the next 6 to 12 months?
Peter: What the US dollar faces is a Fed that’s gonna either blink and pause, which is a growing possibility at the December meeting and I would argue that if they pause, they won’t have the either the guts or the data or the markets to end up hiking. Now granted that they can hike every meeting next year because everyone’s alive meeting. I’m more worried about European bonds and what the ECB has done and I do think that we’ve entered a longer term bear market in bonds generally but that could take awhile to play out.
With the dollar, the challenge the dollar then faces is if the Fed blinks, the dollar is going to be in trouble and interestingly the dollar has two different phases this year.
In the first half of the year, it was strong against emerging markets and traded actually relatively poorly against more developed currencies.
Then the second half, or at least the last couple of months, you’ve seen a rally in emerging market currencies and you’ve seen dollar strength against the Pound, the Euros more related to Italy. But I see these currency movements and the strength of the dollar is not because of something great is going on here, even thought someone could say rates are going up and the economy is better here than elsewhere, but a lot of it is I think shot in the foot type behaviour in overseas economies
But the second the Fed blinks the dollar’s gonna be in trouble, that could be the end of the dollar rally because the US government is still facing massive debts and deficits, which overtime is gonna be very dollar negative and just as the years go on, there’s gonna be less dollar transactions taking place. That’s a very long term story. I know it gets a lot of press now but I see lot of secular headwinds for the US dollar notwithstanding current (inaudible 25:08) against certain currencies.
FRA: And David your forecast for the US dollar, and US interest rate for the next 6 to 12 months?
David: Well I think that, well firstly on the US dollar, its been very tempting to be bullish on the US dollar because the FED, you know textbook economics, easy fiscal policy, tight monetary policy will always and everywhere, give you a bull market in your currency. But I think that story has largely played its course. I’m getting a little nervous over the bull market in the US dollar and I’ll tell you why. Firstly, the chart today looks absolutely ugly of the DXY but I’m looking at latest (inaudible 25:52) in the traders report and I’m looking that on the intercontinental exchange the trade weighted US dollar has a net speculative long position of over 40,000 contracts. I mean we haven’t seen this in about a year and a half. So there’s a huge overhang of speculative naked longs right now that could easily exit this over crowded trade and set the condition for this pretty big reversal in the US dollar going down as opposed to up.
I agree with Peter that the most important determinant in a currency is the relative interest rate differentials and one of the reasons why the US dollar is succumbing right now isn’t just that the naked longs are starting to exit the markets but the reason why and that’s because of the Fed, in a matter of about 6 weeks, has gone from hawkish, and I wouldn’t say dovish, but certainly less hawkish enough that you’ve had already just the matter of weeks of full wage hike priced in for next year come out of the marketplace.
We were supposedly at (inaudible 26:56-26:57) Oct 3rd, a long way from neutral, we may have to beyond neutral and now everyone’s talking about, no neutrals enough and by the way, maybe one or two rate hikes away. So that’s undercutting the US dollar at the current time.
(inaudible 27:13) interest rates, a lot could happen in a year. Probably at this stage, maybe less bearish on treasuries than Peter is, I think we may look back and say that when we approached the 3 and a quarter percent of the 10 year, maybe that was the peak and I think that there’s a lot of cross currents.
You have the cost push inflations forces from extremely tight labour market and from these tariffs but at the same time that’s battling the cyclicality of a decelerating global economy and US economy. So I think that we should just take our (inaudible 27:54) from the market itself. Here we have taken out a full rate cut for next year, here we got a lot of slowing growth, another turn down in the stock market and the best we can do is 3.05 on the 10 year note. You know the 10 year note in this mix of widening credit spread, deteriorating stock market, less bearish view or hawkish views on the Fed and the best you get is 20 basis points off the 10 year note.
I mean normally in the past when you had this sort of condition, especially in the stock market, the 10 year note yield was down 80 basis points not 20. So the market’s telling us something here and maybe it’s over beyond just talking about tariffs, cost push inflation, wages, the cost push inflation, but the fact that we’re really choking on supply. I mean Peter Boockvar comments all the time on what’s happening with these treasury options and the reality is that this time last year, the deficit was supposed to be $600 billion dollars this year. Well it’s gonna be worth more than a trillion dollars. So we were choking on treasuries supply that we weren’t supposed to get except the bright lights in Congress and the White House saw that cutting taxes at a time of full employment was a really great idea. Newton’s 3rd law of motion, every action has an equal opposite reaction is that bond yields are not falling when they should be falling and that ends up being another problem for the stock market because stock markets put in the lows. When you get to a certain relationship between the bond yield and the earnings yield on the stock market, the problem for the stock market and maybe for those people uber long treasuries is that you’re not getting a normal response here.
The reason is that there is too much supply. The streets left with too much product after these auctions and the dealers have to dump this product and this is putting (inaudible 29:42-29:43) on bond yields right now. To me that’s the big story. So I think we’re stuck in a range for the foreseeable future as far as the treasuries markets are concerned.
FRA: And Yra your views?
Yra: Well I’m gonna be very sympatico with this but let me pick up where Peter Boockvar was just talking about on CNBC, which is of course a huge amount of corporate investment debt to throw onto this and how much of it actually is LIBOR based which makes it even more telling. As we’ve talked about, Richard and Peter, and David a little bit, debt, debt, debt, is to financial markets is what location, location, location is to real estate. That’s the way I knew it, and I hold true to that and I think that David’s warnings are very, very important and Peter’s been there too cause we turned bearish a dollar i think at the same time at February of 2017 when we saw the move come, Peter and I. This movement of dollar, the dollar is going up grudgingly and I like David am old enough to know that when you have these interest rate differentials and with negative nominals, forget real, but nominals wage being negative in certain parts of the world, yet those currencies are not really weakening as they ought to and couple that with David’s comments about why aren’t these bonds a lot higher, that poses the question that United States is really drowning in debt and the world sees it. It’s like you hold your nose when you buy dollar assets today because there’s very little else to buy. You buy it cautiously and I think some of it is right because it’s to expensive right now to hedge it away. So a lot of people buy it and go, if I pay for the hedge, I’m basically breaking even so what’s the sense of doing that? So some people stay away from it. With David’s point is absolutely well taken on.I’m watching these curves. Right now, the 530 curve, which I call the speculative curve, is getting interesting because it’s moved while the 210 has kinda stayed stagnant. But I would say that’s because people have more duration matches that they have to put on. But as I tell people, if you buy a US bond of longer than 5 year duration, you need your head examined and ought to go looking for another profession because you’re an idiot. You’re an idiot! Unless you have duration that you have to cover because it makes zero sense cause as David talks about, this budget/ deficit this year is over a trillion. And this is, I’m not an anti-Trump, you know again, I’m from the school of Deng Xiaoping. I don’t care whether the cat is black or white, as long as the cat catches mice.
This is a president who’s never met a debt he doesn’t wanted to take on. So if he really gets into trouble, and that has been my point and that’s why I agree about the structural basis of infrastructure spending, this is somebody who’s looking to spend, spend, spend.
And If he finds sympatico voices from the Democratic party in the house, he will get his way cause he’s already said, he doesn’t care about debt. You know what, the freedom caucus, who was the voice of fiscal austerity and soundness and responsibility, their on their heels right now.
I would not buy a piece of US paper over 5 years. I think you’re out of your mind.
The equity market, that David points out, is telling you that because as we look at this board, (inaudible 33:52-33:55) 3.05? Really? That’s all you got after a 15% drop from the high to the recent low in the equity market.
That’s all you got? To me that’s a warning sign.
Peter: In the month of October, the stock market and bond market went down. Yields rose across the curve in October when equities fell as much as they did.
FRA: And finally lets look at what investors can do for investing or protecting themselves going into 2019. David, you’ve referenced 4 letters, Q.L.D.S, Quality, Liquidity, Defensiveness, and Selectiveness. Can you elaborate?
David: Sure. I think that when your talking about a step up in quality both across the capital structure, equity and debt. If your mandate is equity, I think you have to be very mindful of the degree of cyclicality that you have in your portfolio and focus on earnings visibility, and limit as much as you can your overall GDP sensitivity.
I think classically late cycle, I think we’re in the top of the 9th, and I think when we get to the top of the 9th, historically its the rare period where value outperforms growth and I think that will continue to be a theme, maybe a theme that works for relative terms and absolute terms but it will work in relative terms.
I think as Yra has said and Peter would agree that being very mindful of your duration in the fixed income portfolio is very important. Really until you see the (inaudible 35:44) eyes of the recession, which I think at some point will come next year, is like an odorless gas you know everybody likes to say that, oh I don’t see recession coming. Well most people don’t see recession coming when it’s already hit. So you want to be mindful of that up until a certain point when things start turning around (inaudible 36:03) keeping in mind that inflation is gonna be a problem but at the same time, a bit of a lagging indicator as we saw in 2008. So that’s the quality part. Liquidity, I think it’s pretty obvious, you want to have cash on hand for optionality or maybe more than that.(inaudible 36:24) at the beginning of the next cycle in other words, transitioning out of this long bull market. So you wanna use cash and look at this time last year, cash paid you 1%.Today cash, looking at the 4 year treasury bills are trading, you’re getting well over 2%. You’re getting better than they get in the debit and yield in the stock market. So you’re getting paid to be in cash today and I think that was a very prudent thing to do.
You wanna end up being, when all said and done, a lender in this market not a borrower.
You know LQDS, D for defensiveness, that goes back at the quality, basically perhaps, subsets that again be mindful. The OECD leading indicator is down 10 months in a row so you haven’t seen anything yet. This is a financial wedge. The global economy is gonna be weakening even more next year than it has from the previous year. So that means you have to be defensive and of course I would go back to fixed income markets especially in corporate when you can consider that next year is the first of the next 4 years for you’re gonna have a tsunami of debt refinancing in the corporate sector at a time where 50% of the investment grade universe is rated BBB. There’s gonna be a lot of volatility. Defensive also means very mindful in your fixed income portfolio and credit as to what the maturity schedule of the debt looks like and the companies that you own. Selectivity just means style investing, no different than late cycle value over growth. Late cycle means you wanna own as few stocks and few securities as possible. You wanna cull the portfolio. If early in the cycle, you own 60 stocks and mid cycle you own 40 stocks, you wanna have 20 late cycle. You wanna get down to your most blue chip, liquid, relatively safe names. So that’s what selectivity really means to really just have best idea portfolio and nothing else.
FRA: Peter your thoughts?
Peter: Yeah and to add to that, if you’re going to be in equities, at least for many listening possibly US and Canadian equities, boring is good. Boring businesses, peak valuations, not exciting that’s what people should be focus on. And I think in this downturn overseas, particularly Asian emerging markets that includes China, I think there’s a lot of value being created. The Chinese stock market has been as inefficient as it is. It’s been through a bear market down 60%, well now probably about 50 from its 07 peak let alone where it’s all from its 2015 high. And to add again, short duration, I’d be in gold and silver as part of my weak dollar belief next year when the Fed blinks. I think gold and silver are gonna be up a lot when that happens. I think it’s simple as that and having cash. There’s time to play offense and time to play defense. This is one of those times to play defense. There’s time to own gold and silver. There’s times not to own it. Now’s one of the times to own it.. So boring is good and I would stick to that.
FRA: And finally Yra?
Yra: There’s so much that I agree with here. The medals, I think they’ll have their day. People have been a little bit unnerved because of rising interest rates in the United states. You know its more than just rising interest rates cause we see 8% in Mexico and I would argue that Mexico is a probably a far better investment right now than a lot of other places. Yes I know that (inaudible 40:10) is coming on and there are some uncertainties of course that exist there but US is its own inconsistency. Part of it is who’s running this show. I don’t think we’ve had a high quality secretary of treasury probably since, and we can argue about that, the Rubin Summers years. I was not a Hank Paulson fan. I was certainly not a Jack Lew fan. I was certainly not a Tim Geithner fan. I’m less of a fan Mnuchin and yet all of this is taking place.
So when I buy a country’s sovereign bonds, I’m buying not only what their balance sheet looks like and what their financial statements, I’m also buying the credibility of the people in charge.
So again, you gotta be very careful here. I think that David and Peter are both making really great points about where yields have gotten to this in the face of all this and the inability of the dollar to really have a sizable rally cause David hit this right on the head.
I know I traded my way through Volcker and Reagan so we have the classic case of fiscal stimulus with tight monetary policy and the dollar boomed so the dollar strengthened till much of
the course they had to undo it through the (inaudible 41:36) accord.
We’ve got nothing out of this! Really, when you look at it, if you put up a long term chart or last year’s, okay, you know I can say the Euro was born 1,17,85 in January 1st 1999.
We’re not that far. We’re 1,14,50 and Europe is saddled with nothing but problems and still the dollar doesn’t rally. Now that doesn’t mean today it can’t rally, tomorrow it can’t rally, next week, but when you look at it’s overall performance, I would be very weary. There’s movement afoot here. There’s things underneath the surface, that are bubbling that you have to be attentive to and it’s what ought to be happening that isn’t happening and that should be a warning sign to everyone!
FRA: Great insight gentlemen! How can our listeners learn more about your work? David?
David: Well you could either call me directly at 416-681-8919 or email me at rosenberg@gluskinsheff.com and I’d be happy to get anybody on a trial for me two morning publications at Espresso With Dave and Breakfast With Dave and the best way to reach me once again either phone or email.
FRA: Great, and Peter?
Peter: You can reach me at peter.boockvar@bleakleyadvisory.com and I have a “C” after the double “Os” is my last name. For wealth management advice or macro market advice where you can go to the website boockreport.com.
FRA: Great, and Yra?
Yra: Just notesfromunderground or you can go to yraharris.com and register for there and if you write to notesfromunderground and it’s not low quality trolling but high quality, you’ll get an answer because a lot of people will respond to you tonight, give and take on the blog. Again, it’s not a tout sheet, we’re not a tout. We try to create ideas and you’ll do the work, we’ll just try to point you in a direction to see if there is any possible investment reward. To me is a great place for two way communication and for dialogue which so much in this business is. It’s about dialoguing with people who we respect and nothing does it better than this podcast that we’re sitting on right now.
FRA: Great! Thank you very much and we’ll end it there. Thank you very much gentlemen!
 10/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith On Why Many Millennials Are Promoting Socialism
10/26/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Charles Hugh Smith On Why Many Millennials Are Promoting Socialism

FRA: Hi Welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight .. Today we have Charles Hugh Smith, author, leading global finance blogger, and philosopher, America’s philosopher we call him. He’s the author of nine books on our economy and society, including A Radically Beneficial World: Automation, Technology, and Creating Jobs for All, Resistance Revolution Liberation A Model for Positive Change, and The Nearly Free University & The Emerging Economy. His blog oftwominds.com has logged over 55 million page views and is number 7 on CNBC’s top alternative finance sites. Welcome Charles!
Charles: Thank you Richard. It’s always a pleasure!
FRA: Great and today’s topic is socialism. What is driving the majority of millennial’s to that? So we want to explore, you know, what’s behind that trend (Especially in the US and in Canada)? You know what is socialism? Misconceptions on socialism? We’ll get different models like the Nordic model and how does that look, positives and negatives. And just in general also how this could lead to increasing levels of political instability and even political violence in the coming months.
Charles: Right and it’s a great topic Richard because we all know that the younger generation, the millennials in particular, are publicly attracted to socialism as a more just system than what they see is unbridled capitalism, which in its current iteration has created extremes of inequality and opportunity.
So I thought we’d just start out by laying 3 different flavours of socialism or what’s commonly called socialism. In classical socialism, that means that the state or the government, owns the means of production and in other words, factories and the resources are owned by the democratically-controlled or structure government so that the benefits from the means of production are then distributed relatively equally amongst the population. In today’s world, most young people according to polls understand socialism not by the classical ownership of the means of production but by social welfare. In other words, the government collects taxes and it distributes it in some sort of fair fashion to the entire populous and so I call that the social welfare version of socialism. And the Nordic model, the Scandinavian countries which are often called socialist but as you’ll explain in a moment, is not technically not really true. But what they do have is a model of deep cooperation between unions, you know labour, big corporations and the government and so there’s a there’s sort of a cultural social contract there that creates a more equal society because the wealthy pay very high taxes and there’s a lot of social welfare programs and also programs to create jobs.
FRA: And I think the millennials are coming to this from the social justice perspective so they sort of focus on that first and then they branch out into economics areas in terms of like socialism. Would you agree?
Charles: Right! Exactly! How do you achieve economic justice and they’re looking to socialism as the answer. But you know that start with the Nordic model because it’s widely understood to be successful in these is relatively small countries. I think Denmark has less than 6 million people which makes it smaller than the inter counties of the San Francisco Bay Area and considerably less than the county of LA and I think Sweden is around 13 million people something like that which puts it on par with the County of Los Angeles. So these are really small nations in terms of their population and so it’s a lot easier to have a unifying culture than it is to have a very large multicultural nation like Brazil or the United States but having said that, you mentioned a quote from the prime minister of Denmark which I thought was really insightful about the Nordic model of socialism.
FRA: Yes, exactly! The Prime Minister of Denmark recently said, “Denmark is far from a socialist planned economy. Denmark is a market economy”. And yeah just to further elaborate on that, the Nordic countries do not generally interfere with free markets so they are promoting free markets, they are promoting free trade, global trade, globalization, and generally do not nationalize industries, and do not subsidize favourite Industries which is a common misconception.
Charles: Right and I think the another common misconception is that they just give away a lot of free money to everybody but in actual fact, they have very strong work ethic. In other words, a lot of their social welfare programs are aimed at retraining people and helping small businesses emerge and hire people. So they’re really focused more on creating jobs than giving free money away and so that’s why universal basic income, which a lot of people feel is the source socialist solution. In the Nordic countries, they’re not really big fans of just giving away free money with no strings attached. They want to help people gain livelihoods. That’s really their culture focus. We were having a conversation about the culture aspects of the Nordic modelling and before we started recording, it’d be great if you could elaborate on that that topic.
FRA: Yeah the first question I usually ask when people make reference to that is have they been there before and then I mention I’ve been to Sweden, I’ve been to Norway, and what I have observed in the nature of the people generally, that in the culture, is a very strong sense of fiscal responsibility and a high level of education. Making very efficient use of government resources and even in the buildings they stay generally not looking to build brand new government offices but working in very frugally, meager type of facilities, government offices or old buildings perhaps and making the funds of the government go much farther in terms of very efficiently. That I think would be very difficult in North America given a lot of politicians are more concerned on getting themselves more lavish pensions.
Charles: Right. I think you are absolutely right and I had a chart that flabbergasted me actually that in the state of California, where I live part-time, that the taxpayers contribution to the public union pension plans there was less than a billion dollars in the early 2000’s and now it’s something like 45 billion.
So the people kind of promoting social welfare versions of socialism, they’re not a tuned to the fact that socialism limbs itself, if you have the wrong cultural traits, to cronyism and exploitation of the state rather than as you say of a fiscally prudent use of state funds to help everyone. So that leads us to, I think, Venezuela which pursued as policy both a classical form of socialism meaning that they nationalized a lot of the industries in that country, the oil industry, and so on. And they also instituted a very broad social welfare programs. And so, as we all know, the Venezuelan policies of the government have led to a complete collapse of their currency, trading at something like 300,000 or to $1. Might even be 3 million to one now. I’m not sure but they’ve impoverished of literally everyone in the country except those high officials and cronies who escaped and then it took their money to Miami before the currency collapsed. So that socialism is one version of it and we really have to ask, what did Venezuela do wrong because they pursued socialism as most people understand it
FRA: Exactly and that contrasts between them and the Nordic countries, in terms of their approach, what has resulted?
Charles: Right and the government ownership of means of production doesn’t guarantee you any efficiency and if the enterprise, where its owned by the government or owned by private parties, it’s still has to create a profit, it still has to use the efficient otherwise it just becomes a source of losses and it’ll take or who ever owns it. So Venezuela, I’ve never been there but I have sources there, I have contacts there, and it seems pretty apparent that the government owned infrastructure and resources are very poorly managed. They were undercapitalized, under investment, and cronyism has run wild there. So that raises the question for millennials, how do you make sure the socialist model that you find attractive is more like the Nordic model and less like the Venezuelan model because socialism as an ideology or as a way of organizing the resources and the means of production of society. It’s not one-size-fits-all and you have catastrophic failure right beside so called success. So socialism as a system is not the answer if it goes the path of Venezuela.
FRA: Just to point out a few more facts on the Nordic countries, their countries economic successive before they built their welfare states. A lot of people don’t realize that it was the actual wealth that allowed the luxury of the generous programs that followed so that’s one fact. Another one is a lot of people don’t realize is they don’t have minimum wage laws in the Nordic countries. None of the Nordic countries have a minimum wage law. Another fact is in Sweden, they have complete school choice so whereas your property taxes may go towards government schools only in North America, there’s a choice in Sweden. You could actually apply those funds instead to even go to a private school to attend private run school if you think that’s better for your children so a lot of people don’t realize that but yeah the result though, I mean is it all bliss, not necessarily. If you look at what’s happening now in the Nordic countries, there are problems, maybe not as bad as Venezuela but in terms of the increasing racial tension, ethnic tension, especially from a lot of new recent migrants that are looking to capitalize on that welfare system that they have in place. They’ve also suffered recently from the oil revenues that go in mainly to Norway and Denmark so that hasn’t been as good. A lot of people don’t realize that in many of those areas, there’s actually the highest consumption of antidepressants in the world. So that’s a fact. That is quite amazing as well. And then even recently what they’ve done is moved to a to do a certain activities which a lot of people are not aware of in terms of strong movements now to cut taxes, limit public benefits, reduce welfare spending, pension savings have been partially privatized, for-profit forces have been allowed in the welfare sector, state monopolies have been opened up, so that there’s a lot of change happening even in the Nordic countries.
Charles: Right those are excellent points and it goes to show that what we’re talking about is not a purely economic system that socialism, in whatever flavour we’re speaking of, is a social system and a cultural system. It’s not simply a financial arrangement. So just to kind of speak of change gears a little bit and go through some slides, I have about the social welfare model of a spending on infrastructure and public spending as sort of like a way of distributing the wealth of the nation right (inaudible) and so I have a slide here of infrastructure. Everybody loves infrastructure and it’s a very politically popular way of creating jobs and distributing resources and so we see that globally, China of course has spent huge amount of their capital on infrastructure, you know, and we all know that they have High-Speed Rail and and Subways and they’ve gotten a lot of public benefit as well as jobs from their infrastructure. But at some point, you’ve already built out all the subways you need and all the high-speed rail and then then you wonder what do you spend the money on next if that’s your social welfare program, you know building infrastructure. And here in the US, its well known that in the US infrastructure’s ageing in many ways. The water, electrical systems, roads, and so on all need more investment and that can be seen as a productive useful of public money. In other words, the public is getting some broad based value and jobs are being created as opposed to just giving money away without any strings attached like universal basic income. And then to show another failed way of distributing funds, I have a chart here of higher education student loans in the US and of course, we all know that there were no such things prior to like the 1990’s and now there’s about 1.3 trillion dollars of student loan debt which is guaranteed by the federal government. So it’s a form of socialism that ends up turning students into debts surfs and a lot of people are saying what we need to forgive all that debt. But that debt was issued by for-profit firms and so we have to be really careful when we talk about socialism like who’s skimming profits from these government programs. Then my last slide here is showing the state and local government expenditures, which tend to be the most boots on the ground or the the most visible forms of social welfare spending, tend to be state and local in other words, infrastructure on local roads, local welfare, local school districts, and so on and we can see that all in the US, the state and local government expenditure has soared the rate of expansion far beyond the actual GDP that the domestic economy. And so then we start wondering how are they spending so much money than the economy is creating and then the answer is of course we’re going very deeply into debt. I mean local governments are selling bonds and globally you can see the tremendous expansion of government debt as well as corporate and household debt. So if we’re if we’re funding all of our social welfare and infrastructure with debt, then we’re creating another issue that doesn’t have anything to do with socialism or capitalism. It doesn’t matter! The debt is creating a lot of imbalances and could bring down the entire economy. People always love infrastructure and they love social welfare, they like the government spending more money but where’s the money coming from and what are the consequences of using debt to fund social welfare.
FRA: Yeah essentially putting the burden on future Generations increasingly with the increase in debt as the result. And then some would say maybe we should just say tax income on millionaires but there’s actually a fact that if you even put a 100% tax on income from every millionaire in the US, that would only fund that US government for 4 months. So that’s quite amazing fact. Another one is that even if you confiscated the entire wealth of America’s 537 billionaires, that would not be enough to fund the nation’s budget for even one year. So there’s simply just not enough money out there but there’s a perception that there is.
Charles: Yeah that’s a very good point Richard. I believe the federal budget is pushing for a trillion a year right. I think it was 3.7 trillion and so that’s a big chunk of money and I guess we’re coming back to the question of what’s the downside or the risks of pursuing a socialism and I think if you’re going to follow the classical socialism of the government taking ownership of the means of production, then you risk gross inefficiencies and cronyism, mainly insiders basically pillaging those assets to their own benefit and then impoverishing the nation by under investing or mal investing the state money.
That’s that’s one danger. And in the Nordic model you’ve described it may not be affordable, you know, it as revenues decline even prudent governments end up starting to borrow money and living off of asset bubbles as a way of generating their revenue so that’s the danger. And the US model of just borrowing trillions to pay for infrastructure and social welfare programs. That creates of a really great risk of a currency collapse or a loss of of faith in the entire Financial system.
FRA: And now we go further to that if you look at the history of of socialism and the evolution of it. In particular countries, generally there is a very strong decrease in the standard of living that ultimately results in brain drain and wealth-trained so you get to a point at some point where it nonlinear. A lot of people begin leaving, looking for opportunities elsewhere if they’re educated. Wealthy people don’t sit there as sitting ducks. They’re likely to move at some point together with their wealth somewhere else so that’s also the potential for that to happen, brain drain and wealth drain.
Charles: Yeah and my last point Richard would be that you know socialism like capitalism itself, however you want to define it, it tends to work much better when things are decentralized. When powers decentralized, ownership of assets are distributed, and people have a say both as consumers and owners. My example here is water systems. In very localized places like a city or a county, public ownership of water has been very successful because the agency localized their only specific assets in the community and the community is democratically organized so they have a say about how that resource and asset is managed and they can vote out the board if the board is corrupt or incompetent. And so socialism, on a very small decentralized scale, can work very effectively in protecting public assets in the same way that capitalism really only works if competition is allowed to thrive. So we’re talking about when things are in very large scales like centralized power, then you get rid of competition and you usually get rid of the benefits of public ownership of assets.
FRA: And I think overall the majority of millennials have not been able to understand how and why there was a financial crisis back in 2008, 2009 and what the role of the Federal Reserve and Central Banks in general has been in causing that as well as in causing a wealth and income inequality from various Central Bank activities and Central Bank policies, we’ve covered that a lot in prior podcasts how and why that happens. So I think that’s been also a major driver for the millennials to misinterpret/ misunderstand what’s happened and therefore, go to maybe bad conclusions if you will.
Charles: No I think you’re absolutely right Richard. The financial repression of zero interest rates and quantitative easing for the the banks and so on. Yeah that’s what disrupted the opportunities and created the inequality the millennials want to resolve and we understand their desire the justice of resolving those inequalities but it’s how do we do that? And if we’re going to pursue the Nordic model, then what we’re really talking about is, then you need a market economy and a cooperative government and a culture milieu that supports fiscal prudence and wise investment of resources and not just throwing money away and giving it away.
FRA: Yeah exactly. There was also a recent study I saw where it was pointed out that the minority of radical leftist are actually dominating the Democratic party agenda. So this is interesting because between Democratic Socialist Party of America and the traditional democratic party, which is now having their agenda control or dominated by radical leftist, is quite disconcerting you know in terms of what could happen to the potential for extreme socialism in America.
Charles: Right and again what we’re trying to elucidate here is that there are models of like private or public ownership of assets on a small scale like I said that they have a long history of functioning like public ownership of the water works but what’s being proposed is not really classical socialism. It limbs itself to free money for everybody and if we have to borrow the money, then fine. So that’s not really socialism and it’s not on classical socialism nor is it the Nordic model that so many people look too as a successful model.
FRA: Yeah exactly, and we’re essentially in general agreement to conclude as some final words in terms of what could make sense so we don’t take sides on any parties but generally, we see a more limited government approach that is decentralized with minimal special interest group lobbyist, if any at all that lends itself from a centralized form of government that has been optimal. Would you not agree in terms of that approach?
Charles: Yeah absolutely that a planned economy is a failed economy. That’s really what we’re talking about. A planned economy mean insiders benefit and it’s lost all of its adaptability, flexibility, and efficiency.
FRA: Exactly. What do you see as potentially evolving as a final question to consider in a coming years in terms of the evolution of where America’s going?
Charles: Well that’s a big question Richard. I think people are struggling to find some sort of answer to rising inequality and the concentration of wealth and power and they haven’t really come up with anything and so a lot of millennials view socialism as the answer. Other people view like reforming the government so that there’s less cronyism and so on but I don’t think that they’re going to get the results they want from those kinds of policies. I think we need a radical decentralization of power and a radical redistribution of opportunity and that’s going to be breaking up all the cartels that are, you know, basically state managed cartels, which controls most of the US economy, and get rid of the financial repression that we have described. It’s totally centralized and it benefits centralized wealth and power
FRA: Great insight Charles and we’ll end it on those words of wisdom. How can our listeners learn more about your work?
Charles: Please visit me at oftwominds.com and you can read the first couple chapters for free of my new book, “Money and Work Unchained”.
FRA: Excellent, we’ll end it there. Thank you very much Charles!
Charles: Thank You Richard.
 10/25/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Volatile Financial Markets & Global Risks
10/25/2018 - The Roundtable Insight – Yra Harris & Peter Boockvar On The Volatile Financial Markets & Global Risks

Download the Podcast in MP3 Format Here
OCT 24th Podcast: Yra Harris and Peter Boockvar
By: Tenzin Lekphell
FRA: Hi welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight! .. Today we have Yra Harris and Peter Boockvar. Yra’s a hedge fund manager, global trader in foreign currencies, bonds, commodities, and equities for over 40 years. He was also CME director from 1997 to 2003 and Peter is Chief investment officer for the Bleakley Financial Group in advisory. He has a newsletter product called boockreport.com which has great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentlemen!
Peter: Hey Rich, hi Yra!.
Yra: Hey Rich!
FRA: Great! I thought today we’d focus on a number of aspects for the global economy and financial markets, Central Bank policy. You recently made some observations that the Federal Reserve could be hiking the US into a recession. Can you elaborate on that on your thoughts?
Peter: Well it’s what they typically do. Most rate hiking cycles end that way and not sure why this would be any different. We have to understand that not only are they raising rates but they’re also letting their balance sheet roll down so there is a double tightening going on that only recently markets have began to appreciate it.
FRA: And how do you see that playing out currently in the financial markets globally with all the volatility?
Peter: Well from a market perspective, we’ve already seen a bunch of different potholes this year, I think driven by the rising rate so the 10-year yield of beginning of the year one from 240 to 270 and you blew up the short fixed rate. Then turkey was exposed for the debts and deficits and rising inflation that they have, which is no mystery they have political issues for years but in a rising-rate environment, vulnerabilities get exposed and it started in Turkey then went to Argentina and of course you had a blow up in the Italian bond market just as the ECB is wrapping up there own Q.E program. From an economic standpoint, the rising rates is already slowing down the pace of transactions in the housing market and in the auto sector. And also we have to pay even now closer attention to corporate balance sheets where a lot of the excess has been created in the cycle. You look at small cap stocks particularly those in the Russell 2000. 40% of debt on Russell 2000 balance sheets is floating rate, which is obviously now very susceptible to the rising LIBOR and the question is whether cash flows can then deal with that rising cost of capital. Also from a leverage standpoint, small companies in the Russell 2000 have a debt/equity ratio twice of those in the S&P 500. So this rising rates, this rise in the cost of capital is beginning to have an economic impact and as I mentioned before, a market impact.
FRA: Do you see this being bearish on credit sensitive cyclical sectors ?
Peter: Well so far because you’ve thrown into the mixes, of course the slow down in the global economy, particularly in China and in Europe, so a lot of industrial are obviously cyclical, they have high fixed costs, and very sensitive to changes in economic activity. So a lot of confluence of events are combining for what is obviously a much different market this year compared to what investors are used to over the past couple years.
FRA: And is this all creating an emerging market crisis as well as emerging crisis in the European bond market?
Peter: Well I don’t want to speak broadly when you mention crisis. Certainly in Turkey there has been one. Certainly one in Argentina there has been one with with short rates north of 60%. That’s a crisis. We have to see how it plays out in China but China has a long road to hoe in terms of the enormous amount of debt that they have, the weakening in currency, the capital flows for current account deficit and so on.
So the crisis, I don’t want to say that just yet, but certainly this rise in rates, this drain in global liquidity creates a lot of potholes as I said and if you look at just the ECB, the Fed, and the B.O.J this year or this quarter, beginning October on a monthly basis, there is a net-zero of liquidity injection if you add in the behaviour of those three central banks so that creates also a drain and I think also is responsible for a lot of the fragility that were seeing now in markets.
FRA: Will this all create strengthening of the US dollar?
Peter: Well it has against certain currencies. It has against the Yuan of course, it has against the Turkish lira and Argentinian peso but if you look at the Euro heavy dollar Index, the average level of the dollar index over the past two years is 95 and say we’re a little bit over 95. So for all the talk about Fed rate hikes and how our Central Bank is far ahead of the curve relative to others and US growth is so quick compared to everybody else, the dollar index is basically in line with its average over the past two years. So it’s been strong against certain currencies and it’s done nothing against others.
FRA: And what about in China? You have observed that off balance sheet, government liabilities and the regions of China has amounted to $6 Trillion US dollars. Do you see that as a gigantic credit risk?
Peter: Yeah that on top of the amount of assets in their banking system relative to the GDP so we’re about to see how they handle this enormous debt load. Is it something they can paper over? Is it something that can grow their way out of? Is it something that’s gonna be like Japan that’s just gonna linger for 30 years? We’ll just have to see but there’s some serious challenges in the short-term. I mean long-term, I’m pretty bullish on China. I think that they’re the economy of the 21st century but I certainly don’t discount and don’t take for granted that in the next couple years can be a tough road for them.
FRA: What do you make of the standoff between Italy and the European Union, Brussels? Yra you’ve observed that Rome knows that the higher Italian yields are forced by the rhetoric of Brussels bureaucrats. The greater the losses for institutions forced to sell in any type of panic you have observed in your blog, what do you make at the standoff?
Yra: Well the standoff is real. Unfortunately, I think there are a lot of people who talk in Europe who really fail to understand or they don’t want to understand cause (Inaudible 7:20-7:21). The Italians… they understand perfectly what’s going on here. And I think that, if I were to (Inaudible 7:29-7:36), they know what they have. The problem for the Europeans is of course, and we saw (inaudible 7:46-7:54) it’s a compounding problem for Europe. They have the Italians, who understand whats going on here, they have the Brexit situation, and they have Trump, that they have to worry about. One thing we know about the president is he doesn’t forget flight. We know that. That doesn’t mean he actively pursues a vendetta but he does not do well with flight. In the G7 meeting, Merkel and Macron and two others really (inaudible 8:31) him, you know the famous picture. It wasn’t pretty. So there was an article in the (inaudible 8:41-8:42) last week titled: Donald Trump Looks To Start (inaudible 8:45) US-UK trade talk. There’s three things to look here;
- You have the Italians who understand the pressure because there’s really nothing Brussels can do because the whole QE program has tied them up. I know we talked about this quite a bit over a couple of years that Draghi piling up all that debt.
The bigger problem is the zero risk waiting under the (inaudible 9:20-9:21) rule. They’re carry all this Italian debt, all these banks carry these debts Including the ECB and there’s no risk to it according to the rule of (inaudible 9:31). That presides a potential problem.
- You have Trump who will throw a lifeline to the Brits. Unlike Obama who made a categorical mistake (inaudible 946) in real time that to say, you’re going to the back of the Que, and Donald Trump says, U.K you’re going to the front of the que and we may even create a free trade zone with you involved in it, which would be death for the Germans cause of all the auto capacity, manufacturing capacity that was built by the Germans and the Japanese in Britain. You have that and this really locks up Europe. They don’t have any leverage. But I hear people talking about what leverage they have. What leverage? The Italians say, what are you going to do to me? Our rates are gonna go up. We saw rates in Greece go up by 40%. And you know what? Greece is still here and they’re talking. We need growth. I think there are actually more people in Europe who support the Italians position than we hear reported. So I mean we have the (inaudible 10:48-10:50) really into Salvini and De Mayo’s hands. It gives them a lot of strength. I don’t think Brussels has any strength in this negotiation.
FRA: And Peter your thoughts?
Peter: It’s interesting because one of the proposals from Salvini in this proposed budget, which I only really read about is lowering taxes and having a flat tax. That’s growth encouraging and huge growth incentive. The spending side, that’s not really long lasting in terms of generating growth so you get stuck with more debt, higher deficits, and you don’t really get the growth. So I think that’s what the concern is. The Keynesian side of this budget, that I think is the concern, and the assumption that it’s going to magically improve the long-term competitive and economic growth rate of Italy, which it wont. Only lowering taxes and the massive regulatory state will. Paying people universal income and getting rid of the extension of retirement age and pensions, that’s not growth enhancing and so that’s what I’m worried about that they’re not going to get the growth they’re hoping for. And bigger picture, I keep arguing that the behaviour in the Italian bond market and response to what’s going on is the canary and when now the European Central Bank is 2 months away from stepping away from its purchases, who’s going to buy these bonds? I mean they were really the only buyer. Even Germany, which has a budget surplus which has a grade A fiscal situation, who’s going to buy German bundits 40 basis point when inflation is running 2%? Or PPI today which printed 3.2% for September? Who’s going to buy these French OAT for less than 1%? Who’s going to buy these things? I think that’s a big question and I think that has broader implications for the entire region and that Italy is really the poster boy initially because of the enormous amount of debt that they have and so little growth that they have to the point where their financing cost are now running above the rate of nominal GDP growth which means that their debt to GDP ratio begins to spiral upwards.
FRA: So do you see Italy changing their budget per the request by the EU Brussels?
Peter: I mean I’m sure, Yra has been saying this, there’s some agreement because Italy is really carrying the leverage here. There’s only so much the EU can do but I do think that everyone realizes it’s in their best interest and I think that the end of the day, it’ll be the EU that folds and gives into what Italy wants to do. I don’t think what Italy trying to accomplish, as I mentioned, is going to work but I think the EU has no choice but to at least give them a try. And you know the ultimate decision-maker a year of how this is gonna go is going to be the market. If the market sees that Italy can’t generate the 1.5% GDP growth that they’ve budgeted for next year, and it’s going to be less than that, then the bond markets going to speak up and you’re going to see a much higher rise in interest rates because even at a 3.5 or 3.6% 10 year yield relative to the fiscal situation in Italy, that’s still a historical low yield.
FRA: Yra, did you see that same rise in interest rates?
Yra: I think Peter is right about that but I’m looking more in the short term. What the effects are going to be? Europe needs an infrastructure program bad. Even the Germans seems to be admitting to that. So with that, there is going to be some deal. I truly believe that. If they think this through because if we look at this through those eyes you know of what George Soros and others have been recommending for several years, and not wrong but they’ve just dragged their feet for so long and that’s what they should have done to begin with. They could create a European almost like what Obama did with those infrastructure bonds, build an America Bond.
So you could do a build Europe, and I’m not saying that it’s gonna be responsible in any ways.
You could put together a package, lets say, 500 billion euros to build infrastructure projects all over Europe and use the capital key for those ratios and get this done. If you did it with the European wide bond, you would actually start doing what people have suggested as long as you see this project all the way through to its conclusion so your gonna need a European bond. So you could do this and get the Italians. From everything that I read, the Italians would buy into something like that because that’s what they’re really pushing for anyways. So if they did it across the European wide situation, I think that’s doable. I don’t know if they have the political strength to do it, and again I think Merkel has really dragged her feet here and Macron would have pursue this. He’s been dreaming about this. So I think you could see it and they can sell it in the short term. That way it eases the pressure on the Italians and everybody gets a little something. We’re probably (Inaudible 16:57) equity markets. Any sense of discussion is (inaudible 17:01) of equity markets that are looking for anything in the short term to give them some support. I think we’re gonna see something out of this group cause it’s bad. The election was 2 weeks ago and (inaudible 1750) the results were terrible. There’s an election this week in (inaudible 17:20) so everybody will be watching for this and they’re losing the middle ground so badly. I mean the worst part of the German election, a week and a half ago was that the Social Democrats, who have always been a mainstream, middle of the road policy they polled below the alternative for Germany. So there’s real problems going on and they need something and I think that’s what you’re gonna get out of this cause its a way to placate a lot of people in the short term. I agree. Peters right, who’s going to be buying these bonds? Let’s be serious, it’s a terrible flawed policy that is now coming home to roost. We’re not quite there yet. We still got 15 billion to be bought of fresh money every month so there’s still work in it. Peter’s a hundred percent right. It will come to no good. I just don’t know what the timeline is.
FRA: And what about the effect of any political movements in Europe? How could that affect all of this like the recent elections in Bavaria, trends towards populism, and the movement away from the Merkel government power?
Peter: I’ll leave that to you Yra.
Yra: The populists are trying to make this into a global phenomenon. There are a lot of people that feel like they’ve been disenfranchised by the what I refer to as the (inaudible 18:50) elite, people who sat there and made their policy or projected a sense of making policy with little regard for basically middle classes of the world. Let’s face it, globalization has benefited capital far more than labour put it into Marxist term.
I saw the interview that Alan Greenspan had in (inaudible 19:18) this weekend. It was interesting because he actually gave a Marx high grades for certain things that I thought from him was interesting, because I think that’s right.
And that’s what the world has had to answer was the shift and the reward for global capital vs. labour and its what we’ve dealt with which is why I believe that it’s a major flaw in the modelling of the Phillips curve but that’s a different discussion for another time.
So I think these are real and you have to find someway to placate those voters who really have been….and wages have not kept up and that’s by design.
You know the whole (inaudible 20:07) Germany was to free wages to sustain jobs in Germany rather than moving them to Eastern Europe.
NAFTA, when you go back and look at the beginning of NAFTA, it was meant for the North American region to take advantage of the Canadian natural resource base, combined with US capital and combined with Mexican wage rates. I mean it simplifies it but that’s a big part of it. So wages has been the real drag here and which is why we’ve seen the stock markets to get to levels that are…..we could argue historically where they’re at but they’ve been rewarded vs labour. It’s now starting to change and how everybody adjusts to it, I don’t know.
There’s a movement afoot but we shall see. But to diminish it and to pretend that it doesn’t exist is a major mistake which is why we got Donald Trump.
FRA: You’ve recently observed, Yra, a quote by last vice chairman of the Fed, Stanley Fischer, who said, “we the central Bankers cut interest rates severely to encourage growth and to support equity prices”. That adjustment hasn’t been fully made yet and then you point out a dilemma that Nehru vs Nehru. Can you elaborate?
Yra: Well, we come back to the wage thing. They all admit that they don’t understand why there is no wage inflation. I’m not saying that’s the answer but the Nehru model, I think is flawed I believe it’s flawed for many years and when you have the mobility of capital, and not the mobility of labour, you wind up with a lot of downward pressure on wages. When you’re given the alternative, Do I want my job or do I want a wage increase? Well Peter’s younger than I am Richard and I’m not sure how old you are but in the 60’s and 70’s, when I was a teenager starting to get in the work world, unions had a lot of power because we’re still in the post World War 2 situation capital wasn’t that mobile yet, breakdown Bretton Woods but when capital becomes so mobile that can go in search of lower wages and you have the transportation mechanism, you know ships, and containers today, we can move products today so you have the ability and therefore, labour comes up in the short end. And that’s what we see and so it’s not a surprise and now you have a billion Indians coming up in the global labour markets just like you had over a billion Chinese, of course those aren’t exact numbers. And to the global labour force, you had Eastern Europe unleashed into the global labour force. These have kept wages flat even if profits grew. So we built up this whole Q.E mechanism searching to push inflation higher but if its a phenomenon that has a lot to do with the global capacity, which is vast, the Chinese have a vast amounts of capacity labour force and it keeps prices down. But they built Q.E to push us out but if it’s not happening because the models are flawed, we’re in a serious dilemma. How we resolve it is going to be the big question.
FRA: And your thoughts Peter?
Peter: Well just to quantify a couple years ago the wage for the labour portion of the profit pie, that percent is low since World War 2 and that has now shifted and labour is gaining more leverage. And I do expect and I do think the wage data has been understated, especially over the last 6 months because most of the entrance into the labour force are young people and those with just a high-school degree. So when you measure the average hourly earnings for example, that’s most of the entrance, well that’s lower than the average. For those that are already working, I think wage pressures are pretty persistent and I think that’s being seen and in many different places because if companies are in search of labour and they cant find it, well they just have only a few choice in order to get it and raising wages is a key way of doing it.
And today’s Richmond Fed survey, not really saying anything we don’t already know but highlighting again, they said quote, “firms were unable to find workers with skills they needed as the skills index drops to an all time low”. That’s also a problem as well that there may be some workers out there but there’s a mismatch of between what’s demanded in the labour force and what’s supplied. I mean we know the demand side, there’s a record amount of job openings
But the inability to fill that is a problem and for those that can fill it, at least now has leverage and are gonna be paid a higher wage. And you throw in Amazon, which is raising their minimum wage which then forces and puts pressure on a lot of other companies to respond and sort of raises the lower end of the wage band.
So how that filters into consumer prices is obviously the main question. If productivity picks up, then it would not be a big deal but if companies find the need to pass it on in to higher prices, than you know then you got that wage price spiral that was similar to the 1970’s, not that this it’s gonna be repeated this time around but it gets to a broader picture here.
When you look at, and it combines with my comments on interest rates, the two biggest drivers of profit margin expansion in this recovery was
- Lower interest expense, which allowed companies to dramatically reduce that with low interest rates.
- Low wage costs.
And now both of those are turning upwards. So can revenue growth be quick enough to deal with that? Well likely not if 40% of S&P revenues are sourced overseas and see what’s going on overseas. So you have profit margins that in my opinion have peaked out or going to regress to what portion to the long-term mean we don’t know because technology is so dominant factors nowadays but I think that profit margins have peaked out in this cycle.
FRA: And finally what everybody is wondering about the last few weeks is where are global equity and bond markets heading and what events and risk factors should we be looking out for in that regard starting with Yra?
Yra: Well I think, Peter and I would agree on this. First, I think bond rates are going higher. I was not looking for curve inversion. I was interested in watching to see where they were gonna hold here so it’s interesting that 530 as we talk is breaking out above its 200 day moving average for those who are technically oriented for the first time since I think in 2 years. So I find that interesting.
You have Greenspan again and his interview (inaudible 18:23) but of course he raises the issues of entitlements and the pressure it puts on, well he thinks productivity and bond values. I mean Europe is an abomination and those bonds value, we know, some of the populous fever in especially in Northern Europe, you know, people forget that this populism is taking place in a very healthy environment. Yes it’s starting to slow a little bit but you measure this stuff by historical perspective, this is not when you get populism. You don’t get populism when unemployment rates are as low as they are. This is supposed to be the feel good era but yet something is broken.
This mechanism is broken economically and politically and you can’t divorce one from the other. You certainly can’t divorce politics from the economics. It’ll be healthy if bond rates would actually go up because I believe that interest rates are a very important signalling mechanism for the entire global financial system and its been broken for so long that its trying to reassert itself. Peter is the one is the who really first one to coin the phrase quantitative tightening. Its impact? Well we don’t know the impact was but I think we’re starting to see it.
It’s amazing to me, even the Fed admits it, that they don’t pay enough heed to the fact that they’re raising rates while the balance sheet is beginning to shrink. That’s a dual edged sword. Then of course you have the Europeans cutting back dramatically. And yet you are dealing with lax fiscal conditions especially in the United States, you have the deficits growing regardless of what Larry Kudlow has to say. I’m looking for bond prices especially to be moving higher and we’ll get a good picture in Europe after January 1st because then the ECB will be replenishing rather than increasing the balance sheet.
While there won’t be quantitative tightening, there won’t be the act of participation by the ECB and the Japanese we don’t know what they’re doing. It’s too hard to tell. They own so much of the market so we’re trying to get a sense of it.
The Chinese, the book is still out. Everybody who’s talking about the Chinese…I think what they failed to understand is that China borrowed a lot going forward when they began a lot of stimulus in 2015 and 2016 so I think the stock market in China is more a story about, hey they borrowed a lot from the future and the future is here. They got some issues about how to deal with what they borrowed from the future. So it doesn’t surprise me that the Chinese capital markets are as weak as they are.
FRA: And finally your thoughts up here on the transfer equity and bond markets?
Peter: I definitely agree with Yra on the interest rates and its a variety of reasons why rates are rising and I expect them to continue and it’s very easy for people to take out their historical playbook and say, okay, inflation and growth are the two drivers and whatever that plays out that’s where rates will go but unfortunately, we have to throw in the normalization and reversals of the central bank balance sheets on top of Fed rate hikes. We have to deal with foreign appetite for US treasuries which has been dramatically reduced partly due to the cost of the hedging but certainly also related to the dramatic reduction in reserve buildups that we’ve seen in China. Then you can throw in some other reasons that I think combine for a rising rates which will continue and I think the big question going at the 2019 is how do European bond yields respond to the ECB not adding more to their balance sheet? I probably said this on your show before but just to quantify the extent which ECB was buying European bonds at the peak when they were printing 80 billion Euros a month, they were buying 7 times net issuance. 7 times! An extraordinary ratio! For the Fed was never buying really more than 25% of Net Insurance.
That all changes as of January 1st, granted they’ll be reinvesting but on that basis, they will not be expanding their balance sheets and again who’s going to buy the stuff? So if you get a rise in German Bund yields, you have to believe that you’re going to see a coincident rise in US treasury. With respect to US stocks, it’s been a party for 10 years and what typically ends the party is Fed tightening and I think it would be hard to think that this is not going to happen again. Valuations are very expensive in the US. If you look at metrics other than P multiple(inaudible 33:55-33:56), If you look at variety of other (inaudible 33:58) prices cell ratios and are very expensive. Also, the rising rates are having an economic impact which has potential hurting earnings so I’m pretty defensive when it comes to US equities.
I am becoming more intrigued with the values being created overseas market that have got hammered. You look at China for example and China’s gonna have a couple of years of serious challenges no question but the markets gone pretty cheap and its down almost 60% from its highs in 2007. And even Japan, the Nikkei is down almost 50% where it was from 1989. I know that it’s been the case for a long time now but your looking for value so it’s unlikely going to find much on the US but you’re the potential finding a lot of it overseas.
And then lastly, I remain bullish for gold and silver because I think it’s respite in this crazy environment. The dollar has been strong against some emerging market currencies particularly the Yuan and then the troubled ones like the lira and the Argentinian peso and certainly the British pound related the Brexit but the dollar index over the past two years has done nothing. It’s gone up and gone down. It’s pretty much at the same level it’s been. I think that it points to major headwinds for the dollar and then maybe it’s the twin deficits that people are beginning to focus on.
FRA: Well great insight as always gentlemen. How can our listeners…
Yra: Richard can we come back to one thing?
FRA: Oh yeah sure.
Yra: In regards to China? You know unfortunately the airwaves get filled with ludicrous assessments, I mean it’s really ludicrous. I had to listen to some of these tirades yesterday what the United States, with Trump and Navarro especially, were trying to do is force regime change in China. That’s such a ridiculous concept. If that was the case, then you’d be verge of not a cold war but a hot war because if you think the Chinese would cave to US pressure for regime change… I had to listen it to 10 mins! Its ludicrous! People need to be, this is just a warning, be careful of about what you hear and what you listen to. There are a lot of people out there with ridiculous narratives. Ridiculous narratives! That one was mind boggling because that has not happened. That shows no understanding of how China works of the politics of China. China, we want to think in terms of a western style democratic capitalists model. It’s just not appropriate. You may wish that for the end result for China and they may get there but the present situation is far so from that and any discussion of what the Trump administration is really pushing for and what they think they are able to get because why would you pursue a ridiculous policy if you had no chance of ever attaining it? Let’s just be cautious. You need a filter, that’s what I’m advising. You need a filter and you have to understand what the entire global perspective is rather than somebody who may be selling something so be very careful!
FRA: Great and we’ll end it on those words of wisdom. Thank you very much gentlemen! How can our listeners learn more about your work? Yra?
Yra: By blog at notesfromunderground. It’s a pleasure and of course doing podcasts like these, it makes for important discussion. I advise you, you need to read! You need to subscribe to people like Peter’s work because you can’t do this alone because this is an endeavour. To be a trader and investor takes a lot of effort. It takes a lot of discourse between people. I remember when I was a floor trader, one of the great things on being on the floor was you had opportunities to discuss things with people. Now that we get more isolated, anatomized by computers, we lose that ability. So anytime you can involve yourself in any of these discussions and to read as much as possible. There’s quality work out there. Peter’s work is quality. Avail yourselves of these opportunities and listen to these podcasts.
FRA: Yes exactly and Peter?
Peter: Thank you Yra for that. You can read my daily work by subscribing to boockreport.com. If you’re interested in assistance with wealth management, you can reach out to me at bleakley.com
FRA: Thank you very much gentlemen! We’ll do it again.
 10/01/2018 - FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
10/01/2018 - FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
By: Tenzin Lekphell
FRA: Hi welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight! … Today we have Yra Harris and Peter Boochwar. Yra’s a hedge fund manager, global trader in foreign currencies, bonds, commodities and equities for over 40 years. He was also a CME director from 1997 to 2003, and Peter is Chief investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and advisory. He has a newsletter product called boockreport.com which has great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentleman!
Peter: Hey Rich. Hey Yra.
Yra: Hi Rich. Hi Peter.
FRA: Just thought we’d begin. Today is Wednesday September 26th around noon eastern time and we have the Fed statements coming up shortly, even though this program will be published slightly after, but just wondering your thoughts on what could be said that this afternoon? Yra?
Yra: Well I think we’re all baked in at 25 basis points. I just put something out, a little note on the blog, I don’t know what Peter will say to it. I think the one of more interesting aspect is people are looking to remove the line that policy is not (inaudible 1:23-1:26) anymore. I’m not sure about that but I will be watching the way this vote goes because I want to see, there’s some discussion out there, I don’t know who it is out there of course they never put name’s to it, that there are some who are looking for 50 basis points. I know Peter and I have talked about this in meetings previous. We would of liked to see 50 basis points. I don’t think this one is doable because of the closeness to the November elections but, I want to see the Brainard and Williams will because of their recent hawkishness. I don’t know if Charlie Evans is a voting member but he’s been hawkish of lately. So I want to see some of these Hawks vote in favour of 50 basis points increase. That’d be the most interesting thing to me because that would put up much more hawkish tone to the Fed regardless and we’ll wait for the press conference. Outside of that, I’m not looking for anything else.
Fra: And Peter?
Peter: Evan’s actually is an alternate number so he won’t be voting but we will have some new voters. (Inaudible 2:33) will be voting for the first time and then some relatively new members. (inaudible 2:38), I’ll be voting, and (inaudible 2:41-2:42). It’s a newer complexion and I think that because of it, they’ll be raising 25 basis points and leaning towards a December hike as the market is pricing that in. The Market, or at least the Fad, I think follow up on what Yra said on Brainerd and Williams, they want to keep on hiking and you might as well just do it in December because next year you’re wide open in terms of meetings because every meeting has a press conference. Where is before, the next press conference meeting would have been March and if they did not hike in December, they would have to wait till March.
Now there’s a lot more flexibility next year and then went to hike. You might as well move closer to where they want to go, ultimately that’s 3% or more, and get there sooner rather than later because I think a lot of these Fed people they do speak to a lot of contacts and everyone is telling them wages, wages, wages are going to higher and you can’t find any any workers and these academics still focus on the Phillips curve. They still believe that inflation will likely be triggered by that and then you throw in the tariffs. Hiking today they’re only going to get 2 to 2 ¼ and which tells me that maybe they will keep in that wording that being accommodative because to think that 2 to 2 ¼ is not accommodate is quite comical and Yra can probably speak to this better than I can because he’s seen a long-term level of interest rates much higher and it’s laughable that 2 to 2 ¼ would not be considered accommodative at Fed funds level.
I don’t think Powell wants to be that exciting with the statement. I think the statement will be not much different than the prior one so we’re going to have to wait till the press conference in order to gauge some more details in which way he is leaning but again, whether he raises in December, or January, whatever, they want to get to 3 % plus fed funds rate all else equal and based on what they’re saying right now.
FRA: Any thoughts on that Yra?
Yra: I think that’s absolutely right. Powell and, I think the new voice of (inaudible 5:03), well we don’t have Nelly Ling, that’s her name right?
Peter: Yeah.
Yra: Who seemed to be at least beyond academics and aware of the financial ramifications that emanate from the Fed policy and long held Fed policy, which I find interesting. I think Vince Reinhart was on with (inaudible 5:36) today and I thought that was an interesting discussion because I think Vince Reinhart made a good point which is that these later appointments by Trump, who been pretty responsible Fed appointments, which I’m very surprised, because I wouldn’t put them as easy money people whatsoever. While he’s spoken about easy money, who ever is advising him, who’s ever council he’s taking on, maybe is directly from Powell, these have been responsible Fed appointees and I think these are good thing cause as Peter discussed. We need to get away from the academics. Not that academics don’t have a place, but they dominated the Fed. Greenspan certainly relied on (inaudible 6:19) although he had a gut feeling. Powell said in his (inaudible 6:23) hall of speech he applauded that Greenspan had, what I think Powell would say he has which is, some risk management tools so he’s not knee jerk. Although I would certainly argue that Greenspan, with the start of every meeting raising a quarter like he did at a certain period, really set the Fed at a bad course and the world because every other Central Bank has followed that same policy. For the life of me, I really don’t get it. Your willing to cut 1% which will on only raise ¼ point increments.
Peter: Measure and Pace right? That’s what Greenspan said every meeting in the mid 2000s. Measure and Pace.
Yra: Which I think it’s terrible because you’re not listening to the markets. (inaudible 7:14-7:16) I think a set course is a terrible public (Inaudible 7:18). You can have mandated goals but why should you have set course to reach it. I know that Peter agrees to that. They should have raised half a point long ago. This quarter point is nonsense then they could have stepped back and let the market digest. I’m gonna agree with Peter. It’s a long answer to a short question.
Peter: Here we are in the 10th year of this expansion and today’s hike is only going to bring real rates to zero. For them to call zero real rate not accommodative, if they take that wording out, is laughable. So I’d lean to them leaving it in but we’ll see.
FRA: Let’s go to a macro view on a financial markets. Peter you’ve recently mentioned or observed on the disconnect that you see between the US markets and the Emerging Markets. Can you elaborate on that? Like what and what is behind that?
Peter: Yeah it’s been pretty glaring. The out performance of the U.S versus everybody else. In fact everybody else is down on the year and we know that S&P 500, in particular, has had a great year, even though 40% of S&P 500 revenues are sourced overseas.
Certainly worries about slowing growth in Europe, certainly in China, and by default the rest of Asia and that’s being reflected in their equity markets and we know same problems with emerging markets. I think to believe that the US is immune to that is silly. But right now at least, US growth is well outperforming most other areas. Earnings growth in the first half of the year are very good, still should be fine in Q3, but I do think you’re going to start to see some issues with earnings related to tariffs, related to higher labour costs, that is the largest input for companies and I don’t see how much longer that discrepancy can last. Either overseas is going to catch up or on the upside, we’re going to catch up to them to some extent on the downside. The differential is pretty glaring.
FRA: Right now, has it been due to international capital flows going into the US from emerging market issues, concerns, challenges, and this global slow down looking to the U.S as a safe haven also considering the U.S dollar getting stronger?
Peter: That can be part of it but I think it’s U.S investors are dominated by machines. They don’t respond to speculation about the possibility of a slowdown driven by what’s going on overseas. They only do it when they actually see evidence of it. Whether that’s in earning season over the next couple weeks, if we begin to see some signs of it, or it’s actually in the economic data. So I think that’s why the US market has sort of shrugged off not only the growth story that’s changing overseas but the rates over here where they continue to rise and we have a over levered global economy. We have a very highly levered, over levered U.S corporate balance sheet outside of (inaudible 10:51) and rising rates is usually not a good set up with that. So I think that there’s this belief that somehow the Fed’s can engineer a soft landing. Historically that’s rarely the case. But until they begin to see evidence of weaker data here or (inaudible 11:11) in earnings, they’re not going to respond. So my point is don’t look at the US equity market as a discounting mechanism. I think it’s mostly reactive instead.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra on this?
Yra: I’m going to take a little bit different tactic here. I mean I agree with him but I see things that are going on. The other day, (inaudible 11:35) comments were a 180 degree from his press conference. (inaudible 11:45) sees vigorous pickup in underlying inflation. (inaudible 11:48-11:50) but the dollar didn’t sell off. Thinking that the European are gonna be, as (inaudible 11:54-11:55) says, vigorous. Well this is totally (inaudible 12:00) of what we heard him at the press conference. It’s really raising my (inaudible 12:07) there’s something going on here.
Are the Europeans now all of a sudden are getting a sense that Trump, that if they don’t do something to raise the level of the Euro, that they’re gonna feel the sting of Trump’s tweet or whatever. That really boggled my mind. I just don’t see it. Everything has been the other way from all the other conversation. Then of course (inaudible 12:37-12:39) walked it back even though Watney from Austria was still adamant (inaudible 12:46) by pulling back.
Yesterday, there was a tweet out by, I don’t know who she is, Dr.Julia (inaudible 12:57) that said, “Hawkish Yellen, Unemployment rate is half the full point below the natural rate (inaudible 13:04-13:05) stabilize it and they need to nudge it higher”. It’s almost a hawkish comment but yet 2 weeks ago on the 14th of September, we had Yellen speaking at bookings in that group meeting. In her speech, it’s been lower for longer, lower for longer, lower for longer!
Peter: (inaudible 13:33-13:34) that don’t work and keep on doing things that doesn’t work is what she’s saying.
Yra: Its sending mixed messages. That’s a great point and it’s all making it to the headlines. I think it’s really confusing for markets even though Yellen carries no weight whatsoever. None. But the way people throws these things out, I don’t see (inaudible 14:02-14:03) that Peter’s talking about. Where’s Europe going? Europe’s going nowhere. As I’ve maintained and I know we’ve discussed this for more than a few years already. (inaudible 14:13) locked himself in this terrible trap here and it gets (inaudible 14:16) more and more. I know Peter talked about it this morning with the Italians and what happens and now the French are really caught in this similar trap because they need Macron’s poll ratings are dropping dramatically and even as Peter pointed out, the (inaudible 14:32) strongest of the majors European stock markets. His poll numbers are dropping and he gonna need to placate some on the left with greater spending but their not going to be able to do it and Germany is really in dire (inaudible 14:49) politically. Merkel is having the legs cut under her all over the place and October brings the election in Bavaria in which the S.C.U (inaudible 15:00) is under dire threat and it’ll be interesting to see if they even hold to be the most popular party because that would really bring pressure on Merkel in many other ways.
Europe is a difficult (inaudible 15:14) and I don’t see them, yes they’re going to end QE at the end of December but even (inaudible 15:20) said, ending QE their not shrinking the balance sheet. He was explicit about that and that made the capital key such a dangerous situation for him because he’s got to abide by definition and buy 18% of the assets ECP buys which are German Bunds or German instruments. Well with German surpluses growing, I don’t know where their going to find that much to buy without pushing German rates, even on the long end, further down. So there’s here’s all these things confronting us.
FRA: Could that issue, in terms of the amount of German debt being used as diminishing, prompt the emergence of a Eurobond for the ECP?
Yra: Well there are certainly those who won’t (inaudible 16:07) cause I think that’s what the end game is.
Peter: Germans (inaudible 16:12) try to push that into the future as long as they can.
Yra: As far as they can cause that would mean that the German would have to underwrite the whole debt load. I don’t see any unless you had a denaturalization meaning sell off a lot of publicly held companies, meaning, government held companies in order to be able to buy back some of the bonds with real assets rather than ECP money. It will take a major political upheaval in Germany from those who are (inaudible 16:51) of that because right now the rising forces in Germany, the rising political voices are not in favour of that. In fact, I would say that one of the staunchest platform policies of the (inaudible 17:06) for Germany is less German involvement into the guarantee of the European financial system. The winds are blowing in the opposite direction and Peter exactly is right, they’ll delay that as long as possible. Macron….when he was a rising star couldn’t get her to sign on to a unified financial system, which is the risk that would be absorbed by the European stability mechanism, with the German’s guarantee in that cause the Germans saw through that and she wouldn’t even sign on that when Macron was maybe somebody (inaudible 1742). Right now, he’s a weakened force as she is and it’s the Italians, in my mind, who are holding the cards here.
FRA: So as we go towards the end of the year, could the German-French yield spreads on bonds likely increase as the ECP buys less assets going in to the end of the year? Your thoughts? Peter?
Peter: That’s a good question. I actually just think they’re both going higher, whether the spread widens or not, I’m not sure. As Yra said they both now have political issues. I can’t fully understand why the Macron’s poll numbers are dropping as fast as they are. Maybe it’s the French just don’t like change that he’s trying to bring, but I’m surprised by that. I think either way, you’re going to see a rise in yields in both countries and I think people don’t understand how much of an influence the ECP was and still is barely in terms of their buying in those markets in while they’re continue to reinvest proceed.
They were buying 7 times net issuance of European bonds. The Fed QE at its peak was 25% of net issuance of treasury (inaudible 19:03-19:04). That’s how dominant the ECP was. While we all know what they’re going to do, they told us what they’re going to do, I still think there is this level of nonchalant as somehow European bond yields can stay around these current levels even with the reinvestment. And that’s what I’m most worried about is a rate shock in Europe that could have a ripple effects.
We already seen the Bank of Japan pulling back and you’ve seen a jump in longer (inaudible 19:32) yields there and you’ve seen the 10 year yield creeping closer to 15 basis points as Bank of Japan is more tolerant of that. You’ve seen the US 10-year just a few basis points from breaking out to multi year highs. If you seen these rise in yields, its not for all good reasons, it’s not that the economy is great and the markets are just doing it, it’s that you have this Gorilla in this room thats walking out and buying less and a combination with other things including inflation and others. I think people are way to nonchalant with this move up in the interest rates.
FRA: And Yra, what do you see happening as we go towards the (inaudible 20:09-20:10)?
Yra: I think that’s right. (Inaudible 20:11-20:12) the reason I dig through the plumbing… if you look, German issuance is diminished because they’re running surpluses. France has grown over these last years. The real canary in the coal mine is that their running these budget deficits, meaning France and Italy, with these ultra low interest rates. Lets not minimize that..
Peter: (inaudible 20:49-20:51) by 2%.
Yra: These deficits haven’t shrunk whatsoever and if interest rates start to rise, as Peter and I believe that they’re going to do, it’s gonna put even greater pressure on these deficits. I don’t know if they will get better growth. I applaud Macron. I think he’s trying to turn the tables on what has been a (inaudible 20:19) economic policy from Halland, and even Sarkozy. They did some stupid things. He’s trying to undo them but the deficit is still growing. Its like with Greece. You hear everybody talk about how Greece turned around. Well the Greece debt to GDP ratio, even with all this austerity, it’s still bigger then when it started down that path of austerity and thats with interest rates dropping dramatically. And that’s where the real risk here lies. And from the (inaudible 21:53) aspect of it, German credits are far better than the rest of the credits. Maybe the Dutch and Austrian certainly without the ECP would be able to stand on their own. But the others, (inaudible 22:06-22:08), and that includes France because France is not without its problems. And if Macron fails, the issues in france are really gonna get worse as Peter points out. Politically they don’t like this type of change. The unions in France still have a lot of power. Macron would like to diminish that power but they still have a lot of power. That’s the reason why I like to be long German and short French because right now the spread on 10 years is about 32 basis points which is about mid range over last 3 or 4 years. But based on the shrinking amount of German assets and the fact that German assets are needed for REPO financing, their high quality liquid assets, that will put demand in there regardless. Unless (inaudible 23:00) openly breaks with the capital key, which he has to be very careful because there are those in Germany that will return back to the German Constitutional court and say that this is illegal because your financing individual countries and in violation of the entire edifice of the Central Banks and what their supposed to do. (inaudible 23: 27) there are things waiting out there.
Peter: It will be a real disappointment if Macron is gone at some point. He was the right guy for that job at the right time for France. It’s amazing people don’t appreciate it.
FRA: Given these thoughts on Europe and what we mentioned earlier in the US, could we see another round of more easing by central banks globally? If we go to China and look at the currency there, if the Yuan weakens and we get global disinflation, could that cause more easing by Central Banks globally? Peter?
Peter: It’s a good question. I don’t think the Chinese want to go down the route of seeing a dramatically weaker currency. They are trying to shift their economy from a manufacturer infrastructure, (inaudible 24:23-24:26) investment type economy to more services and more consumption. You don’t want a weaker currency, if that’s the transition you’re trying to make. You don’t want to damage the purchasing power of consumers if your trying to improve consumer spending. I think they are more interested in having a stable currency not a dramatically weaker one. I’m sure the weakness we’ve seen will be tolerant of because it’s relatively modest and it can help cushion the impact of the tariffs but I wouldn’t look for major decline in the currency.
I think the currency that trades (inaudible 25:07-25:08) is the U.S dollar and people should be asking what’s going on with US dollar considering the out performance economically, the Central Bank that is far ahead of the curb relative to others, and why outside of emerging markets where the dollar has strengthened, why against the Euro or the Yen or some of the others has it not traded well? I’m putting aside the pounds because that’s obviously very Brexit related. That’s where I think people should be asking is What’s going on with the dollar and less so with the Yuan?
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I think that’s dead right on target. I know Peter that’s the Michael Pettis argument which is, “hey, if your trying to build your domestic economy, and China’s certainly is, if I look at the copper market, the copper market is telling me that China’s going to embark on another round of massive infrastructure project whether it’s in the road initiative or just in China itself but that’s what the market is sensing here. You don’t want a weaker currency. Your trying to ramp up domestic spending. You’d like to have a stronger currency because then you can buy cheaper imports so I’m hundred percent agreement and I agree with Peter with the dollar.
The dollar is interesting here because the cost of carry is quite expensive. If we use overnight money in Europe, let’s say German money, it’s 250 basis points going higher. If we’re using 2 year differential, it’s well over 3 percent because German 2 years are about negative 50 and US is of course 2.8. I don’t ever remember, I wont say ever, it’s been certainly over 3 decades that we’ve seen a spread that wide and 2 years or less. So these are things that should be (inaudible 27:24-27:25) the strengthening dollars as a lot of people are positioning for. Peter, from 107,108, but that was based on the Trump Whitehouse as much as anything. Bob White Heiser, who is the power here, is not afraid to promote a weaker currency. I think the markets are starting to accept to (inaudible 27:52) that in but they really haven’t yet. That may be one of the tools they utilized.
FRA: What about Brazil? Are they intentionally driving their currency lower to help their agricultural exports and hurting U.S grain exports?
Peter: They don’t need the help. It’s a business to them.
Yra: They don’t need the help. Its bad politics. Their in a great position now because the Chinese (inaudible 28:31) knows the US for the moment because their agricultural exports from Brazil are so cheap. Even if though they had a (inaudible 28:42) crop because they’re so cheap, it will be interesting to see how much plant the Brazilian farmer grew this year. Even international prices are lower, priced in terms of Real, which the farmers ultimately get paid in as they take their dollars they receive in the international market and convert to domestic currency. Their not suffering whatsoever. The United States farmers are suffering under Tariffs as well as having to compete against the weakened Brazilian Real. They don’t need any help. I think they believe the currency is to weak relative to other policy aims that they have.
FRA: And the finally moving over to Japan. How will the Bank of Japan be able to extricate itself from five years of QQE, qualitative and quantitative easing, since they’ve accumulated so much Japanese debt and equities? Your thoughts Yra?
Yra: Well, I don’t know if they know how to extricate themselves. They’ve just been muddling along here and I mean muddling. They preceded down this path for way too long. Supposedly we heard last week that Abe was backing away from the inflation targets after his new found political strength is (inaudible 30:07-30:09) although he’s got his plate full but I don’t how they get out of here. They’re not going to do it with a weaker currency. We listen to Trump, the sense that he’s looking to throw tariffs on to the Japanese because they run to large of surpluses with the US, the Japanese have to be very careful here and the Europeans can’t be too happy because the Euro against the Yen has been rallying dramatically. The European auto industry is (inaudible 30:51) head wind of a weaker Yen and US tariffs and some really bad fall for Brexit, which not enough people talk about it but the European auto industry could really get hit. But I don’t know what the Japanese are going to do here. They follow this Bernanke down this rabbit hole for way to long and i don’t know what they do here.
FRA: Peter?
Peter: Yeah it’s a great point. I don’t know what they’re going to do. I think that their acknowledging the squeeze that they’re in by allowing a whole 10 basis points extra of a yield grab (inaudible 31:36-31:37) can get in Japan, which is quite amazing from 10 to 20 basis points. They are certainly slowing the rate of purchases. I think they’ve basically cut QE in half. I think they’ve suddenly realized that they are a dominant player in the ETF market and are a top 10 holder in about 40% of Japanese Nikkei companies. I think they got their fingers crossed on generating some higher inflation so they can further get out of what they’ve done but I don’t see how they can ever get out of what they’ve done. I think they’ll just continue to try to lessens their influence and see what happens but Kuroda….talk about overstaying one’s welcome.
Yra: And to add to that, I think one of their plans was, at some point, that they’ll be able to start buying foreign bonds if they needed to but now that they run in Trump, there is no way that the (inaudible 32:39) or even some of those pension funds have to be very careful. The government pension investment fund. They can’t just willy nilly because that will move to weaken the end and they have to be very careful here.
Peter: That’ll be dangerous.
FRA: On that note, we’ll end it there. How can our listeners learn more about your work? Peter?
Peter: They can search it in wealth management. They can go to bleakley.com and reach out to me. If they want to see my daily (inaudible 33:10-33:11), they can subscribe at boockreport.com.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: My blog post, notes from underground, and you can go to Yraharris.com. It’ll come up notesfromunderground you can get access to it and join the conversation that takes place on regular basis about many of these same issues. It’s just a discussion on what’s going on in the world and hopefully you can find your way to profitable investment from them.
FRA: Great insight as always. Thank you very much gentlemen! We’ll do it again.
 10/01/2018 - FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
10/01/2018 - FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
FRA Roundtable Insight: Yra and Peter Podcast
By: Tenzin Lekphell
FRA: Hi welcome to FRA’s Roundtable Insight! … Today we have Yra Harris and Peter Boochwar. Yra’s a hedge fund manager, global trader in foreign currencies, bonds, commodities and equities for over 40 years. He was also a CME director from 1997 to 2003, and Peter is Chief investment Officer for the Bleakley Financial Group and advisory. He has a newsletter product called boockreport.com which has great macroeconomic insight and perspective with lots of updates on economic indicators. Welcome gentleman!
Peter: Hey Rich. Hey Yra.
Yra: Hi Rich. Hi Peter.
FRA: Just thought we’d begin. Today is Wednesday September 26th around noon eastern time and we have the Fed statements coming up shortly, even though this program will be published slightly after, but just wondering your thoughts on what could be said that this afternoon? Yra?
Yra: Well I think we’re all baked in at 25 basis points. I just put something out, a little note on the blog, I don’t know what Peter will say to it. I think the one of more interesting aspect is people are looking to remove the line that policy is not (inaudible 1:23-1:26) anymore. I’m not sure about that but I will be watching the way this vote goes because I want to see, there’s some discussion out there, I don’t know who it is out there of course they never put name’s to it, that there are some who are looking for 50 basis points. I know Peter and I have talked about this in meetings previous. We would of liked to see 50 basis points. I don’t think this one is doable because of the closeness to the November elections but, I want to see the Brainard and Williams will because of their recent hawkishness. I don’t know if Charlie Evans is a voting member but he’s been hawkish of lately. So I want to see some of these Hawks vote in favour of 50 basis points increase. That’d be the most interesting thing to me because that would put up much more hawkish tone to the Fed regardless and we’ll wait for the press conference. Outside of that, I’m not looking for anything else.
Fra: And Peter?
Peter: Evan’s actually is an alternate number so he won’t be voting but we will have some new voters. (Inaudible 2:33) will be voting for the first time and then some relatively new members. (inaudible 2:38), I’ll be voting, and (inaudible 2:41-2:42). It’s a newer complexion and I think that because of it, they’ll be raising 25 basis points and leaning towards a December hike as the market is pricing that in. The Market, or at least the Fad, I think follow up on what Yra said on Brainerd and Williams, they want to keep on hiking and you might as well just do it in December because next year you’re wide open in terms of meetings because every meeting has a press conference. Where is before, the next press conference meeting would have been March and if they did not hike in December, they would have to wait till March.
Now there’s a lot more flexibility next year and then went to hike. You might as well move closer to where they want to go, ultimately that’s 3% or more, and get there sooner rather than later because I think a lot of these Fed people they do speak to a lot of contacts and everyone is telling them wages, wages, wages are going to higher and you can’t find any any workers and these academics still focus on the Phillips curve. They still believe that inflation will likely be triggered by that and then you throw in the tariffs. Hiking today they’re only going to get 2 to 2 ¼ and which tells me that maybe they will keep in that wording that being accommodative because to think that 2 to 2 ¼ is not accommodate is quite comical and Yra can probably speak to this better than I can because he’s seen a long-term level of interest rates much higher and it’s laughable that 2 to 2 ¼ would not be considered accommodative at Fed funds level.
I don’t think Powell wants to be that exciting with the statement. I think the statement will be not much different than the prior one so we’re going to have to wait till the press conference in order to gauge some more details in which way he is leaning but again, whether he raises in December, or January, whatever, they want to get to 3 % plus fed funds rate all else equal and based on what they’re saying right now.
FRA: Any thoughts on that Yra?
Yra: I think that’s absolutely right. Powell and, I think the new voice of (inaudible 5:03), well we don’t have Nelly Ling, that’s her name right?
Peter: Yeah.
Yra: Who seemed to be at least beyond academics and aware of the financial ramifications that emanate from the Fed policy and long held Fed policy, which I find interesting. I think Vince Reinhart was on with (inaudible 5:36) today and I thought that was an interesting discussion because I think Vince Reinhart made a good point which is that these later appointments by Trump, who been pretty responsible Fed appointments, which I’m very surprised, because I wouldn’t put them as easy money people whatsoever. While he’s spoken about easy money, who ever is advising him, who’s ever council he’s taking on, maybe is directly from Powell, these have been responsible Fed appointees and I think these are good thing cause as Peter discussed. We need to get away from the academics. Not that academics don’t have a place, but they dominated the Fed. Greenspan certainly relied on (inaudible 6:19) although he had a gut feeling. Powell said in his (inaudible 6:23) hall of speech he applauded that Greenspan had, what I think Powell would say he has which is, some risk management tools so he’s not knee jerk. Although I would certainly argue that Greenspan, with the start of every meeting raising a quarter like he did at a certain period, really set the Fed at a bad course and the world because every other Central Bank has followed that same policy. For the life of me, I really don’t get it. Your willing to cut 1% which will on only raise ¼ point increments.
Peter: Measure and Pace right? That’s what Greenspan said every meeting in the mid 2000s. Measure and Pace.
Yra: Which I think it’s terrible because you’re not listening to the markets. (inaudible 7:14-7:16) I think a set course is a terrible public (Inaudible 7:18). You can have mandated goals but why should you have set course to reach it. I know that Peter agrees to that. They should have raised half a point long ago. This quarter point is nonsense then they could have stepped back and let the market digest. I’m gonna agree with Peter. It’s a long answer to a short question.
Peter: Here we are in the 10th year of this expansion and today’s hike is only going to bring real rates to zero. For them to call zero real rate not accommodative, if they take that wording out, is laughable. So I’d lean to them leaving it in but we’ll see.
FRA: Let’s go to a macro view on a financial markets. Peter you’ve recently mentioned or observed on the disconnect that you see between the US markets and the Emerging Markets. Can you elaborate on that? Like what and what is behind that?
Peter: Yeah it’s been pretty glaring. The out performance of the U.S versus everybody else. In fact everybody else is down on the year and we know that S&P 500, in particular, has had a great year, even though 40% of S&P 500 revenues are sourced overseas.
Certainly worries about slowing growth in Europe, certainly in China, and by default the rest of Asia and that’s being reflected in their equity markets and we know same problems with emerging markets. I think to believe that the US is immune to that is silly. But right now at least, US growth is well outperforming most other areas. Earnings growth in the first half of the year are very good, still should be fine in Q3, but I do think you’re going to start to see some issues with earnings related to tariffs, related to higher labour costs, that is the largest input for companies and I don’t see how much longer that discrepancy can last. Either overseas is going to catch up or on the upside, we’re going to catch up to them to some extent on the downside. The differential is pretty glaring.
FRA: Right now, has it been due to international capital flows going into the US from emerging market issues, concerns, challenges, and this global slow down looking to the U.S as a safe haven also considering the U.S dollar getting stronger?
Peter: That can be part of it but I think it’s U.S investors are dominated by machines. They don’t respond to speculation about the possibility of a slowdown driven by what’s going on overseas. They only do it when they actually see evidence of it. Whether that’s in earning season over the next couple weeks, if we begin to see some signs of it, or it’s actually in the economic data. So I think that’s why the US market has sort of shrugged off not only the growth story that’s changing overseas but the rates over here where they continue to rise and we have a over levered global economy. We have a very highly levered, over levered U.S corporate balance sheet outside of (inaudible 10:51) and rising rates is usually not a good set up with that. So I think that there’s this belief that somehow the Fed’s can engineer a soft landing. Historically that’s rarely the case. But until they begin to see evidence of weaker data here or (inaudible 11:11) in earnings, they’re not going to respond. So my point is don’t look at the US equity market as a discounting mechanism. I think it’s mostly reactive instead.
FRA: And your thoughts Yra on this?
Yra: I’m going to take a little bit different tactic here. I mean I agree with him but I see things that are going on. The other day, (inaudible 11:35) comments were a 180 degree from his press conference. (inaudible 11:45) sees vigorous pickup in underlying inflation. (inaudible 11:48-11:50) but the dollar didn’t sell off. Thinking that the European are gonna be, as (inaudible 11:54-11:55) says, vigorous. Well this is totally (inaudible 12:00) of what we heard him at the press conference. It’s really raising my (inaudible 12:07) there’s something going on here.
Are the Europeans now all of a sudden are getting a sense that Trump, that if they don’t do something to raise the level of the Euro, that they’re gonna feel the sting of Trump’s tweet or whatever. That really boggled my mind. I just don’t see it. Everything has been the other way from all the other conversation. Then of course (inaudible 12:37-12:39) walked it back even though Watney from Austria was still adamant (inaudible 12:46) by pulling back.
Yesterday, there was a tweet out by, I don’t know who she is, Dr.Julia (inaudible 12:57) that said, “Hawkish Yellen, Unemployment rate is half the full point below the natural rate (inaudible 13:04-13:05) stabilize it and they need to nudge it higher”. It’s almost a hawkish comment but yet 2 weeks ago on the 14th of September, we had Yellen speaking at bookings in that group meeting. In her speech, it’s been lower for longer, lower for longer, lower for longer!
Peter: (inaudible 13:33-13:34) that don’t work and keep on doing things that doesn’t work is what she’s saying.
Yra: Its sending mixed messages. That’s a great point and it’s all making it to the headlines. I think it’s really confusing for markets even though Yellen carries no weight whatsoever. None. But the way people throws these things out, I don’t see (inaudible 14:02-14:03) that Peter’s talking about. Where’s Europe going? Europe’s going nowhere. As I’ve maintained and I know we’ve discussed this for more than a few years already. (inaudible 14:13) locked himself in this terrible trap here and it gets (inaudible 14:16) more and more. I know Peter talked about it this morning with the Italians and what happens and now the French are really caught in this similar trap because they need Macron’s poll ratings are dropping dramatically and even as Peter pointed out, the (inaudible 14:32) strongest of the majors European stock markets. His poll numbers are dropping and he gonna need to placate some on the left with greater spending but their not going to be able to do it and Germany is really in dire (inaudible 14:49) politically. Merkel is having the legs cut under her all over the place and October brings the election in Bavaria in which the S.C.U (inaudible 15:00) is under dire threat and it’ll be interesting to see if they even hold to be the most popular party because that would really bring pressure on Merkel in many other ways.
Europe is a difficult (inaudible 15:14) and I don’t see them, yes they’re going to end QE at the end of December but even (inaudible 15:20) said, ending QE their not shrinking the balance sheet. He was explicit about that and that made the capital key such a dangerous situation for him because he’s got to abide by definition and buy 18% of the assets ECP buys which are German Bunds or German instruments. Well with German surpluses growing, I don’t know where their going to find that much to buy without pushing German rates, even on the long end, further down. So there’s here’s all these things confronting us.
FRA: Could that issue, in terms of the amount of German debt being used as diminishing, prompt the emergence of a Eurobond for the ECP?
Yra: Well there are certainly those who won’t (inaudible 16:07) cause I think that’s what the end game is.
Peter: Germans (inaudible 16:12) try to push that into the future as long as they can.
Yra: As far as they can cause that would mean that the German would have to underwrite the whole debt load. I don’t see any unless you had a denaturalization meaning sell off a lot of publicly held companies, meaning, government held companies in order to be able to buy back some of the bonds with real assets rather than ECP money. It will take a major political upheaval in Germany from those who are (inaudible 16:51) of that because right now the rising forces in Germany, the rising political voices are not in favour of that. In fact, I would say that one of the staunchest platform policies of the (inaudible 17:06) for Germany is less German involvement into the guarantee of the European financial system. The winds are blowing in the opposite direction and Peter exactly is right, they’ll delay that as long as possible. Macron….when he was a rising star couldn’t get her to sign on to a unified financial system, which is the risk that would be absorbed by the European stability mechanism, with the German’s guarantee in that cause the Germans saw through that and she wouldn’t even sign on that when Macron was maybe somebody (inaudible 1742). Right now, he’s a weakened force as she is and it’s the Italians, in my mind, who are holding the cards here.
FRA: So as we go towards the end of the year, could the German-French yield spreads on bonds likely increase as the ECP buys less assets going in to the end of the year? Your thoughts? Peter?
Peter: That’s a good question. I actually just think they’re both going higher, whether the spread widens or not, I’m not sure. As Yra said they both now have political issues. I can’t fully understand why the Macron’s poll numbers are dropping as fast as they are. Maybe it’s the French just don’t like change that he’s trying to bring, but I’m surprised by that. I think either way, you’re going to see a rise in yields in both countries and I think people don’t understand how much of an influence the ECP was and still is barely in terms of their buying in those markets in while they’re continue to reinvest proceed.
They were buying 7 times net issuance of European bonds. The Fed QE at its peak was 25% of net issuance of treasury (inaudible 19:03-19:04). That’s how dominant the ECP was. While we all know what they’re going to do, they told us what they’re going to do, I still think there is this level of nonchalant as somehow European bond yields can stay around these current levels even with the reinvestment. And that’s what I’m most worried about is a rate shock in Europe that could have a ripple effects.
We already seen the Bank of Japan pulling back and you’ve seen a jump in longer (inaudible 19:32) yields there and you’ve seen the 10 year yield creeping closer to 15 basis points as Bank of Japan is more tolerant of that. You’ve seen the US 10-year just a few basis points from breaking out to multi year highs. If you seen these rise in yields, its not for all good reasons, it’s not that the economy is great and the markets are just doing it, it’s that you have this Gorilla in this room thats walking out and buying less and a combination with other things including inflation and others. I think people are way to nonchalant with this move up in the interest rates.
FRA: And Yra, what do you see happening as we go towards the (inaudible 20:09-20:10)?
Yra: I think that’s right. (Inaudible 20:11-20:12) the reason I dig through the plumbing… if you look, German issuance is diminished because they’re running surpluses. France has grown over these last years. The real canary in the coal mine is that their running these budget deficits, meaning France and Italy, with these ultra low interest rates. Lets not minimize that..
Peter: (inaudible 20:49-20:51) by 2%.
Yra: These deficits haven’t shrunk whatsoever and if interest rates start to rise, as Peter and I believe that they’re going to do, it’s gonna put even greater pressure on these deficits. I don’t know if they will get better growth. I applaud Macron. I think he’s trying to turn the tables on what has been a (inaudible 20:19) economic policy from Halland, and even Sarkozy. They did some stupid things. He’s trying to undo them but the deficit is still growing. Its like with Greece. You hear everybody talk about how Greece turned around. Well the Greece debt to GDP ratio, even with all this austerity, it’s still bigger then when it started down that path of austerity and thats with interest rates dropping dramatically. And that’s where the real risk here lies. And from the (inaudible 21:53) aspect of it, German credits are far better than the rest of the credits. Maybe the Dutch and Austrian certainly without the ECP would be able to stand on their own. But the others, (inaudible 22:06-22:08), and that includes France because France is not without its problems. And if Macron fails, the issues in france are really gonna get worse as Peter points out. Politically they don’t like this type of change. The unions in France still have a lot of power. Macron would like to diminish that power but they still have a lot of power. That’s the reason why I like to be long German and short French because right now the spread on 10 years is about 32 basis points which is about mid range over last 3 or 4 years. But based on the shrinking amount of German assets and the fact that German assets are needed for REPO financing, their high quality liquid assets, that will put demand in there regardless. Unless (inaudible 23:00) openly breaks with the capital key, which he has to be very careful because there are those in Germany that will return back to the German Constitutional court and say that this is illegal because your financing individual countries and in violation of the entire edifice of the Central Banks and what their supposed to do. (inaudible 23: 27) there are things waiting out there.
Peter: It will be a real disappointment if Macron is gone at some point. He was the right guy for that job at the right time for France. It’s amazing people don’t appreciate it.
FRA: Given these thoughts on Europe and what we mentioned earlier in the US, could we see another round of more easing by central banks globally? If we go to China and look at the currency there, if the Yuan weakens and we get global disinflation, could that cause more easing by Central Banks globally? Peter?
Peter: It’s a good question. I don’t think the Chinese want to go down the route of seeing a dramatically weaker currency. They are trying to shift their economy from a manufacturer infrastructure, (inaudible 24:23-24:26) investment type economy to more services and more consumption. You don’t want a weaker currency, if that’s the transition you’re trying to make. You don’t want to damage the purchasing power of consumers if your trying to improve consumer spending. I think they are more interested in having a stable currency not a dramatically weaker one. I’m sure the weakness we’ve seen will be tolerant of because it’s relatively modest and it can help cushion the impact of the tariffs but I wouldn’t look for major decline in the currency.
I think the currency that trades (inaudible 25:07-25:08) is the U.S dollar and people should be asking what’s going on with US dollar considering the out performance economically, the Central Bank that is far ahead of the curb relative to others, and why outside of emerging markets where the dollar has strengthened, why against the Euro or the Yen or some of the others has it not traded well? I’m putting aside the pounds because that’s obviously very Brexit related. That’s where I think people should be asking is What’s going on with the dollar and less so with the Yuan?
FRA: And Yra, your thoughts?
Yra: I think that’s dead right on target. I know Peter that’s the Michael Pettis argument which is, “hey, if your trying to build your domestic economy, and China’s certainly is, if I look at the copper market, the copper market is telling me that China’s going to embark on another round of massive infrastructure project whether it’s in the road initiative or just in China itself but that’s what the market is sensing here. You don’t want a weaker currency. Your trying to ramp up domestic spending. You’d like to have a stronger currency because then you can buy cheaper imports so I’m hundred percent agreement and I agree with Peter with the dollar.
The dollar is interesting here because the cost of carry is quite expensive. If we use overnight money in Europe, let’s say German money, it’s 250 basis points going higher. If we’re using 2 year differential, it’s well over 3 percent because German 2 years are about negative 50 and US is of course 2.8. I don’t ever remember, I wont say ever, it’s been certainly over 3 decades that we’ve seen a spread that wide and 2 years or less. So these are things that should be (inaudible 27:24-27:25) the strengthening dollars as a lot of people are positioning for. Peter, from 107,108, but that was based on the Trump Whitehouse as much as anything. Bob White Heiser, who is the power here, is not afraid to promote a weaker currency. I think the markets are starting to accept to (inaudible 27:52) that in but they really haven’t yet. That may be one of the tools they utilized.
FRA: What about Brazil? Are they intentionally driving their currency lower to help their agricultural exports and hurting U.S grain exports?
Peter: They don’t need the help. It’s a business to them.
Yra: They don’t need the help. Its bad politics. Their in a great position now because the Chinese (inaudible 28:31) knows the US for the moment because their agricultural exports from Brazil are so cheap. Even if though they had a (inaudible 28:42) crop because they’re so cheap, it will be interesting to see how much plant the Brazilian farmer grew this year. Even international prices are lower, priced in terms of Real, which the farmers ultimately get paid in as they take their dollars they receive in the international market and convert to domestic currency. Their not suffering whatsoever. The United States farmers are suffering under Tariffs as well as having to compete against the weakened Brazilian Real. They don’t need any help. I think they believe the currency is to weak relative to other policy aims that they have.
FRA: And the finally moving over to Japan. How will the Bank of Japan be able to extricate itself from five years of QQE, qualitative and quantitative easing, since they’ve accumulated so much Japanese debt and equities? Your thoughts Yra?
Yra: Well, I don’t know if they know how to extricate themselves. They’ve just been muddling along here and I mean muddling. They preceded down this path for way too long. Supposedly we heard last week that Abe was backing away from the inflation targets after his new found political strength is (inaudible 30:07-30:09) although he’s got his plate full but I don’t how they get out of here. They’re not going to do it with a weaker currency. We listen to Trump, the sense that he’s looking to throw tariffs on to the Japanese because they run to large of surpluses with the US, the Japanese have to be very careful here and the Europeans can’t be too happy because the Euro against the Yen has been rallying dramatically. The European auto industry is (inaudible 30:51) head wind of a weaker Yen and US tariffs and some really bad fall for Brexit, which not enough people talk about it but the European auto industry could really get hit. But I don’t know what the Japanese are going to do here. They follow this Bernanke down this rabbit hole for way to long and i don’t know what they do here.
FRA: Peter?
Peter: Yeah it’s a great point. I don’t know what they’re going to do. I think that their acknowledging the squeeze that they’re in by allowing a whole 10 basis points extra of a yield grab (inaudible 31:36-31:37) can get in Japan, which is quite amazing from 10 to 20 basis points. They are certainly slowing the rate of purchases. I think they’ve basically cut QE in half. I think they’ve suddenly realized that they are a dominant player in the ETF market and are a top 10 holder in about 40% of Japanese Nikkei companies. I think they got their fingers crossed on generating some higher inflation so they can further get out of what they’ve done but I don’t see how they can ever get out of what they’ve done. I think they’ll just continue to try to lessens their influence and see what happens but Kuroda….talk about overstaying one’s welcome.
Yra: And to add to that, I think one of their plans was, at some point, that they’ll be able to start buying foreign bonds if they needed to but now that they run in Trump, there is no way that the (inaudible 32:39) or even some of those pension funds have to be very careful. The government pension investment fund. They can’t just willy nilly because that will move to weaken the end and they have to be very careful here.
Peter: That’ll be dangerous.
FRA: On that note, we’ll end it there. How can our listeners learn more about your work? Peter?
Peter: They can search it in wealth management. They can go to bleakley.com and reach out to me. If they want to see my daily (inaudible 33:10-33:11), they can subscribe at boockreport.com.
FRA: And Yra?
Yra: My blog post, notes from underground, and you can go to Yraharris.com. It’ll come up notesfromunderground you can get access to it and join the conversation that takes place on regular basis about many of these same issues. It’s just a discussion on what’s going on in the world and hopefully you can find your way to profitable investment from them.
FRA: Great insight as always. Thank you very much gentlemen! We’ll do it again.